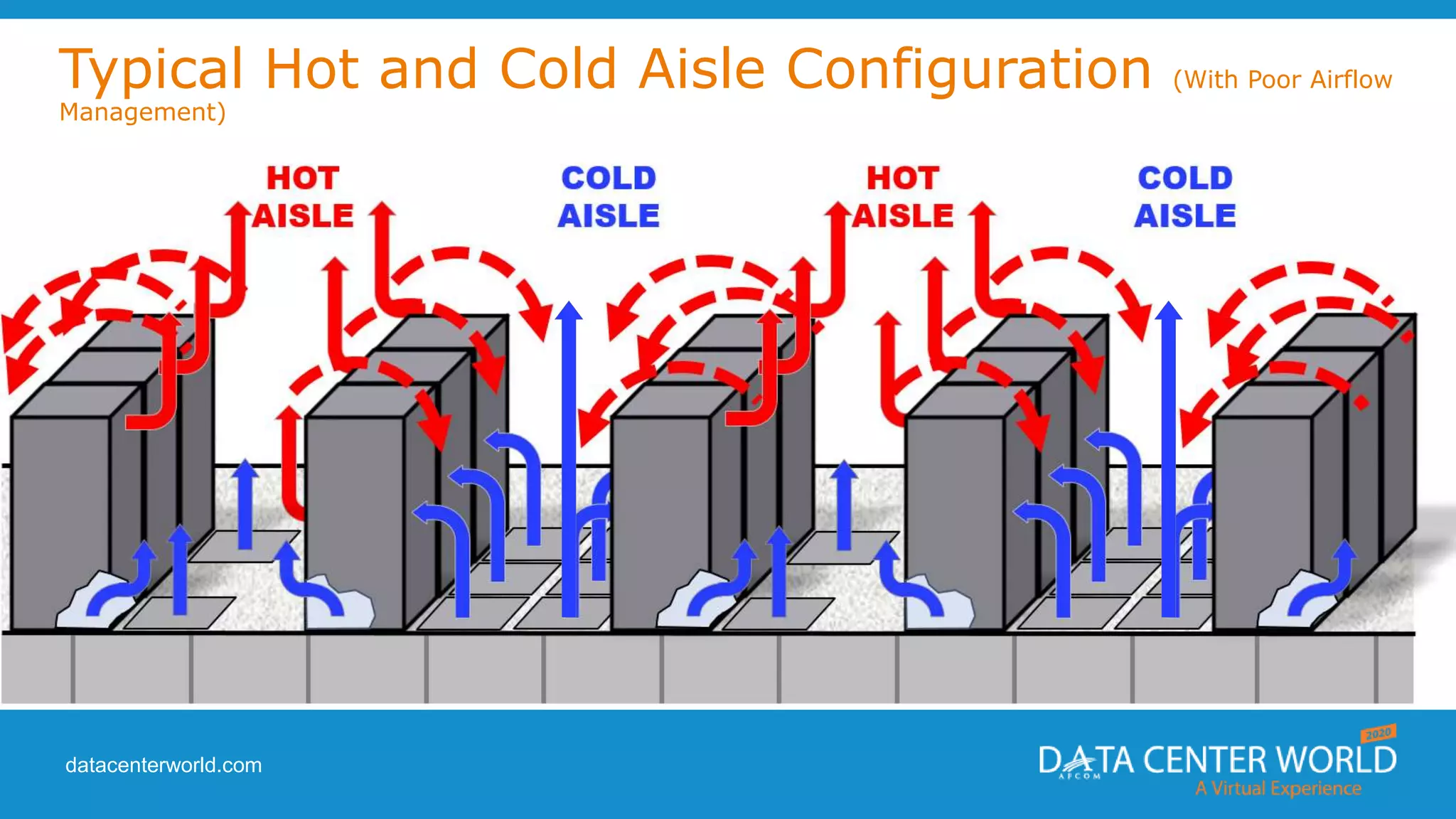
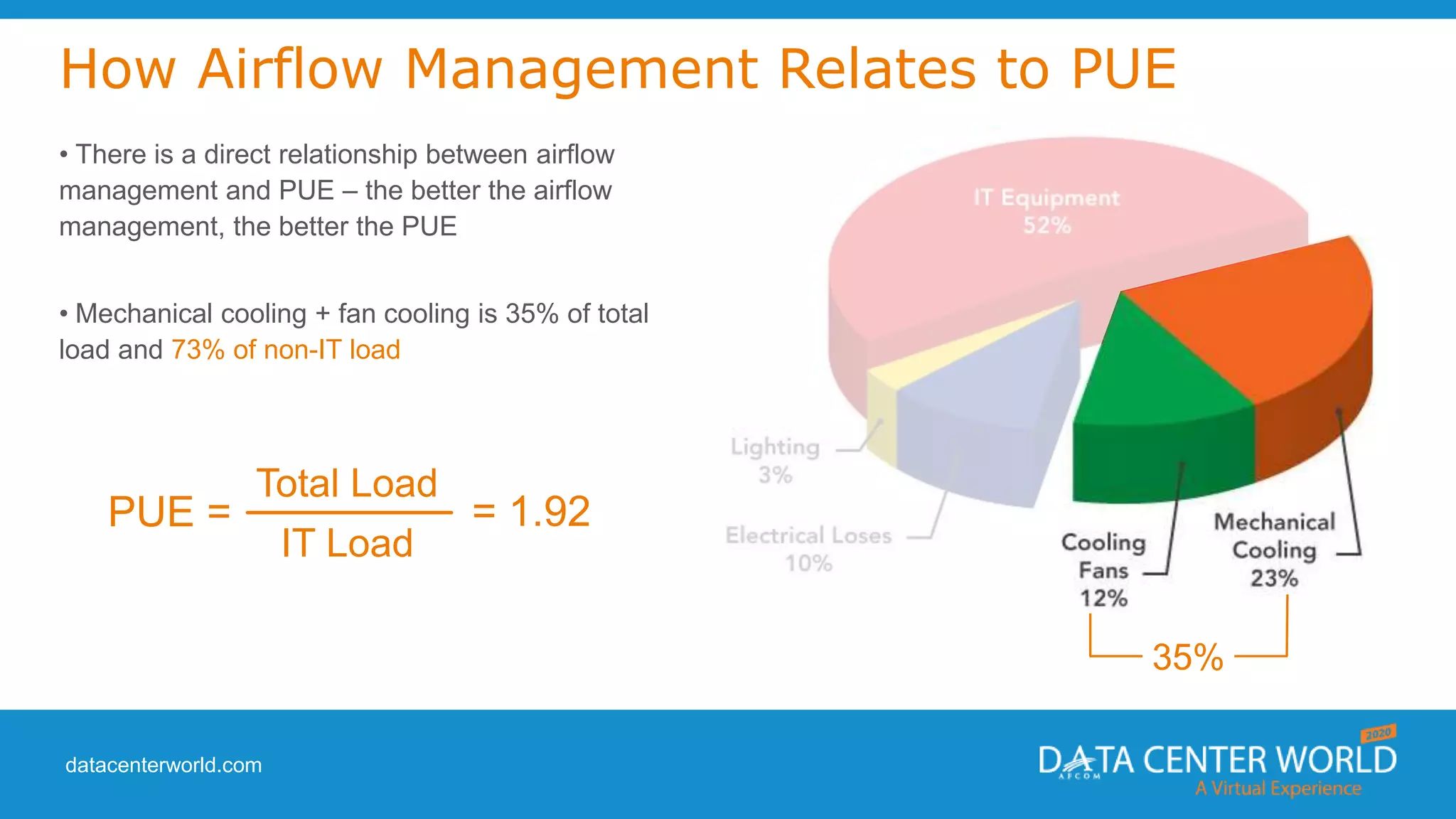
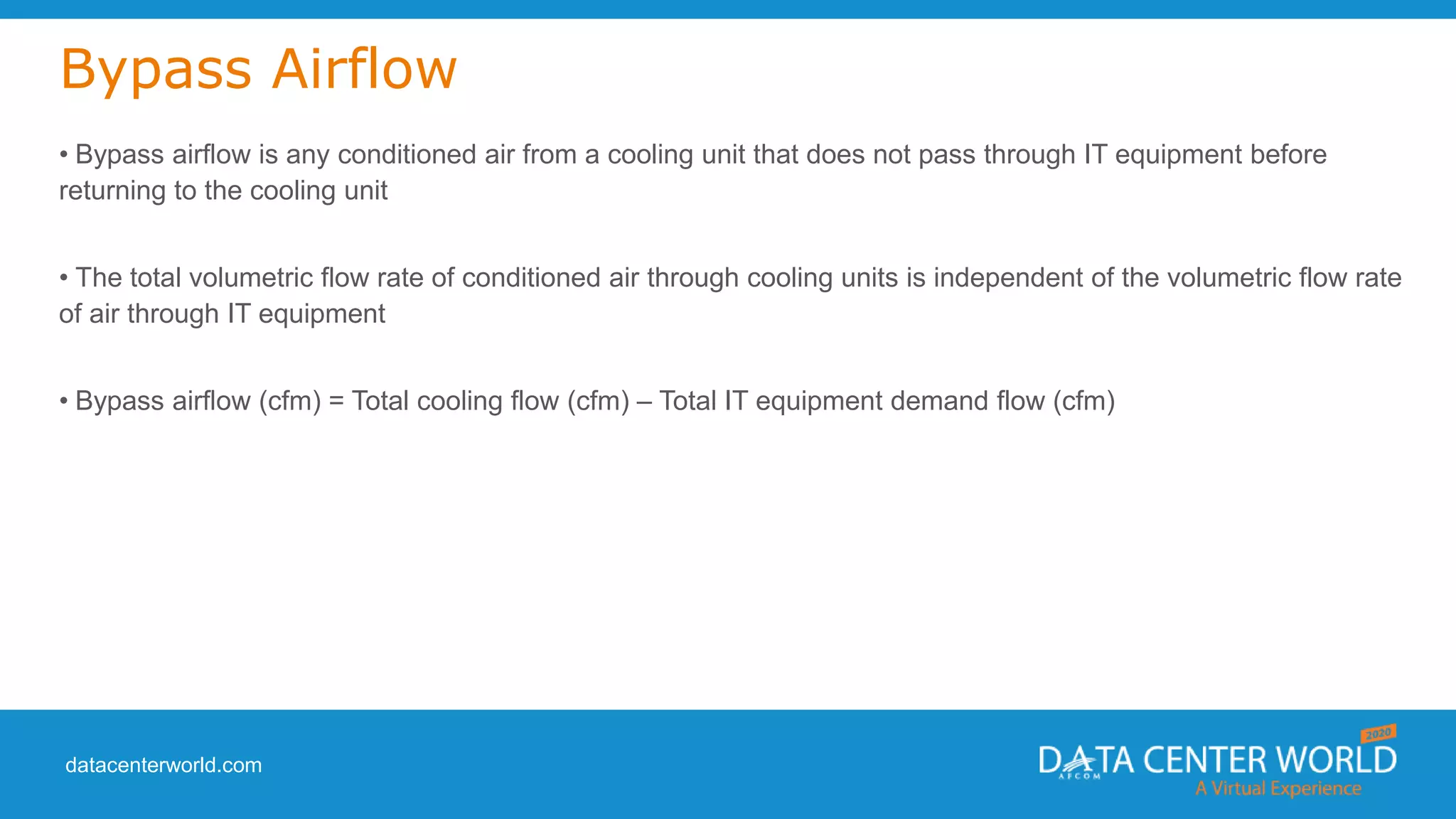
