More Related Content
PPTX
Excavation safety as per 1926 subpart P.pptx PDF
Excavation Safety Presentation as part of COSH PPSX
PPT
Excvation Safety for safety officers reference PPT
dftvgebhjijh bed7 gbwe d bwenp dgbwe ubdwueb djhweb jhb wejh b jhwe bdhbwejhb... PDF
PPTX
PPTX
Similar to construction hazards and standards from OSHA
PPT
OSHA Trenching and Excavation Requirements PPTX
PPTX
Excavation and Demolition powerpoint presentation PPT
PPT
Excavation Safety Training Module 1 PPTX
Excavator.pptx training powerpoint safety PPT
Excavation OSHA Safety with safety and OSHA standards PPT
PPT
038 Trenching and Shoring.PPT PPTX
PPTX
1926_ExcavatnTrenchiquesmmmmmmmmmmmmmmmm PPT
03 Safety in Excavation & Blasting for t PPTX
Excavation training module.pptx agar lbh PPT
PPTX
Excavation-Safety-1. Construction safety and health PPT
PPTX
PDF
PDF
PPTX
ASP Study Group_Safety Programs Part Two Revised dec 13 2015.pptx More from msiskenderoglu
PPT
innovative frameworks on social statistics-final PPT
construction scheduling and cost control PPT
CONSTRUCTION SCHEDULING & COST CONTROL PPT
Building technology for construction and buildings PPT
building tech unit 6 Framed buidings.ppt PPT
economy and construction industry in korea PPT
Construction definitions and abbreviations Recently uploaded
PDF
The Science Behind Why Accountability Works in Alcohol Recovery.pdf PPTX
PPTX
Compassionate Hospice Care Services in Orange County, NY PDF
cytokines 2025.pdf -ytokines are small proteins that help control the growth ... PPTX
Cells and Organs of immune system [Autosaved].pptx PDF
Evaluation of Antidepressants (Preclinical & Clinical) PPTX
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA and its importance .pptx PPT
Investigation of an Epidemic ...outbreak investigation PDF
A Guide to Your Benefits: 2026 MVP Medicare Advantage Plans PPTX
The autoclave is also called a steam sterilizer that is commonly used in heal... PDF
MedWorks Advantage Your Trusted Partner in Medical & Surgical Equipment PDF
Reticulin Stain (Gordon & Sweet Method) | Special Stain in Histopathology PDF
Patient lifting robot concept presentation PPTX
Geriatric Health in Nepal: Aging Process, Health Problems, and Care Services PPTX
Ophthalmic lens power and form presentation PPTX
"Strategic Approaches to Enhancing Healthcare Management & Leadership Effecti... PPTX
Prism and Its Uses in Ophthalmic Dispensing PPTX
Corneal Topography: Principles, Techniques, Patterns, and Clinical Applications PPT
National child policy.ppt child health nursing PPTX
PPTS HEALTHCARE.pptx NON-COMMUNICABLE DISEASES construction hazards and standards from OSHA
- 1.
- 2.
2 ©2006 TEEX
Constructionvs. General
Industry
“Construction, alteration and/or repair,
including painting and decorating” is
under 29 CFR 1926 – 29 CFR 1910.12
Repair of existing facilities; replacement
of structures and their components
Interpretation: Construction vs.
Maintenance
- 3.
3 ©2006 TEEX
29CFR 1926 Organization
A. General
B. General Interpretations
C. General Safety and Health Provisions
D. Occupational Health and Environmental
Controls
E. Personal Protective and Life Saving
Equipment
F. Fire Protection and Prevention
G. Signs, Signals, and Barricades
H. Materials Handling, Storage, Use, and
Disposal
I. Tools – Hand and Power
- 4.
4 ©2006 TEEX
29CFR 1926 Organization
J. Welding and Cutting
K. Electrical
L. Scaffolds
M. Fall Protection
N. Cranes, Derricks, Hoists, Elevators, and Conveyors
O. Motor Vehicles, Mechanized Equipment, and
Marine Operations
P. Excavations
Q. Concrete and Masonry Construction
R. Steel Erection
- 5.
5 ©2006 TEEX
29CFR 1926 Organization
S. Underground Construction, Caissons,
Cofferdams, and Compressed Air
T. Demolition
U. Blasting and the Use of Explosives
V. Power Transmission and Distribution
W. Rollover Protective Structures; Overhead
Protection
X. Ladders
Y. Commercial Diving Operations
Z. Toxic and Hazardous Substances
- 6.
6 ©2006 TEEX
Hazardsand Standards
What hazards are employees exposed to:
When they set up a drilling site?
When they grade land or excavate?
When they clear a site for use?
