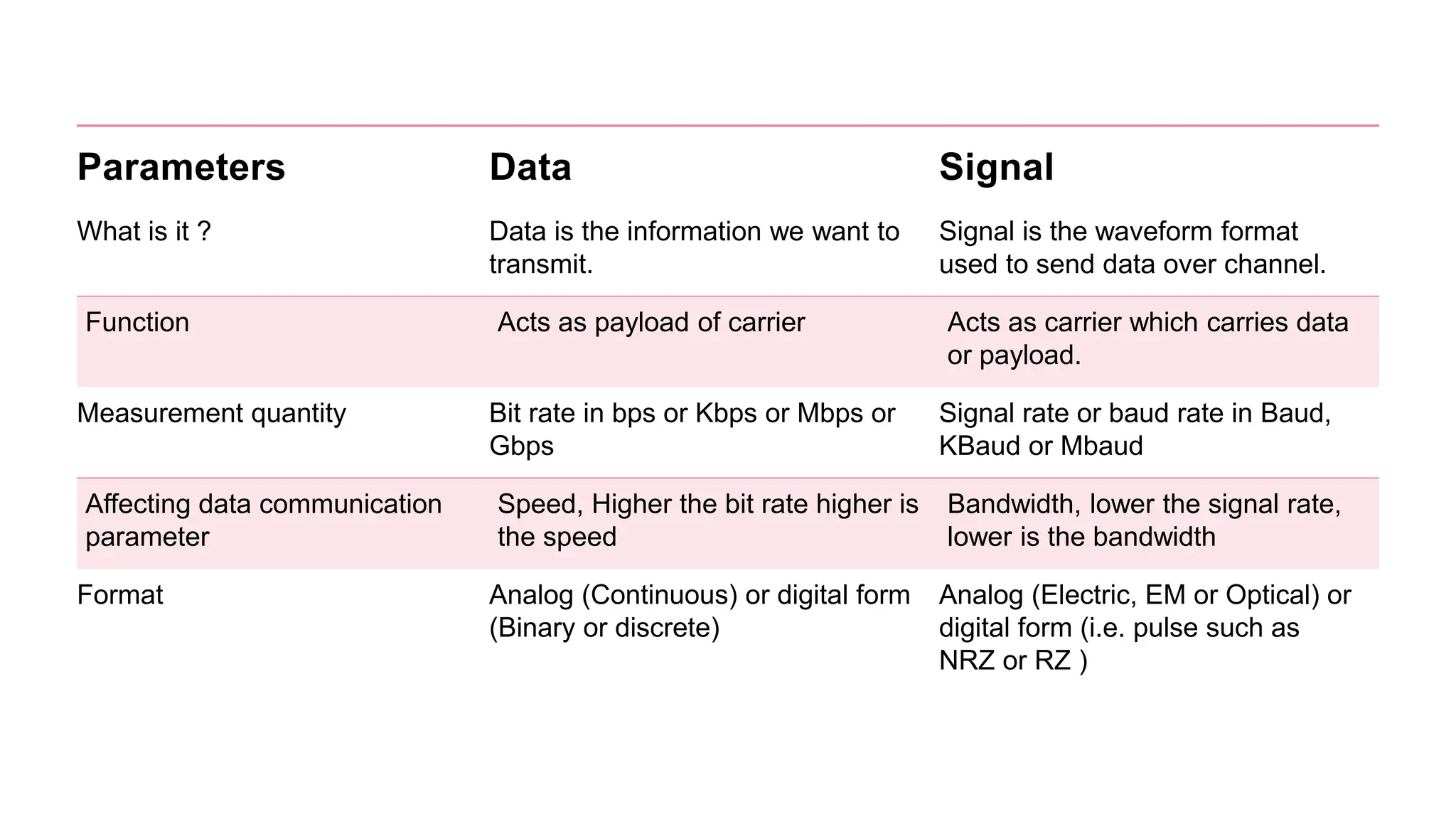
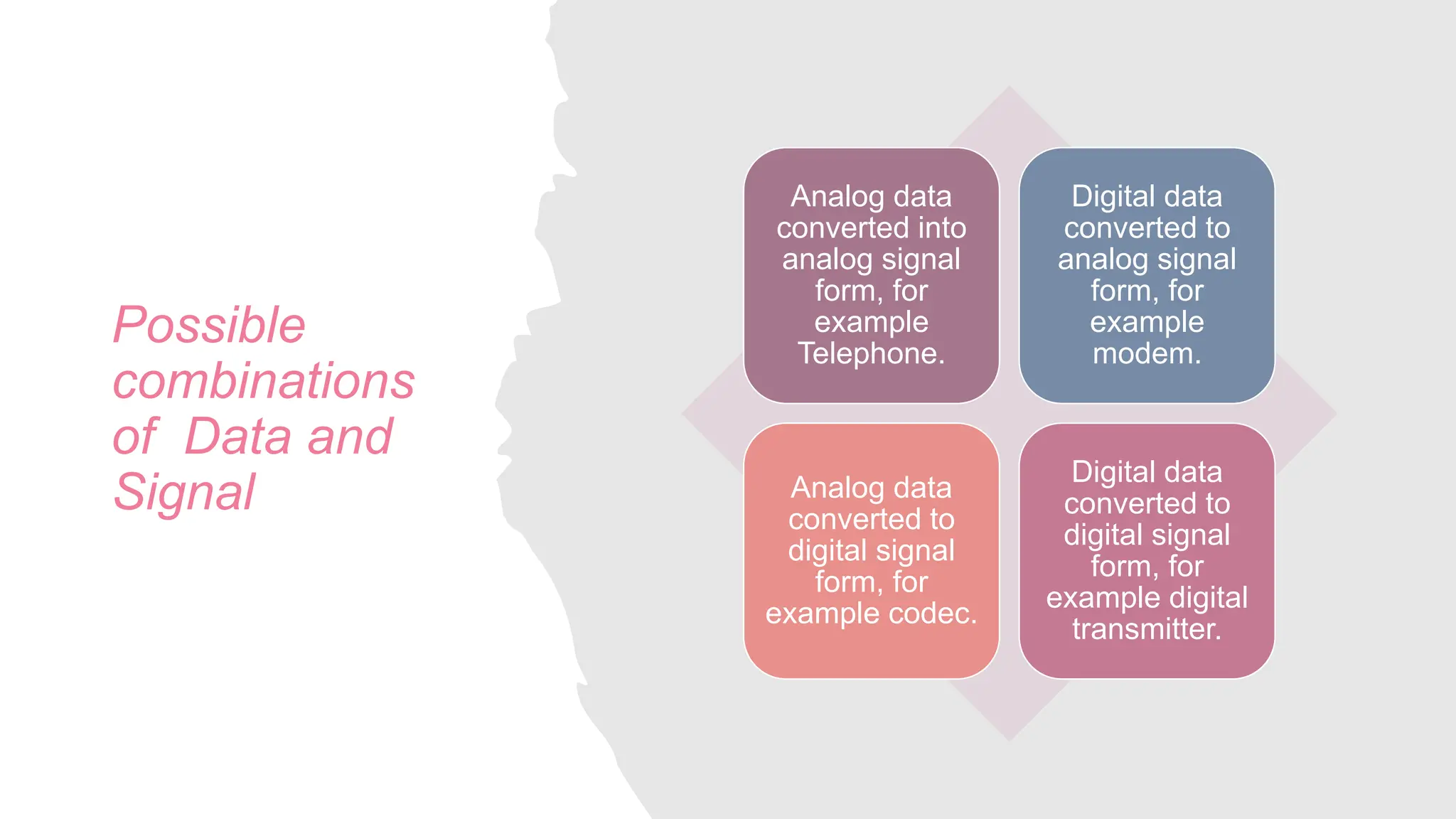
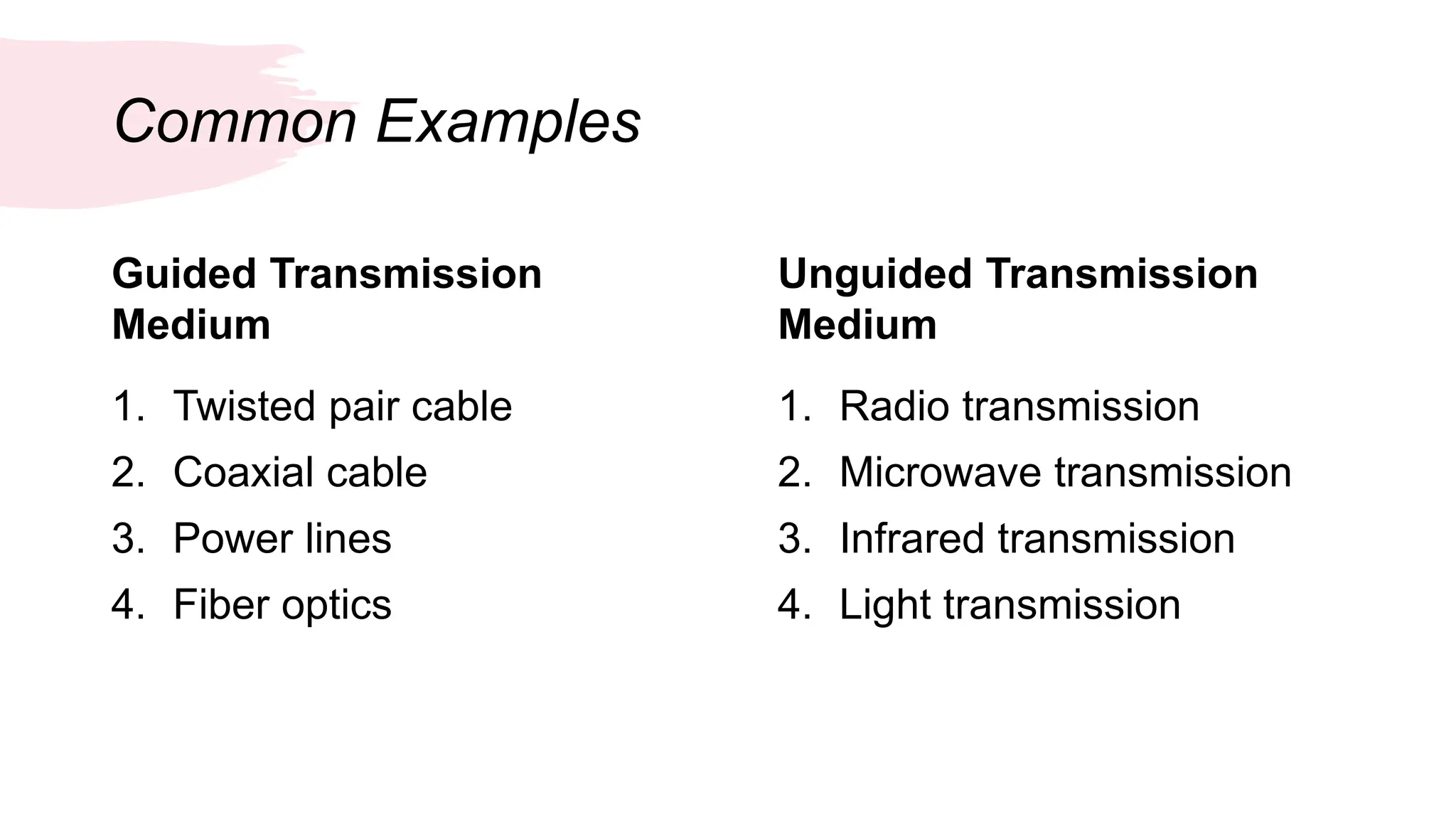
The document discusses computer networks and data communication, explaining key terminologies such as data, signals, and transmission media. It outlines the four basic parameters of signals (amplitude, frequency, bandwidth, and phase) and differentiates between guided (wired) and unguided (wireless) transmission media. Additionally, it describes the data transfer rate as the speed at which digital data is transmitted from one location to another.