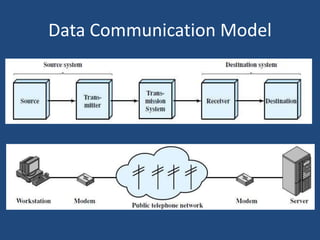
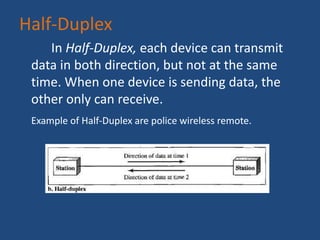
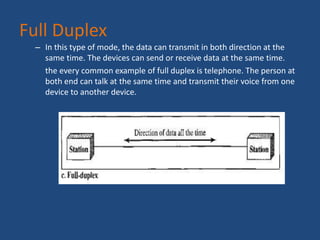
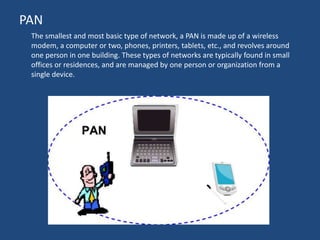
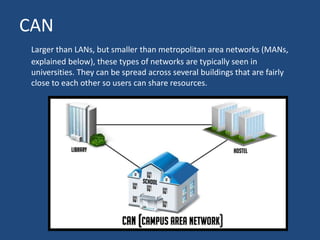
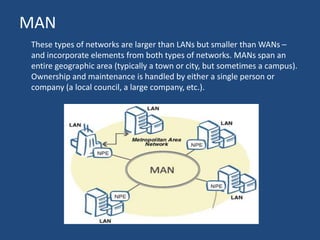
The document provides an overview of data communication, including its definition, history, and types, such as simplex, half-duplex, and full-duplex modes. It also discusses various network types, including PAN, LAN, WLAN, CAN, MAN, and WAN, highlighting their characteristics and applications. Additionally, the document covers basic connectivity methods like broadband, mobile internet, VPNs, and dial-up connections.