Regulations in 29 CFR 1926:
Subpart P – Excavations
Subpart O – Motor Vehicles, Mechanized
Equipment, and Marine Operations
If blasting: Subpart O
- 7.
- 8.
8 ©2006 TEEX
ExcavationHazards
Excavating is
recognized as one of
the most hazardous
construction operations
Fatality rate for
excavations is twice that
of construction as a
whole
Cave-ins: More likely to
result in fatalities than
other excavation
hazards
- 9.
9 ©2006 TEEX
Hazardsof Excavation Work
Cave-ins
Underground utilities
Materials/equipment falling into
excavation sites
Asphyxiation
Explosion
Falls
Drowning
- 10.
10 ©2006 TEEX
SoilMechanics
Unit weight of soils:
Varies with type and moisture content
1 cubic foot can weigh 100 to >140 lbs
1 cubic meter can weigh >3000 lbs
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
13 ©2006 TEEX
Definitions
Excavation: any man-made cut, cavity,
trench, or depression in an earth
surface, formed by earth removal.
Trench (Trench excavation): a narrow
excavation (in relation to its length)
made below the surface of the ground.
Depth>width; width <15 feet
<15 feet between structure and side
- 14.
14 ©2006 TEEX
Definition– Competent Person
Training, experience, and knowledge of:
Soil analysis
Use of protective systems
Requirements of 29 CFR Part 1926 Subpart P
Ability to detect:
Conditions that could result in cave-ins
Failures in protective systems
Hazardous atmospheres
Other hazards including those associated with confined
spaces
Authority to take prompt corrective measures to
eliminate existing and predictable hazards and to
stop work when required
- 15.
15 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651Specific Excavation
Requirements
a. Remove or support surface
encumbrances (competent person)
b. Determine location of all underground
utilities before opening excavation
OneCall system / 811
Use safe means to determine exact
locations & protect underground utilities
- 16.
16 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651(c)Access & Egress
Structural ramps for access and egress
designed by competent person &
constructed according to design
Bar is higher for equipment ramps
Access & egress ramps designed to
avoid slipping or tripping
- 17.
17 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651(c)Access & Egress
Stairway, ladder, ramp, other safe
egress within 25 feet of employees in
trenches >4 feet deep
Ladder requirements apply, including
extending 3 feet above top surface
Every 25'
4' or greater
- 18.
18 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651Specific Excavation
Requirements
d. In traffic areas, reflective
vests required
e. No workers underneath
loads handled by lifting or
digging equipment.
f. Barricades, stop logs or
hand signals for mobile
equipment operating near
excavations
- 19.
19 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651(g)Hazardous
atmospheres
In excavations 4 feet or more where
hazardous atmospheres are likely to
exist must test atmosphere before
entering and retest as necessary
Unsafe below 19.5% oxygen
Stay below 20% of lower flammable limits
Ventilation or PPE must be used as
required
Rescue equipment available
- 20.
20 ©2006 TEEX
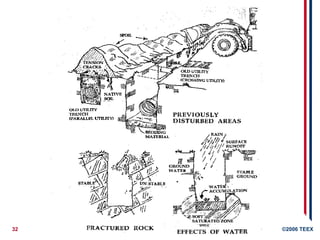
1926.651(h)Water Accumulation
Precautions required
before working for water
in excavations
Competent Person must
monitor control measures
If diverting surface water,
must take steps to
prevent water from
entering trench
- 21.
21 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651(i)Stability of adjacent
structures
Structures adjacent to excavations must
be supported if stability is affected
No excavation below adjacent footings
unless underpinned, or stable rock, or
approved by PE
No undermining pavements unless
supported
- 22.
22 ©2006 TEEX
1926.651Specific Excavation
Requirements
j. Protect employees from falling rock,
soil, or materials/equipment falling into
excavations.
Keep materials 2 feet from edge
Retaining devices/barricades
k. Inspections by competent person,
daily and as needed during shift
l. Walkways to cross excavations
- 23.
23 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652Requirements for
protective systems
Protection of employees in
excavations
Design of sloping and
benching systems
Design of support
systems, shield systems,
and other protective
systems
Materials and equipment
Installation and removal
- 24.
24 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652(a)Protection of
employees in excavations
Use adequate protective system, except
Excavations entirely in stable rock
<5 feet and competent person sees no
potential for cave-in
Capacity for all reasonably
expected loads
- 25.
25 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652(b)and (c) Design of
sloping and benching systems
Four choices for sloping:
Slope for type ‘C’, no steeper than 34°
Use sloping choices from Appendices A, B
Tabulated data determined by a PE
Designed by a PE
For support systems, shield systems, other:
Design using Appendices A, C, D
Manufacturer’s tabulated data
Other tabulated data determined by a PE
Designed by a PE
- 26.
