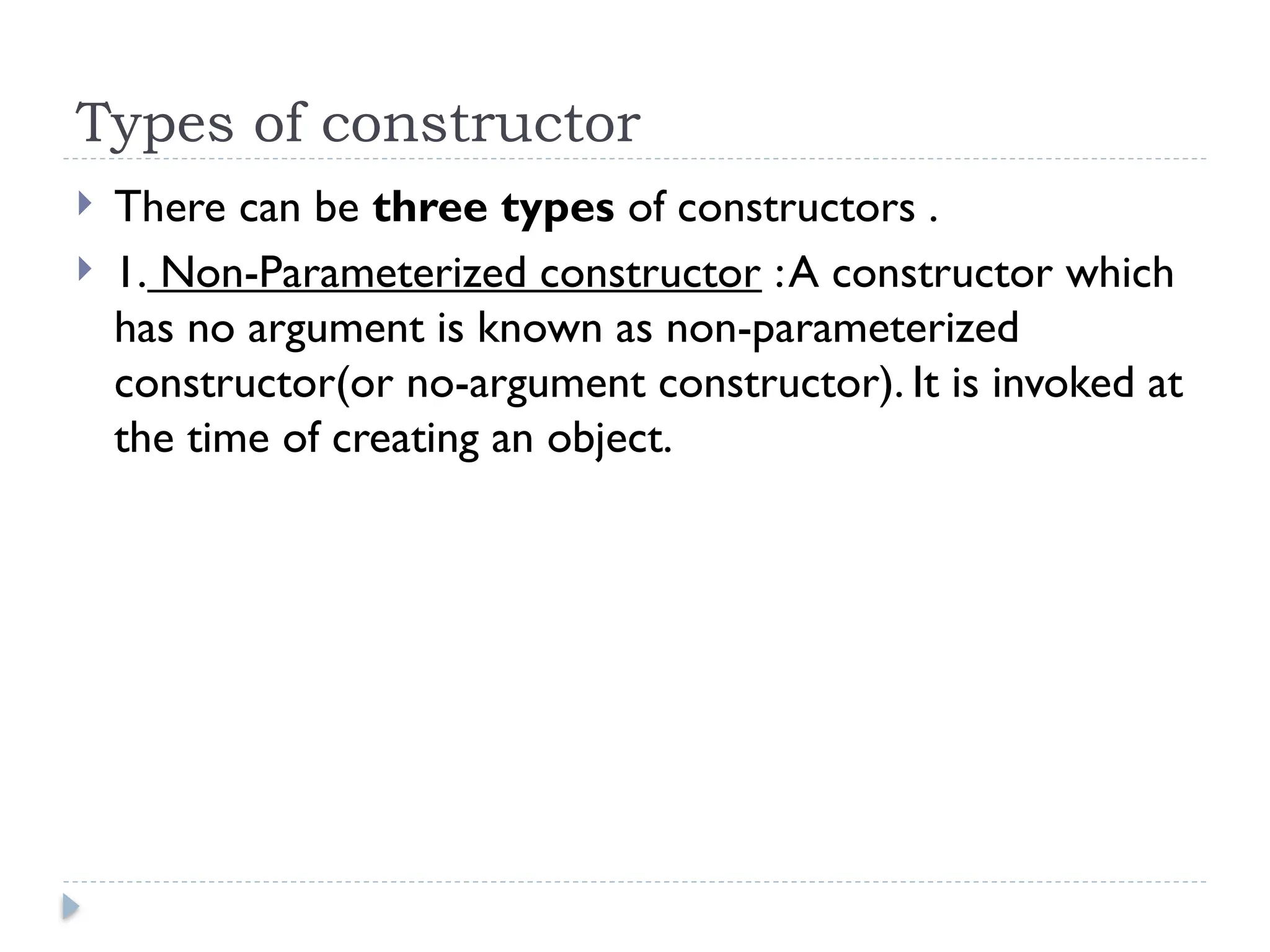
The document explains constructors in programming, specifically in C++, highlighting their purpose, types, and usage. It details three types of constructors: non-parameterized, parameterized, and copy constructors, with code examples for each. Constructors are special methods used to initialize object data at the time of creation and do not have a return type.