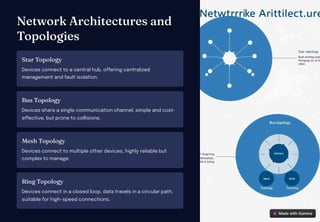
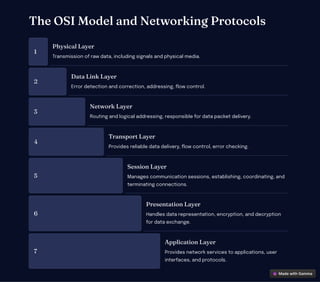
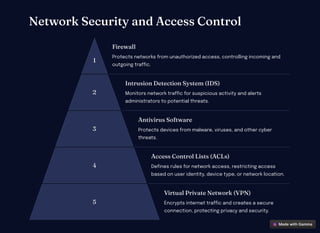
Computer networking facilitates communication and data sharing between interconnected devices, vital for modern life and business. It encompasses various architectures, protocols, and technologies, such as wired Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi, while also emphasizing security measures like firewalls and VPNs. The future of networking includes advancements like 5G, IoT, cloud computing, and AI to enhance performance and automation.