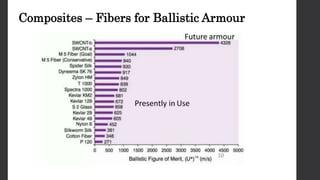
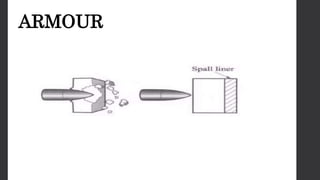
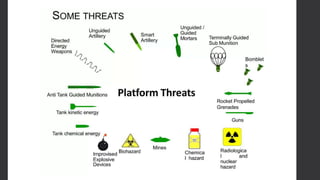
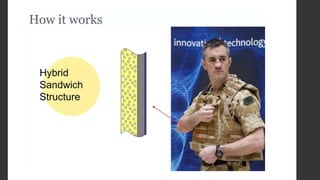
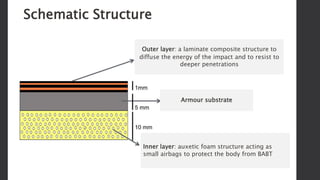
Composites are desirable for ballistic armor due to their ability to provide mobility and absorb impact energy through deformation and fracturing. Effective armor must resist penetration from threats like kinetic impacts, explosions, and debris. Composites rely on brittle fiber fracture to stop impacts but are soft against hard projectiles. However, composite and ceramic laminates provide an effective solution, with composites diffusing impact energy and ceramics resisting deeper penetration. An armor system may use composites as an outer layer, with an inner layer of auxetic foam to protect the body from behind armor blunt trauma.