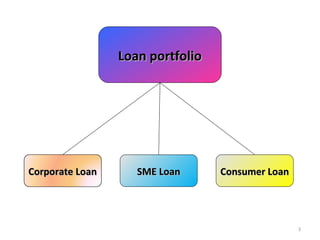
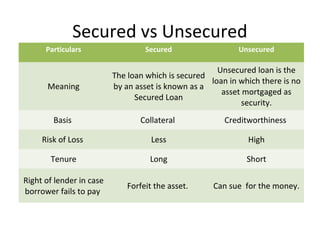
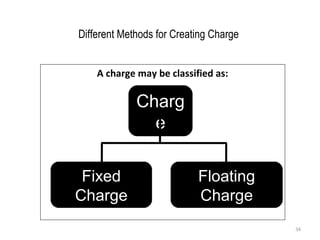
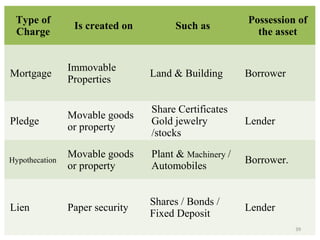
This document discusses various types of consumer loans. It defines consumer loans as loans given to individuals for personal or household purposes. Consumer loans can be secured by collateral like a home or car, or they can be unsecured. The document then describes different types of secured and unsecured consumer loans such as home loans, vehicle loans, credit cards, and others. It also discusses key terms related to consumer loans like interest rates, loan amounts, repayment periods and more.