26 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652(d)Materials and
equipment
Materials for protective systems free
from damage & defects
Used according to manufacturer’s
specifications
If damaged,
competent person
must determine
suitability for
continued use
- 27.
27 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652(e)Installation and
removal of support
Support system members securely
connected together
Installed & removed to assure employee
safety
Keep within design
capacity
Remove from bottom
first, and backfill as
you remove
- 28.
28 ©2006 TEEX
1926.652(f)Sloping and
benching systems
No working on sloped or benched faces
unless employees below are protected
- 29.
29 ©2006 TEEX
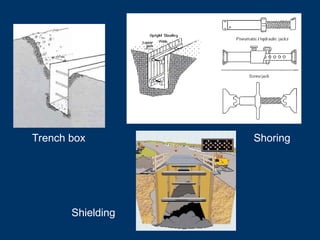
1926.652(g)Shield systems
Shield systems not subject to loads
exceeding their capacity
Installed to restrict lateral movement
Employee protection provided while
entering/exiting shields
No employees in trench during installation or
removal of shields
May excavate up to 2 feet below shield with
proper conditions
- 30.
- 31.
31 ©2006 TEEX
1926Subpart P Appendix A -
Soil Classification
A method of categorizing soil and rock
deposits in a hierarchy:
Stable Rock
Type A – cohesive soil >1.5 tsf – with
exceptions
Type B – cohesive soil >.5-1.5 tsf or
granular, disturbed, vibrated, fissured,
layered
Type C – cohesive soil <.5 tsf or granular,
submerged, layered…
- 32.
- 33.
33 ©2006 TEEX
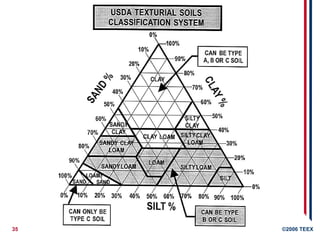
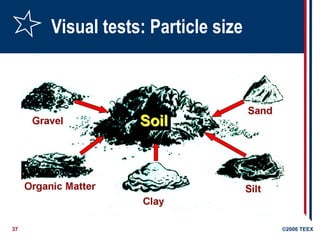
Soils- Types & Particle Size
Gravel
larger than 2 millimeters
Sand
Between 0.075 and 2 millimeters
Silt
Between 0.002 and 0.075 millimeters
Clay
Smaller than 0.002 millimeters
.
- 34.
34 ©2006 TEEX
Additionalsoil classification
Layered geological strata: based on
weakest layer
May be classified individually if weaker
is on top of stronger
- 35.
- 36.
36 ©2006 TEEX
1926Subpart P Appendix A -
Soil Classification
Each soil and rock deposit shall be
classified by a competent person
Classification made based on at least
one visual and one manual analysis
- 37.
- 38.
38 ©2006 TEEX
Visualtests
Clumping
Cracks or spalling
Existing utilities/previously disturbed soil
Layers and slope
Water in surface, seeping, water table
Vibration sources
- 39.
39 ©2006 TEEX
Manualtests
Plasticity
Dry strength
Thumb penetration
Pocket penetrometer or shearvane
Drying test
- 40.
- 41.
41 ©2006 TEEX
Organizationof Subpart O
1926.600 - Equipment.
1926.601 - Motor vehicles.
1926.602 - Material handling equipment.
1926.603 - Pile driving equipment.
1926.604 - Site clearing.
1926.605 - Marine operations and equipment.
1926.606 - Definitions applicable to this
subpart.
- 42.
42 ©2006 TEEX
1926.600(a)Equipment - General
Requirements
Lights/reflectors on unattended equipment
next to highway
Protection for tire changes on split rims
Elevated equipment: protect from falling
Parking brake, plus chocks for inclines
Batteries: by Subpart K
Cab glass: safety glass with no visible
distortion
Movement around power lines or transmitters
Stops for railroad cars on spurs
- 43.
43 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601– Motor Vehicles
a. Coverage.
Motor vehicles that operate within an off-
highway jobsite, not open to public traffic
Not for material handling equipment
covered under 1926.602.
- 44.
44 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601(b)General
requirements
Brake system in operable condition:
Service brake system
Emergency brake system
Parking brake system
2 headlights & 2 taillights if needed,
depending on visibility
Brake lights regardless of visibility
- 45.
45 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601(b)General
requirements
Audible warning device (horn)
Obstructed rear view: must have
Reverse signal alarm audible above
surrounding noise level or
Backed up only when observer signals that
it is safe
Windshields & powered wipers on cabs
Fix cracked glass
Defogger/defroster where necessary
- 46.
