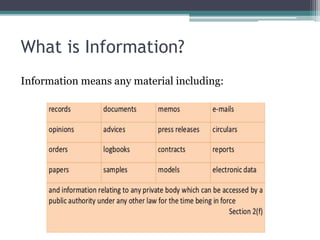
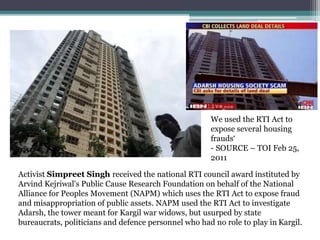
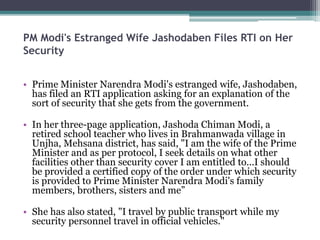
The Right to Information Act was passed in 2005 in India to promote transparency, accountability, and better governance. Some key provisions include granting citizens the right to request information from public authorities, specifying timelines for responses, and exempting certain types of information like cabinet papers and personal information. The Act has uncovered several corruption scandals since its enactment and empowered citizens to expose issues like housing frauds and anomalies in public distribution systems. However, greater awareness efforts are still needed for citizens to fully utilize their rights under the Act.