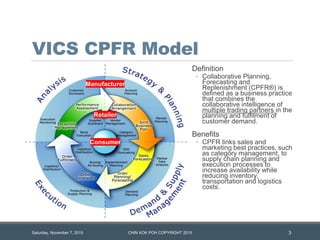
The document outlines strategies for enhancing supply chain collaboration through techniques like sharing forecasts and managing inventory to improve efficiency and reduce costs. It introduces the concept of Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR), emphasizing its role in linking sales and marketing with supply chain processes. Additionally, it discusses the integration of advanced technologies like RFID and Internet of Things solutions to optimize logistics and track goods within the supply chain.