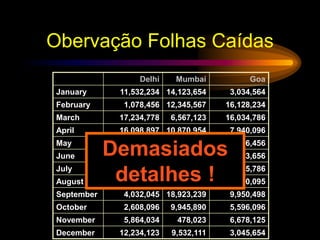
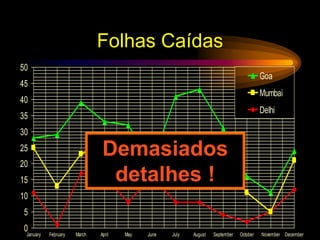
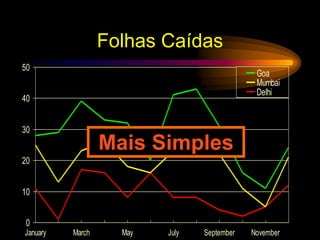
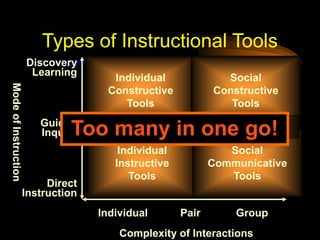
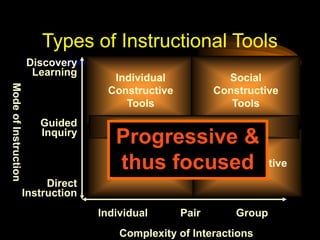
The document provides tips for designing effective PowerPoint presentations with simple, clear, progressive and consistent design. It emphasizes keeping presentations simple with no more than 6 lines and 7 words per slide. Graphics and animations should be used to supplement rather than distract from the content. Consistency is important to avoid drawing unnecessary attention to differences. When presenting, speakers should speak loudly and clearly while maintaining eye contact and engaging the audience.