Structures in C Programming
In C, a structure is a user-defined data type that allows you to group different types of variables under a single name. It is very useful when you want to represent a real-world entity (like a student, employee, or gene record) with multiple attributes.
### **Structures in C Programming**
In **C**, a **structure** is a user-defined data type that allows you to group **different types of variables** under a single name. It is very useful when you want to represent a real-world entity (like a student, employee, or gene record) with multiple attributes.
---
## **1. Definition of Structure**
A structure is defined using the `struct` keyword.
```c
struct Student {
int roll_no;
char name[50];
float marks;
};
```
Here, `Student` is a structure that contains **int, char array, and float**.
---
## **2. Declaring Structure Variables**
```c
struct Student s1, s2;
```
OR during definition:
```c
struct Student {
int roll_no;
char name[50];
float marks;
} s1, s2;
```
---
## **3. Accessing Structure Members**
Use the **dot (.) operator**.
```c
s1.roll_no = 101;
s1.marks = 85.5;
strcpy(s1.name, "Amina");
```
---
## **4. Structure Initialization**
```c
struct Student s1 = {101, "Amina", 85.5};
```
---
## **5. Array of Structures**
Used to store multiple records.
```c
struct Student s[3];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
scanf("%d %s %f", &s[i].roll_no, s[i].name, &s[i].marks);
}
```
---
## **6. Structures and Functions**
### Passing structure to a function
```c
void display(struct Student s) {
printf("%d %s %.2f", s.roll_no, s.name, s.marks);
}
```
### Passing structure by reference
```c
void display(struct Student *s) {
printf("%d %s %.2f", s->roll_no, s->name, s->marks);
}
```
---
## **7. Structure Pointer**
```c
struct Student s1;
struct Student *ptr = &s1;
ptr->roll_no = 102;
```
(`->` is called the **arrow operator**)
---
## **8. Nested Structures**
Structure inside another structure.
```c
struct Address {
char city[20];
int pincode;
};
struct Student {
int roll_no;
struct Address addr;
};
```
---
## **9. typedef with Structure**
Used to avoid writing `struct` repeatedly.
```c
typedef struct {
int id;
float salary;
} Employee;
Employee e1;
```
---
## **10. Advantages of Structures**
* Groups related data
* Improves program readability
* Useful for large programs and data management
* Widely used in **file handling**, **databases**, and **bioinformatics data structures**
---
## **11. Structure vs Union (Short Note)**
| Structure | Union |
| -------------------------------- | ------------------------------ |
| Each member has its own memory | Members share same memory |
| Larger size | Sm-
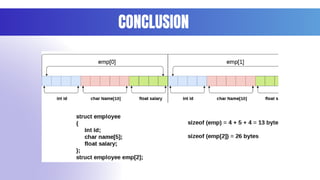
### **Conclusion – Structures in C Programming**
Structures in C provide an efficient way to store and manage related data of different data types under a singl


![INTRODUCTION
Structure are collection of different datatype grouped
together under a single variable name for convienient
handling. 'struct' is a keyword, struct type is a name
which identifies the structure.
syntax: struct <structure name >
{
datatype member1;
datatype member2;
};
Example:
struct employee
int id;
char name[10];
Float salary;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-3-320.jpg)
![DECLARING STRUCTURE VARIABLES
• Structure variable declaration is similar to the declaration of variables of any other data types.
• Structure variables can be declared in following two ways
1.Declaring Structure variable separately
Struct employee,
{
int id;
char name [10];
float salary;
};
void main()
{
struct employee e1, e2;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-4-320.jpg)

![•Like any other data type, structure variable can also be initialized at compile time.
Syntax: struct structure_name variable={value 1,value 2,value 3,......value n}
Eg: struct employee
{
int id;
char name [10];
float salary;
}
void main()
{
struct employee e1= {01, "Joy", 1000 };
struct employee e={02, "Ram",2000};
STRUCTURE INITIALIZATION](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-6-320.jpg)
![ACCESSING MEMBER OF STRUCTURE
•By using dot (.) operator or member operator
Syntax: structure variable.member
Eg: struct employee
{
int id;
char name [10];
float salary;
};
void main();
{
struct employee e1 = {01, "Joy", 1000 };
printf("%d",e1.id);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-7-320.jpg)
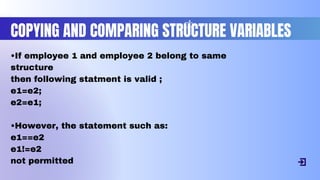
![Eg: for copying:
struct employee
{
int id;
Char name [20];
Float salary;
};
void main ()
Struct employee e1;
Struct employer e2 {02,"Joy", 1000);
e1=e2;
printf("Details of e1");
printf("%d %s %f,e1.id, e1.name,e1.salary);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![Eg: for comparing:
struct employee
{
int id;
Char name [10];
Float salary;
};
void main ()
Struct employee e1{01,"ram",1000);
Struct employer e2 {02,"Joy", 2000);
If (e1.id<e2.id)
printf("Yes");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-10-320.jpg)
![Consider a case ,where we need to store data of 3 students we can store it
by using the structure as shown below,
#include <stdio.h>
struct employee
{
int id;
Char name [20];
Float salary;
};
void main ()
{
ARRAY OF STRUCTURES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-11-320.jpg)


![Eg: struct employee
{
int id;
char name;
float salary;
}
void main ()
{
Struct employee e[3]
for(i=0;i < 3;i++)
{
scanf("%d %s %f", &e[i]. id, &e[i].name, &e[i] .salary);
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("%d %s %f", &e[i]. id ,&e[i] .name. &e[i]. salary);
}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming1-260118094140-e2dfef91/85/Cprogramming_structures_into_types_conclusion-pdf-14-320.jpg)