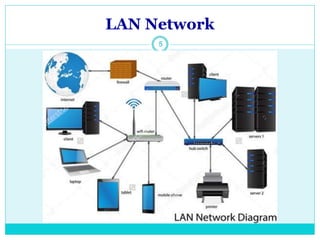
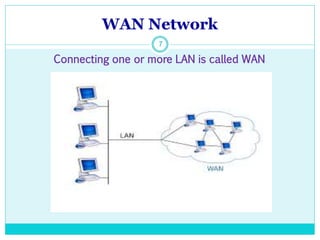
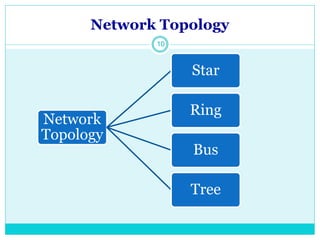
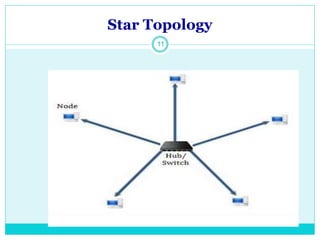
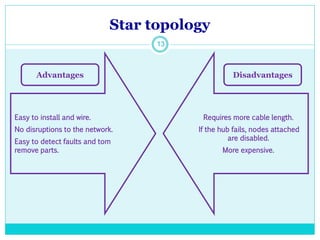
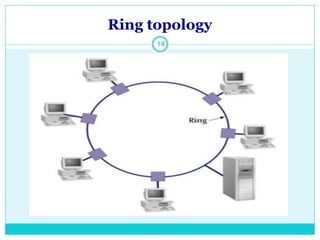
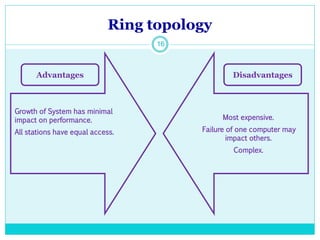
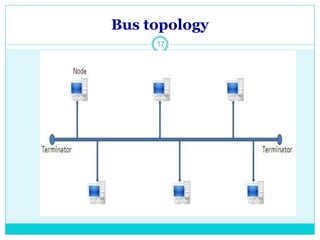
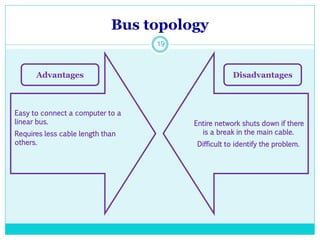
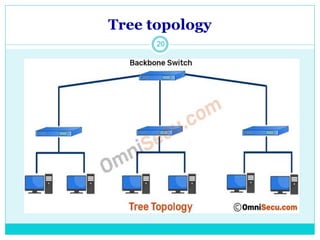
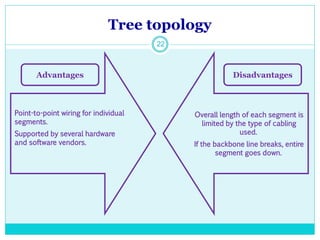
The document discusses computer networks and their key components. It defines a computer network as a group of computers linked together that allows them to communicate and share resources. It then describes the main types of networks as local area networks (LANs) for geographically close computers, and wide area networks (WANs) for computers farther apart connected by telephone lines or radio waves. The document proceeds to outline some common network topologies (arrangements) including star, ring, bus and tree configurations, and notes advantages and disadvantages of each.