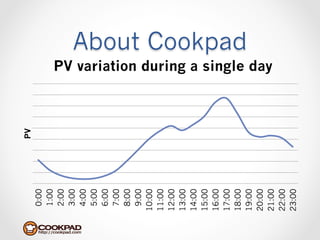
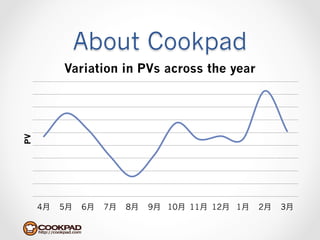
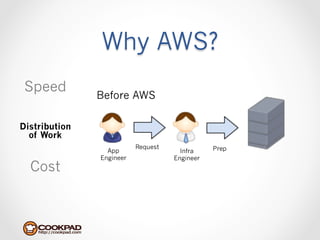
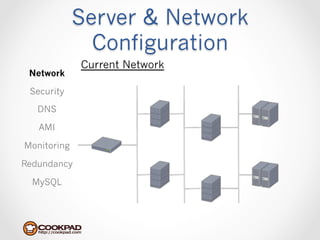
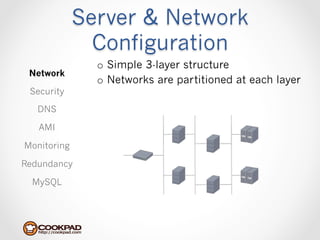
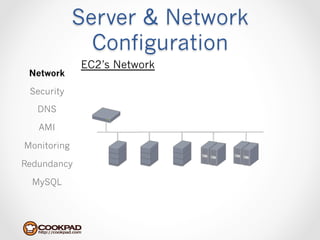
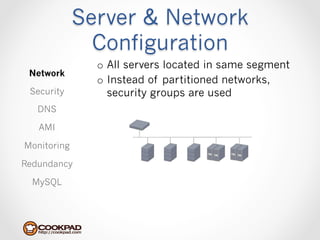
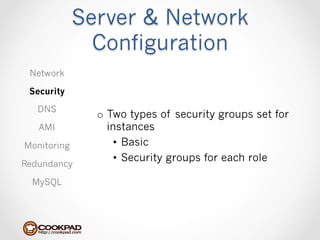
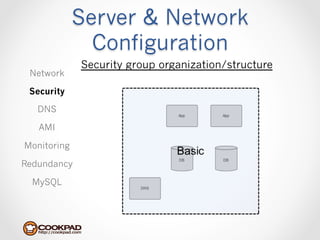
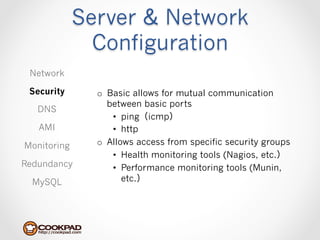
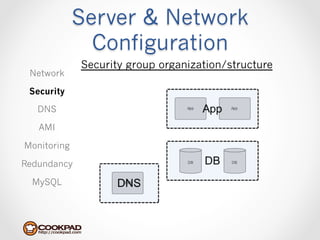
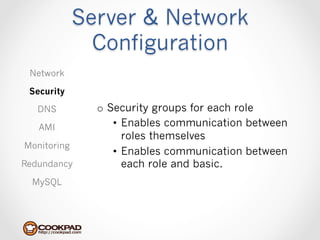
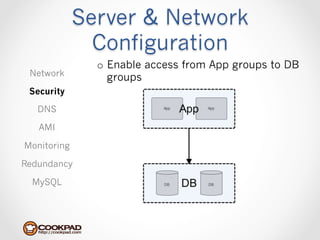
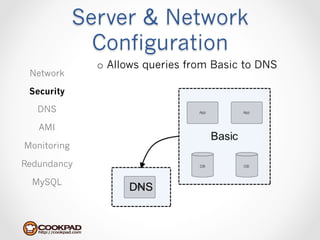
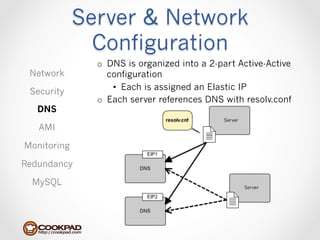
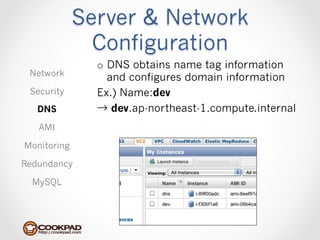
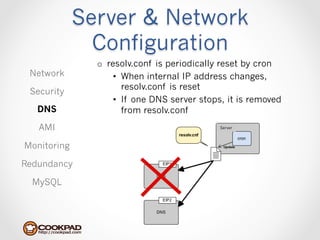
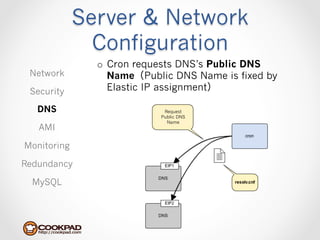
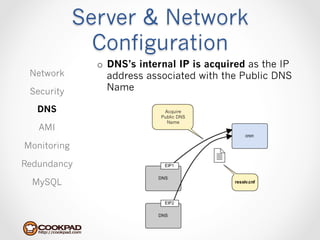
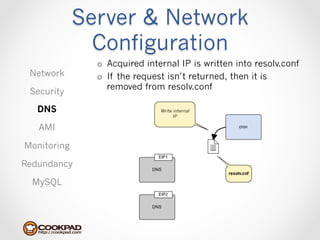
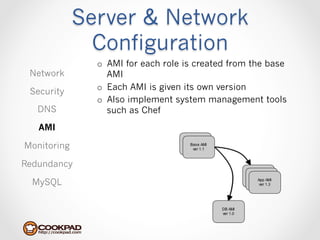
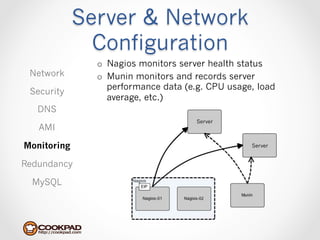
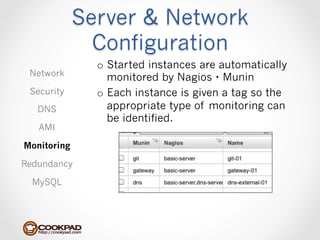
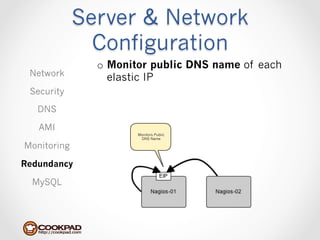