46 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601(b)General
requirements
Haulage vehicles: cab shield and/or
canopy adequate to protect the operator
from shifting or falling materials
Secure tools and material from
movement in compartments with
employees
Seats firmly secured and adequate for
employees being carried
- 47.
47 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601(b)General
requirements
Seat belts and anchorages meeting 49
CFR Part 571
Dump bodies supported, locked into
position for maintenance or inspection
Latch on hoisting/dumping devices to
prevent accidental operation
Trip handle of dump truck tailgate:
operator must be clear when dumping
- 48.
48 ©2006 TEEX
1926.601(b)General
requirements
Rubber-tired equipment must have
fenders or mud flaps
Vehicles checked at beginning of shift:
All brake systems
Tires
Horn
Steering
Coupling
Seat belt
Controls
Safety devices
Lights/reflectors
Wipers/defrosters
Fire extinguishers
- 49.
49 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602– Material Handling
Equipment
Application:
Scrapers, loaders, crawler or wheel
tractors, bulldozers, off-highway trucks,
graders, agricultural and industrial tractors,
and similar equipment
Compactors and rubber-tired "skid-steer"
equipment: reserved
- 50.
50 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(a)(2)Seat belts
Provided and must meet standards
Not necessary for standup operations
Not necessary for equipment without
roll-over protective structure (ROPS) or
canopy protection
ROPS: See 1926 Subpart W
- 51.
51 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(a)Earthmoving
equipment; General
Access roadways and grades
Must be constructed and maintained for
safe movement of equipment involved
Emergency access ramps or berms to
restrain and control runaway vehicles
Service braking system
Capable of stopping and holding fully
loaded equipment
SAE standards apply
- 52.
52 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(a)Earthmoving
equipment; General
Fenders on pneumatic-tired earth-
moving equipment >15 mph
Suspended pending reevaluation
ROPS and overhead protection: Subpart
W
Horns for bidirectional machines
Reverse signal alarm
Guard all scissor points
- 53.
53 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(b)Excavating and
other equipment
Seatbelts for tractor operation
Power Crane and Shovel Associations
Standards No. 1 and No. 2 of 1968, and
No. 3 of 1969 adopted
- 54.
54 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(c)Lifting and hauling
equipment
Other than that covered by Subpart N
1926.600 and:
Ratings clearly visible and not exceeded
No modifications or additions without
manufacturer’s written approval
Multiple trucks together: proportion of load
must not exceed capacity
Steering knobs not attached unless
spinning prevented
- 55.
55 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(c)Lifting and hauling
equipment
Overhead guards for high lift rider
industrial trucks
ANSI B56.1-1969
Riding on industrial trucks:
No unauthorized personnel
Safe place to ride
- 56.
56 ©2006 TEEX
1926.602(c)(1)(viii)Lifting
Personnel
Only where designed for that purpose
by manufacturer! (interpretation)
Safety platform secured to lifting
carriage or forks
Riding personnel must be able to shut
off power to truck
Falling object protection
- 57.
- 58.
58 ©2006 TEEX
1926.603Pile driving equipment
General requirements
Barges or floats: 1926.605
Pile driving equipment
- 59.
59 ©2006 TEEX
1926.604Site clearing
Protect from toxic/irritant plants
Instruct in first aid treatment
Rollover guards
Overhead and rear canopy guards:
At least 1/8” steel plate or 1/4” wire mesh
with up to 1” openings
Rear of canopy: at least 1/4” wire mesh
with up to 1” openings
- 60.
60 ©2006 TEEX
1926.605Marine operations and
equipment
Material handling: 1918, Longshoring
Access to barges
Working surfaces of barges
First-aid and lifesaving equipment
Commercial diving operations: 1926
Subpart T
- 61.
61 ©2006 TEEX
1926Subpart W: Rollover
Protective Structures (ROPS)
This construction equipment must have
ROPS meeting minimum performance
standards:
Rubber-tired, self-propelled scrapers
Rubber-tired front-end loaders
Rubber-tired dozers
Wheel-type agricultural and industrial tractors
Crawler tractors
Crawler-type loaders
Motor graders, with or without attachments
NOT sideboom pipe laying tractors
- 62.
62 ©2006 TEEX
RolloverProtective Structures
Purpose: Prevent complete overturn;
minimize possibility of crushed operator
Driver could still be crushed if not
wearing a seatbelt!
Also in subpart W:
Testing provisions
Rule for overhead protection
- 63.
- 64.
64 ©2006 TEEX
Applicationof Scaffold
Regulations
What is a scaffold?
What is covered by 29 CFR 1926
Subpart L?
Where are scaffolds used in oil and
gas?