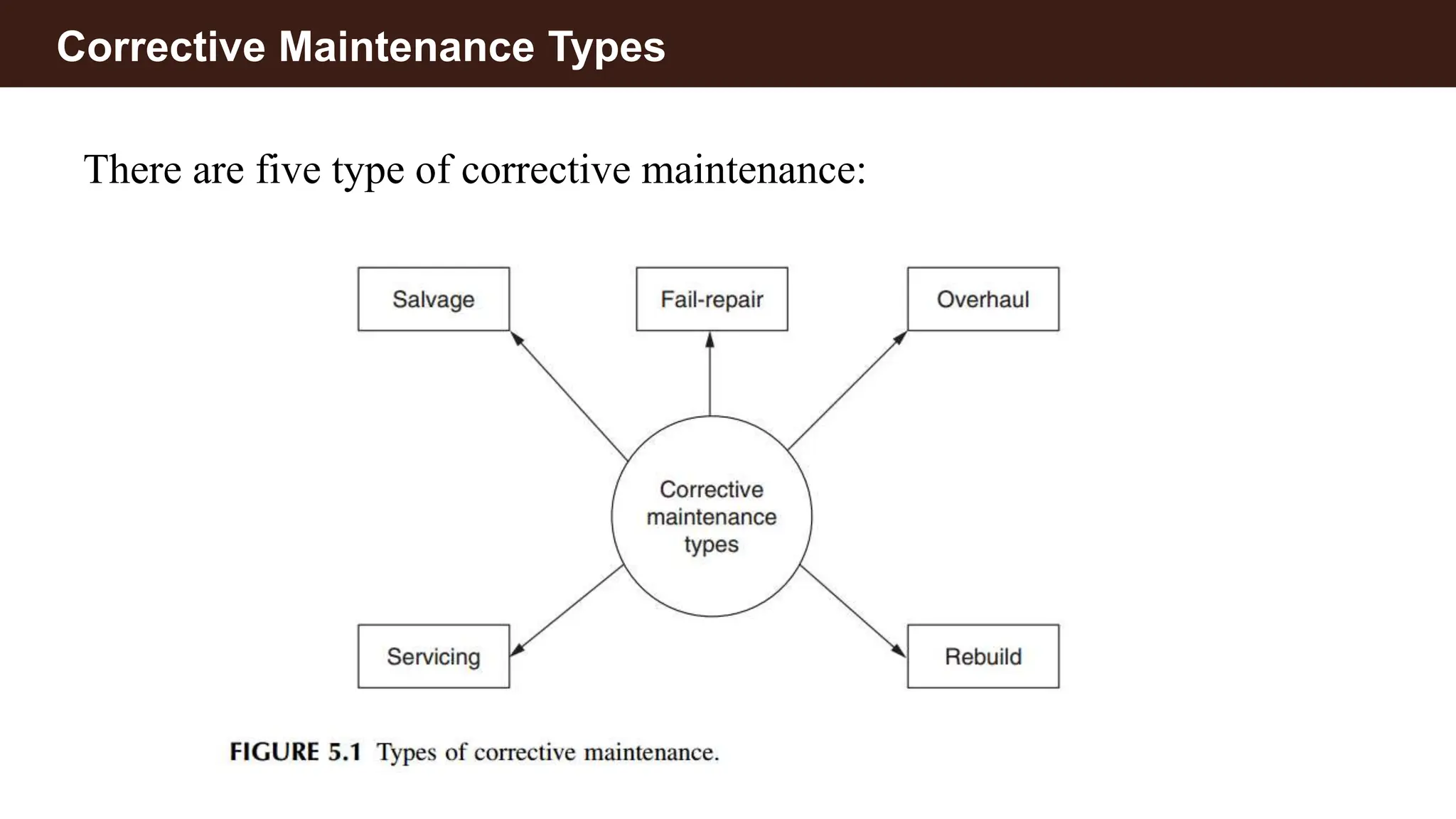
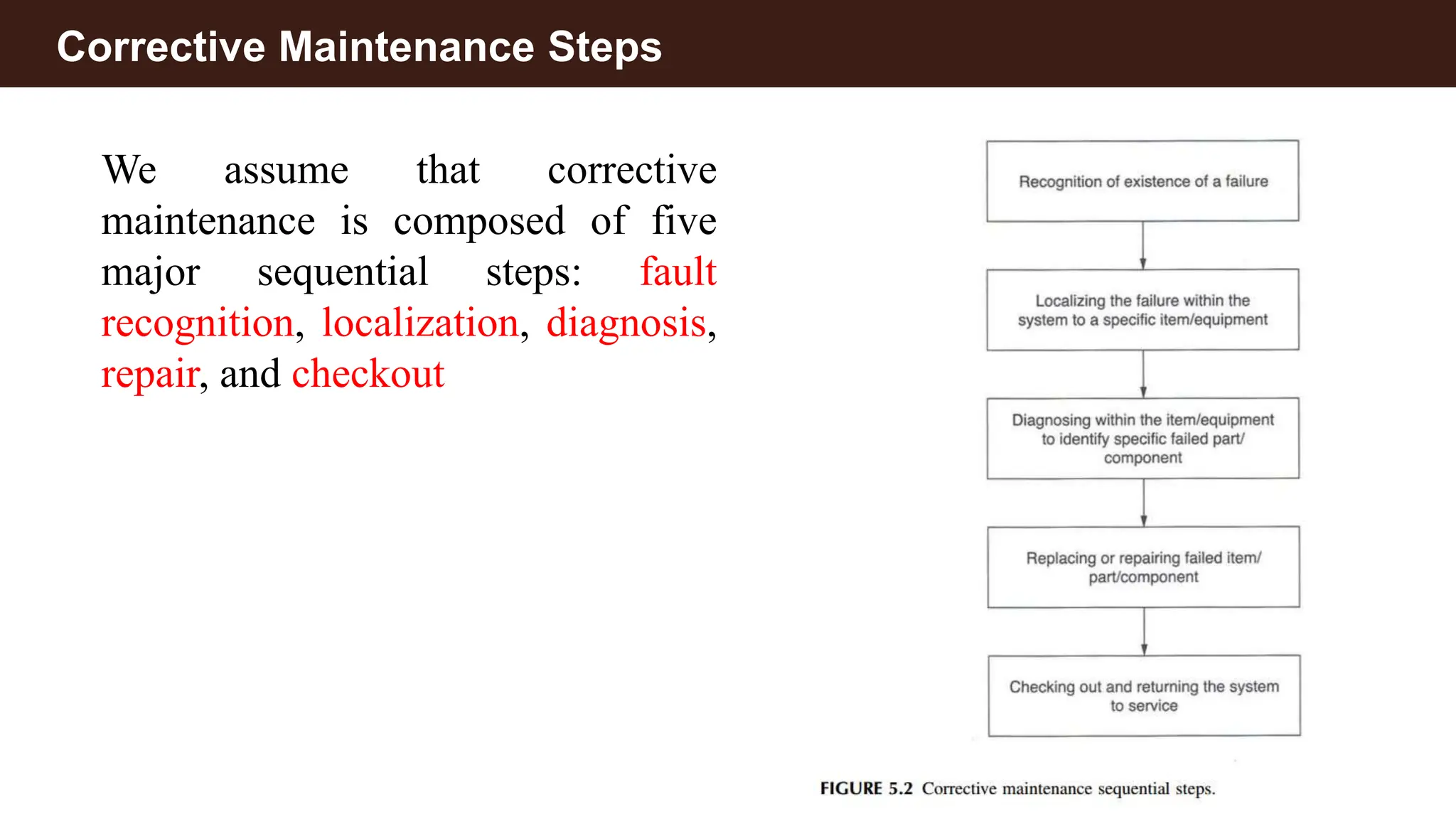
Corrective maintenance (CM) refers to unscheduled actions taken to restore equipment to operational condition after failures are discovered. It includes five types: fail-repair, salvage, rebuild, overhaul, and servicing, each addressing different aspects of equipment restoration. The corrective maintenance process involves five sequential steps: fault recognition, localization, diagnosis, repair, and checkout, with various components contributing to downtime.