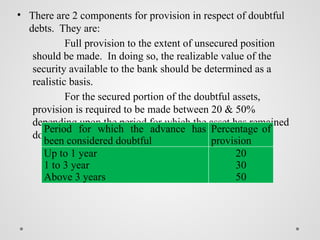
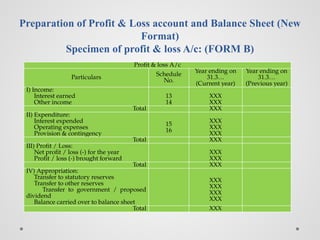
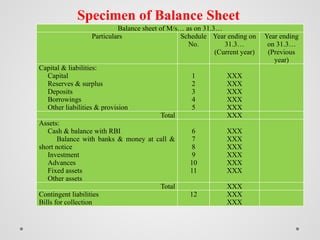
The document outlines the regulatory framework for banking companies in India, as defined by the Banking Regulation Act 1949, including the legal requirements such as licensing, capital reserves, and provisions for non-performing assets. It describes various accounting practices related to banking operations, such as handling bills for collection, cash credits, and the preparation of profit and loss accounts and balance sheets in a new format. Additionally, it categorizes assets into standard, sub-standard, doubtful, and loss assets, detailing the required provisions for each category.