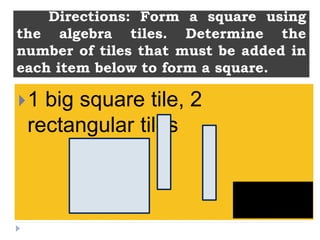
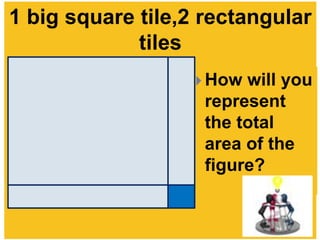
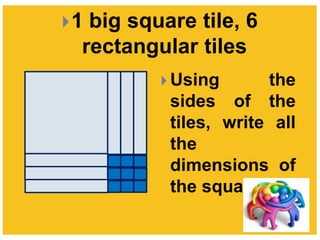
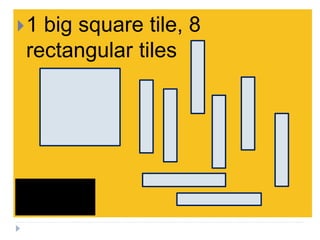
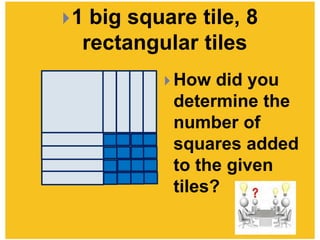
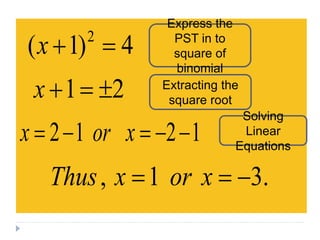
This document provides examples of completing the square to solve quadratic equations. It begins by showing how to factor a quadratic expression into a perfect square trinomial. It then demonstrates how to complete the square when the expression is not already a perfect square by adding or subtracting terms to make it a perfect square. The document provides step-by-step workings for several examples of completing the square to solve quadratic equations. It concludes by providing practice problems requiring students to find the solutions of quadratic equations by completing the square.