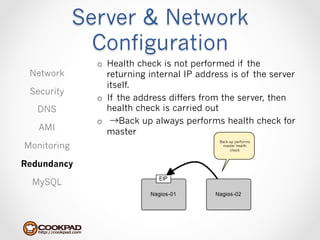
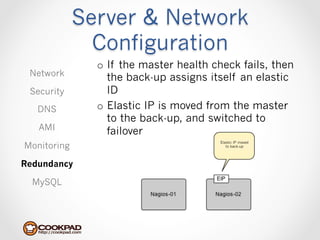
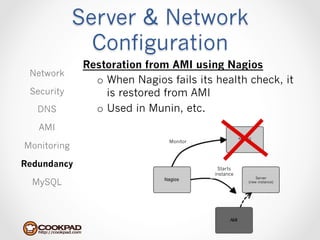
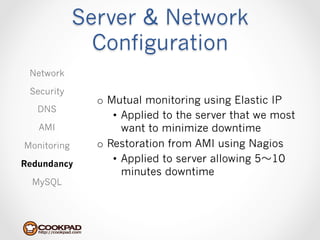
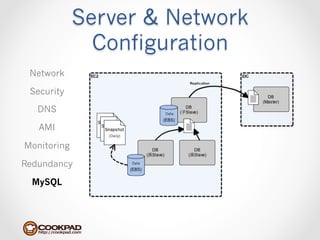
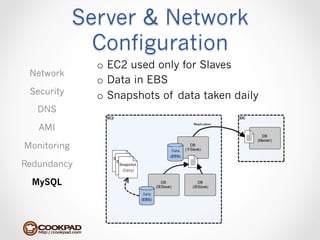
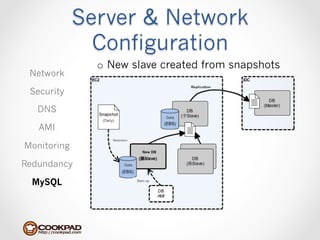
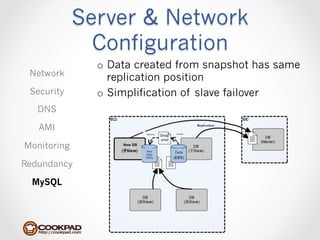
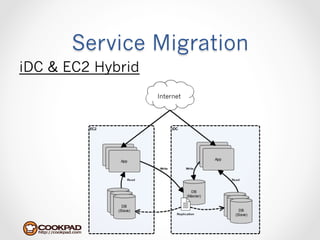
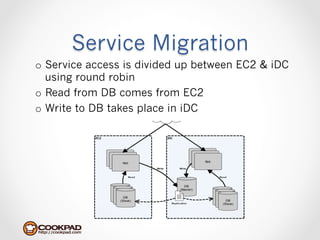
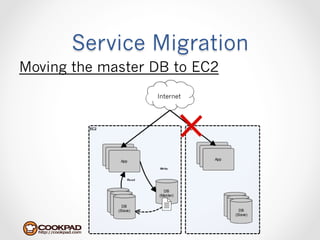
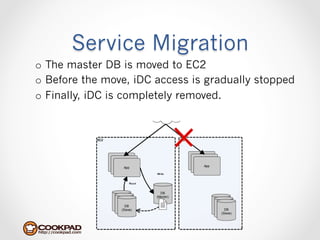
Cookpad migrated their infrastructure from self-managed data centers to AWS to improve speed, distribute workloads more efficiently, and reduce costs. They configured AWS servers and networks with security groups that allow communication between roles and basic access. Internal DNS was set up for name resolution since internal IP addresses can change. The migration involved moving services to AWS and optimizing the server and network configuration for the cloud environment.