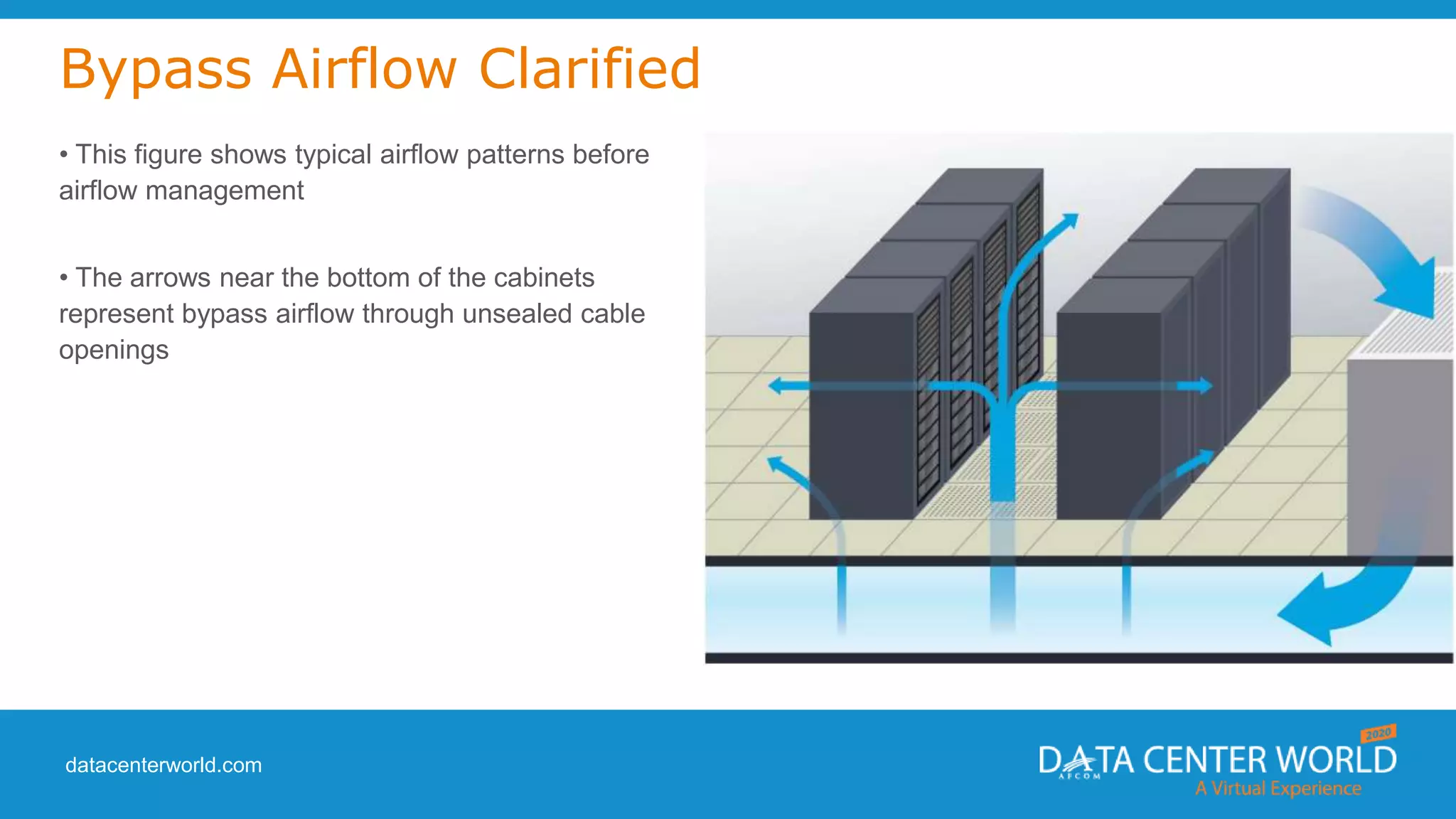
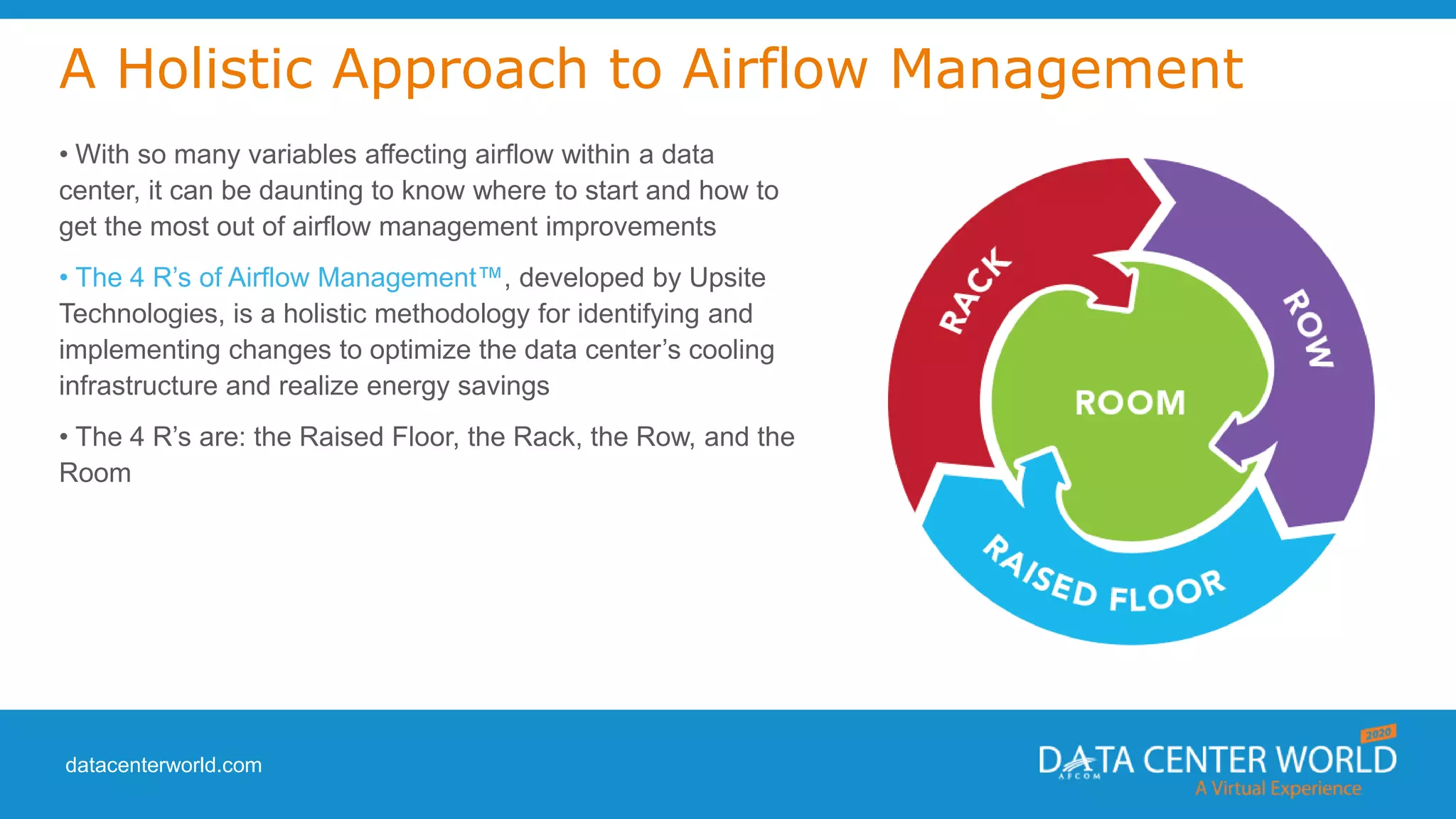
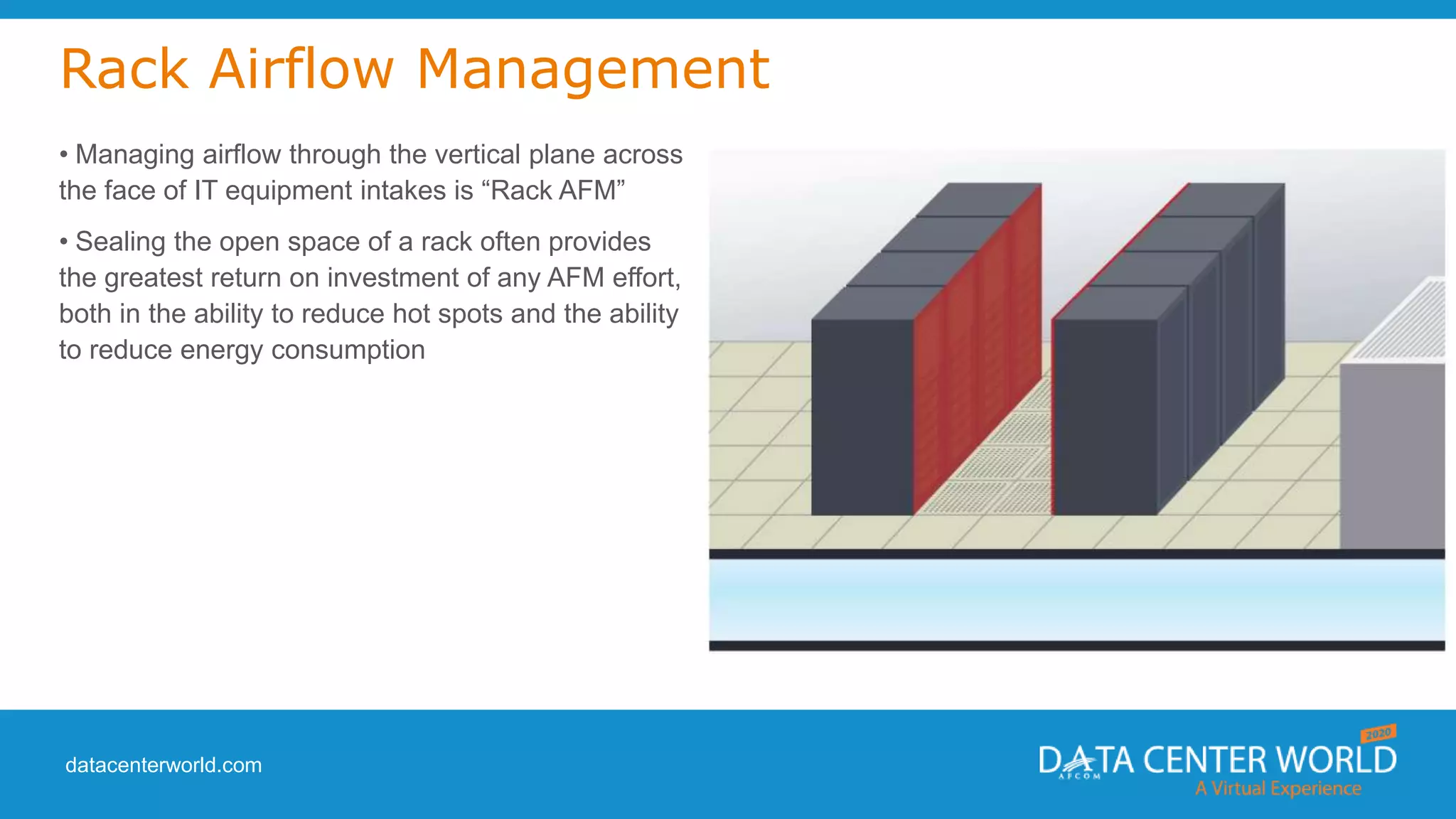
