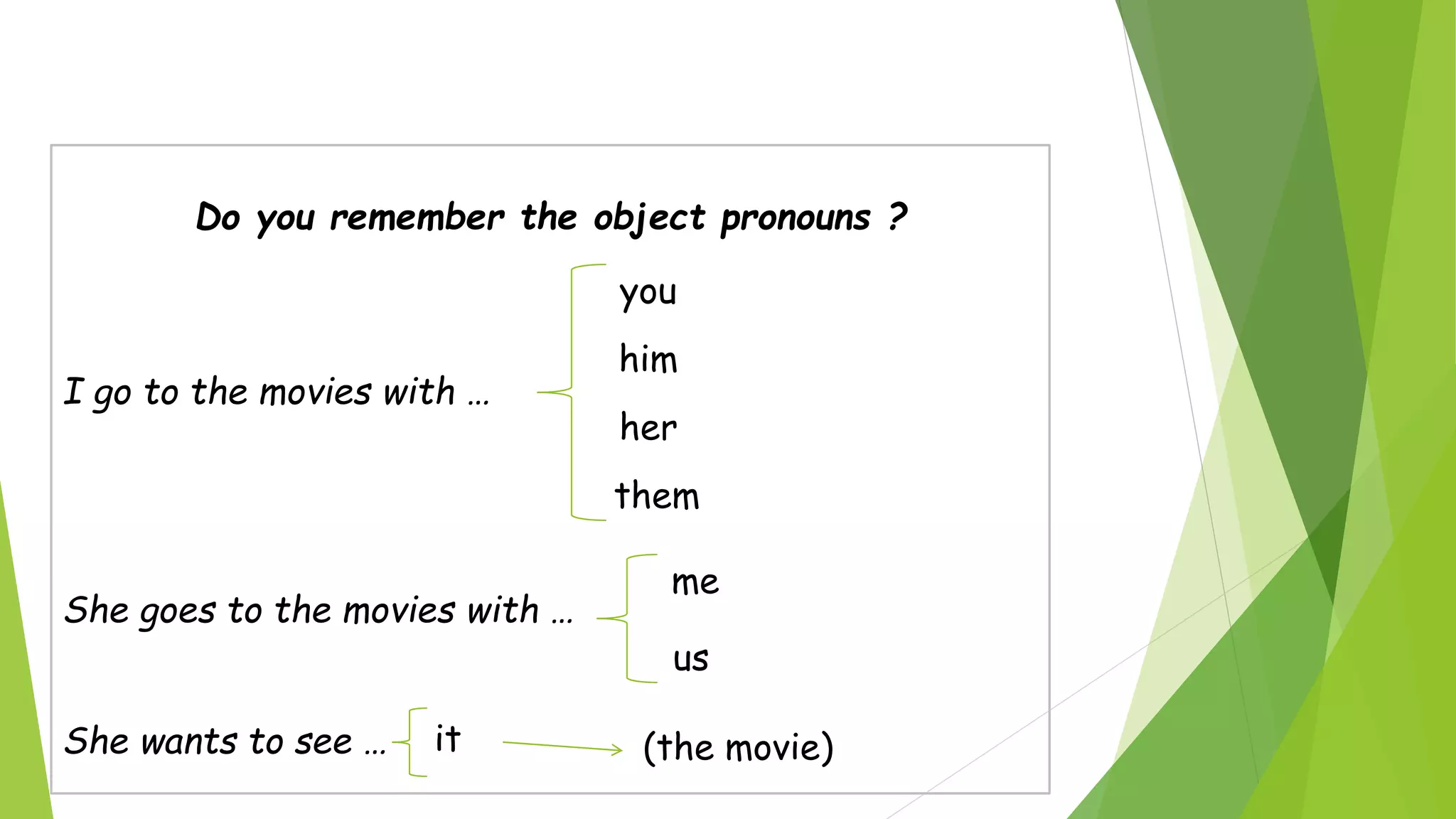
The document discusses pronouns. It begins by defining a pronoun as a word that replaces a noun to avoid repetition. It then covers the different types of pronouns including personal, reciprocal, demonstrative, relative, interrogative, indefinite and distributive pronouns. The summary also discusses the different cases of personal pronouns including subjective, possessive and objective cases. It provides examples of how pronouns are used as subjects and objects in sentences.