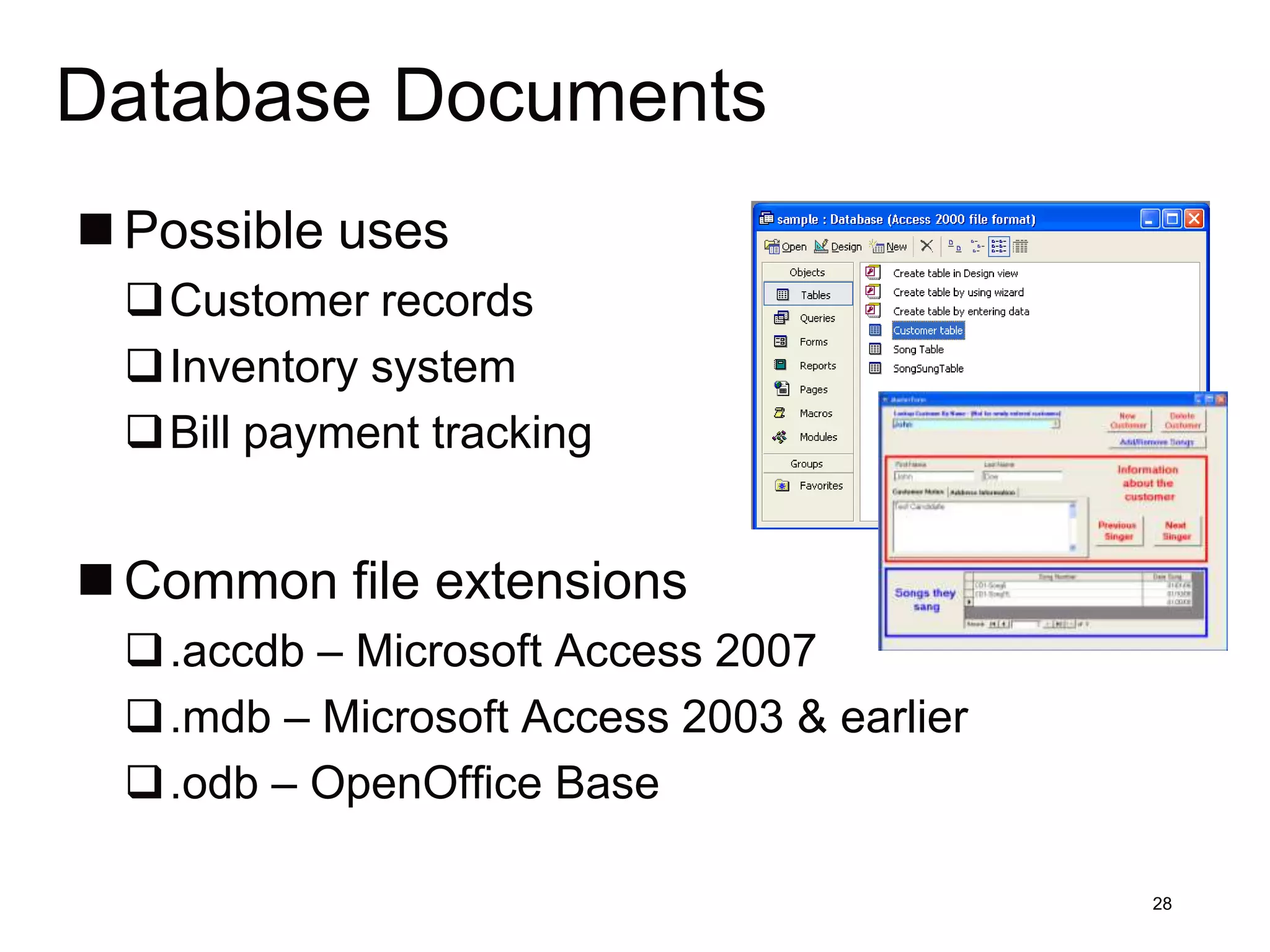
This document provides an overview of computing fundamentals including hardware and software interaction, types of software, and the software development process. It discusses how users interact with computers through input and output devices and application programs. It also summarizes different types of software including word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, databases, graphics, and multimedia software. It describes the basic concepts, features, and file formats for each type of software. Finally, it covers the software development lifecycle including programming, debugging, beta testing, documentation, updates, and upgrades.