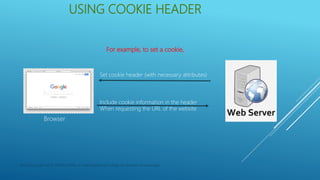
Cookies are small files containing information stored on a user's computer by a web server. Cookies are used to identify users and customize content. PHP allows creating, reading, and deleting cookies using the setcookie() function. Sessions are used to store information on the server across multiple pages while cookies store data on the user's computer. Cookies and sessions can be exploited by hackers to steal user information.







![READING COOKIES
We a user visits a page that can read cookie which is present in the user’s
computer, PHP automatically reads the cookie into a variable named the
same as the cookie, but prefixed with a $ sign.
To read a cookie, simply reference its variable name.
<?php
echo “Reading Cookie value…<br>”;
echo “User Name = $_COOKIE[‘username’]”;
?>
Mrs.M.Priyavani, MCA, DCHN, M.Phil., V.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women, Virudhunagar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cookies-210401071408/85/Cookies-PHP-9-320.jpg)

![STORING ARRAYS IN COOKIES
We can store an array in a Cookie. But we need to store each element of the array
separately within the cookie.
<?php
$address = $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_ADDR’];
$browser = $_SERVER[‘HTTP_USER_AGENT’];
$os = $_SERVER[‘OS’];
setcookie(“cookie[0]”,”$address”,time()+200);
setcookie(“cookie[1]”,”$browser”,time()+200);
setcookie(“cookie[2]”,”$os”,time()+200);
?>
Although the array elements are stored separately, when we read the array it will be
returned as an array which can be accessed as follows:
$list = $_COOKIE[“cookie”];
Mrs.M.Priyavani, MCA, DCHN, M.Phil., V.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women, Virudhunagar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cookies-210401071408/85/Cookies-PHP-11-320.jpg)
![STORING ARRAYS IN COOKIES
<?php
$address = $_SERVER[‘REMOTE_ADDR’];
$browser = $_SERVER[‘HTTP_USER_AGENT’];
$os = $_SERVER[‘OS’];
setcookie(“cookie[0]”,”$address”,time()+200);
setcookie(“cookie[1]”,”$browser”,time()+200);
setcookie(“cookie[2]”,”$os”,time()+200);
?>
<html>
<body>
<?php
$list = $_COOKIE[“cookie”];
echo “IP ADDRESS = $list[0] <br>”;
echo “CLIENT BROWSER = $list[1] <br>”;
echo “OPERATING SYSTEM = $list[2] <br>”;
?>
</body>
</html>
Mrs.M.Priyavani, MCA, DCHN, M.Phil., V.V.Vanniaperumal College for Women, Virudhunagar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cookies-210401071408/85/Cookies-PHP-12-320.jpg)