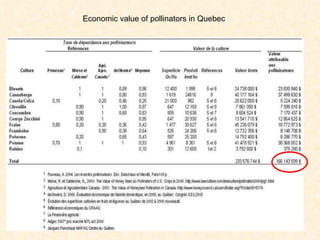
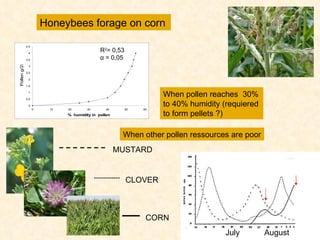
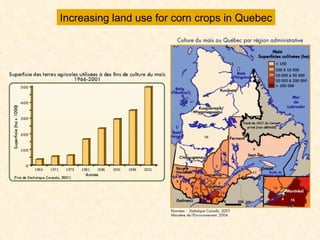
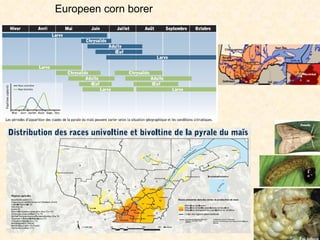
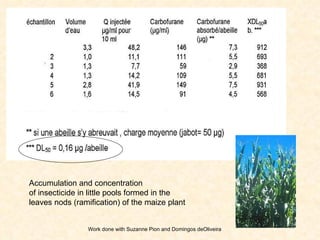
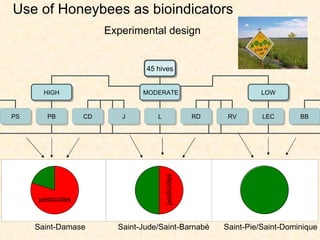
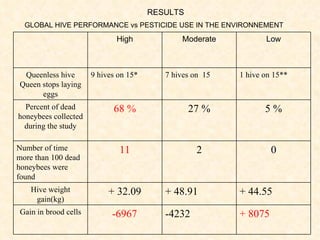
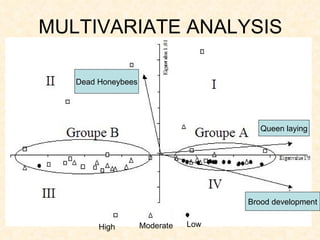
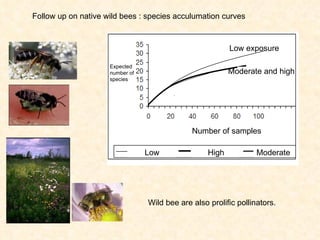
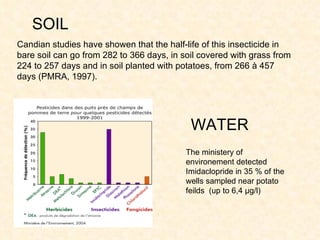
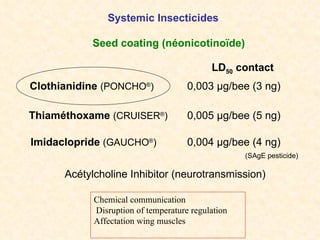
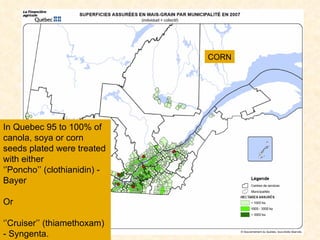
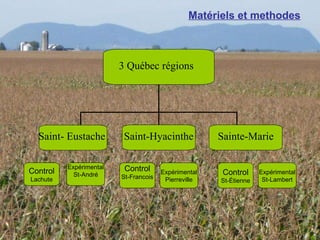
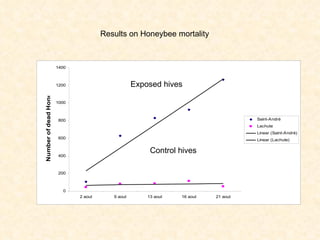
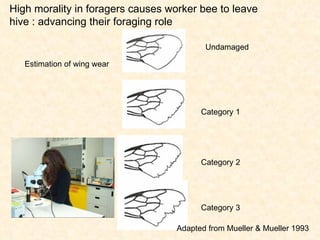
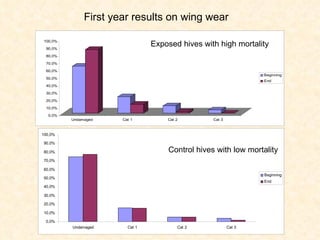
1) The study examined the impacts of pesticides used in corn fields in Quebec on honeybee colonies. Experiments showed higher honeybee mortality and weaker hives in fields with moderate-to-high pesticide usage compared to low usage or control fields.
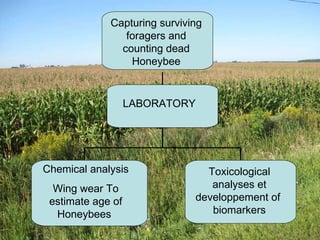
2) Laboratory analysis found that honeybees exposed to pesticides had increased levels of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, indicating exposure. Biomarkers are being developed to better evaluate pesticide impacts on honeybee health.
3) Ongoing work includes measuring vitamin A and immune system enzymes in honeybees to study how pesticides may weaken immunity and facilitate viral infections.