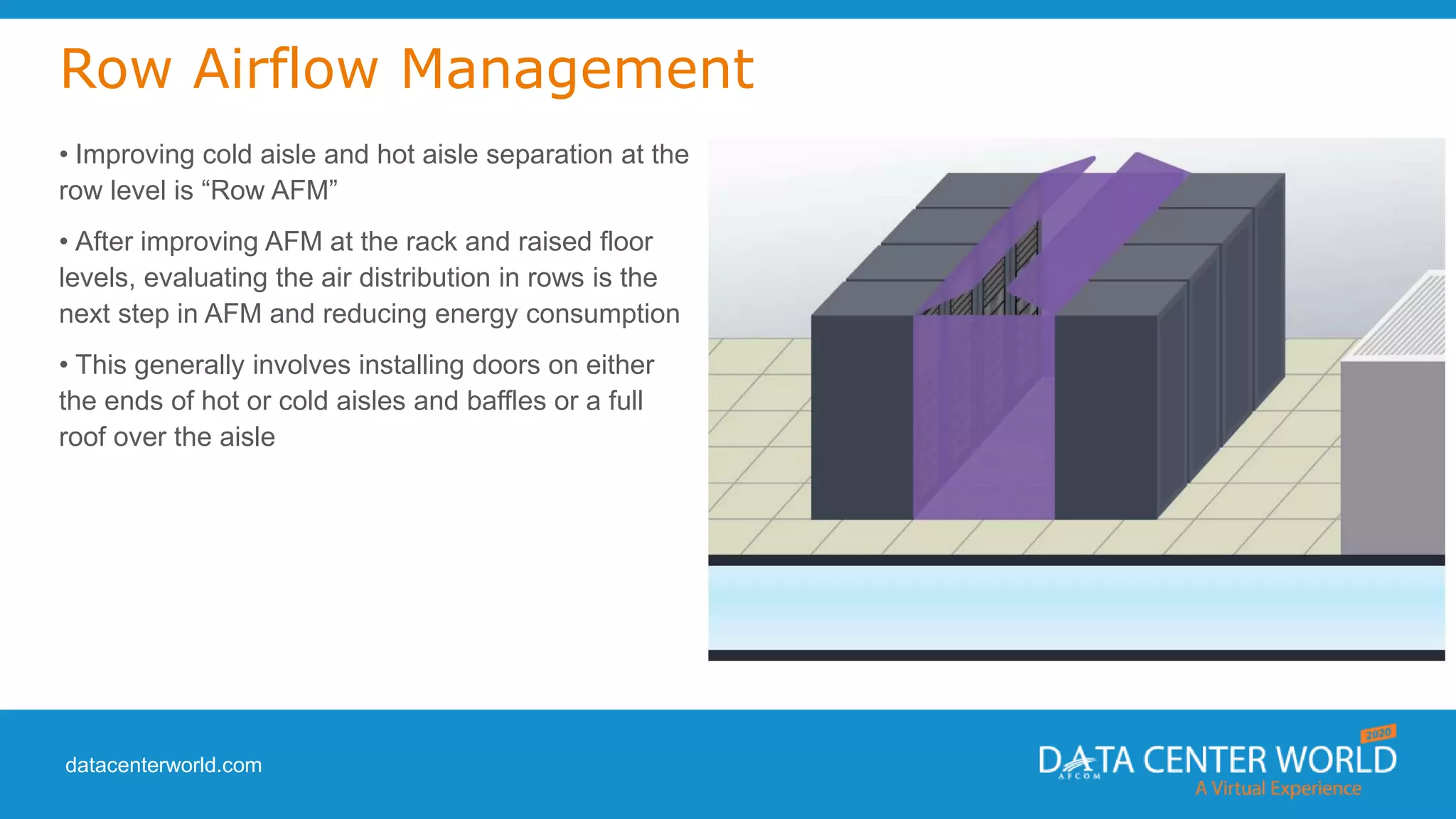
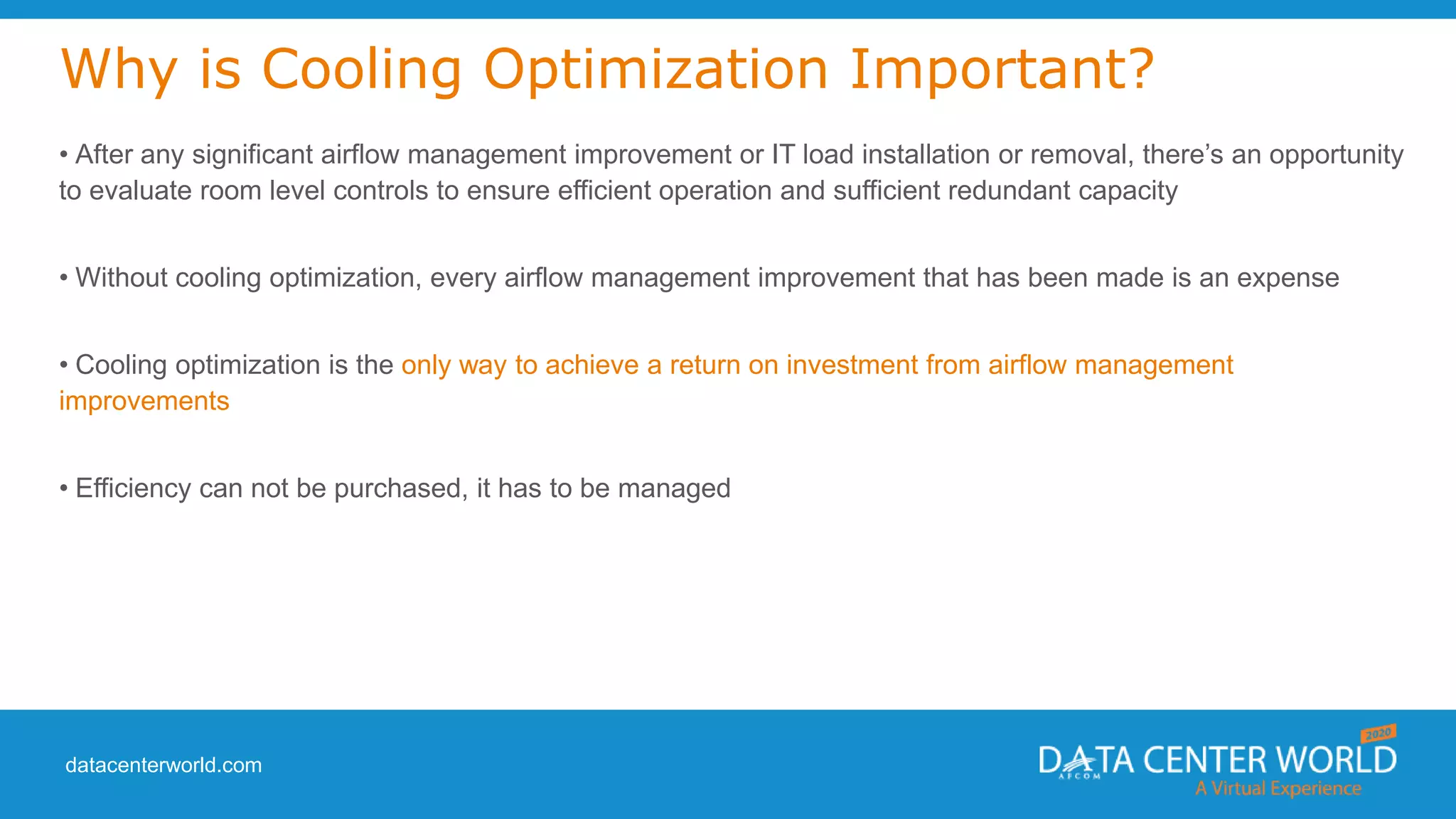
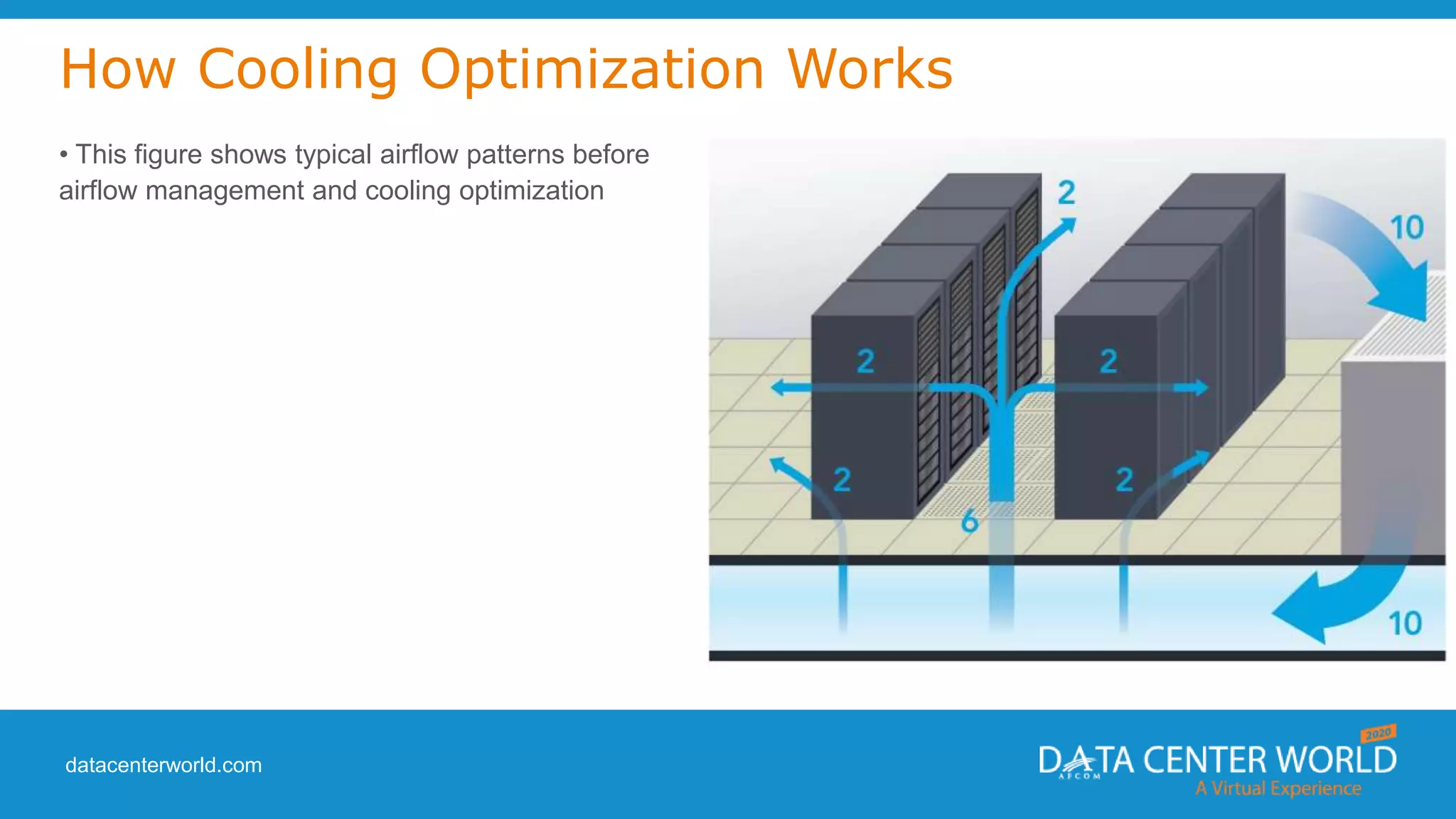
