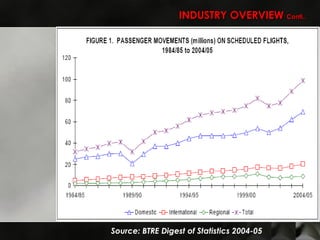
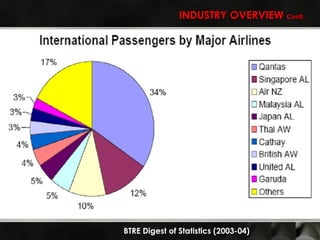
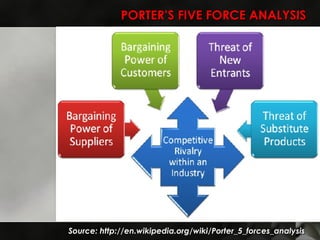
The Australian airline industry is dominated by two major airlines, Qantas and Virgin. A PEST analysis identified key political, economic, social and technological factors impacting the industry, such as industry deregulation, rising fuel costs, a tight labor market, and advances in airplane and information technology. A Porter's Five Forces analysis found competition to be intense between Qantas and Virgin due to their dominance, with potential new entrants facing moderate to high barriers. Opportunities for the airlines include regional expansion and taking advantage of international route designations, while threats include rising costs and potential new competition. The document recommends strategies like cost cutting, differentiation, and workforce efficiencies for the airlines to gain competitive advantages.