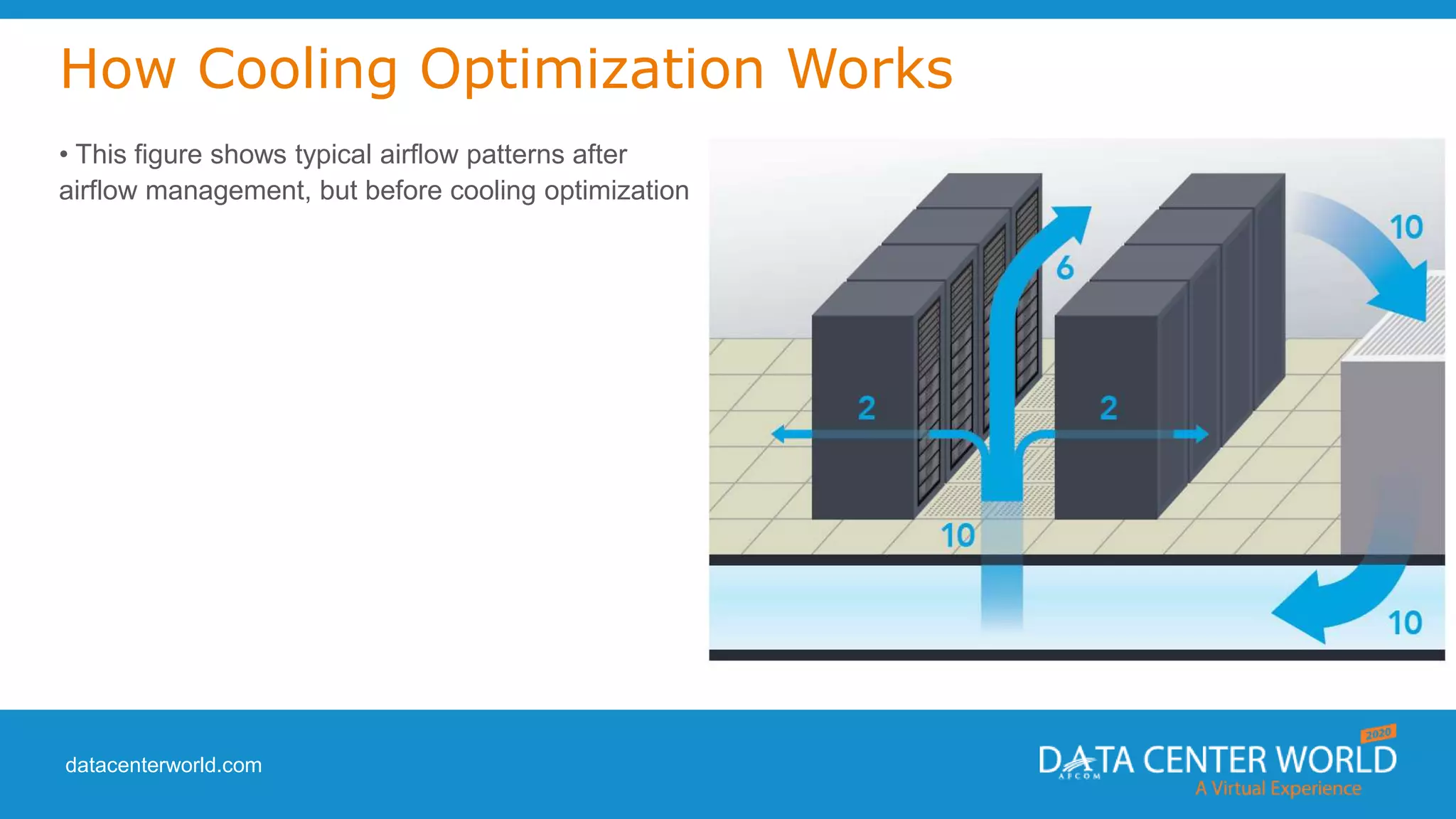
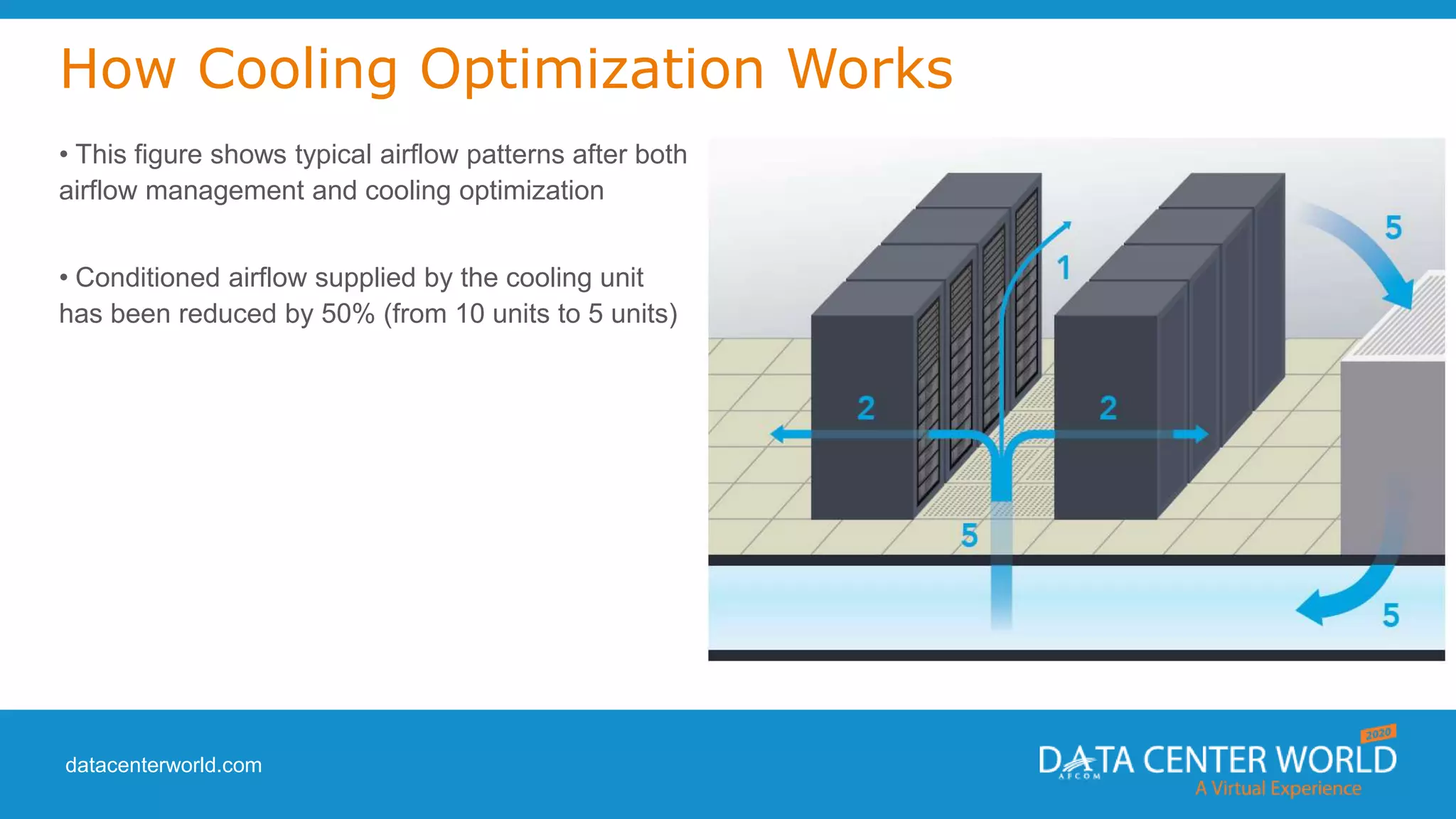
The document provides a guide on data center cooling optimization, led by expert Lars Strong, focusing on airflow management's significance related to cooling efficiency. It outlines best practices for managing air circulation between IT equipment and cooling units, emphasizing the importance of proper airflow configurations to enhance reliability and reduce energy costs. Key strategies include the '4 R's of airflow management’ and the iterative nature of cooling optimization to achieve substantial financial benefits and efficiency improvements.