Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX

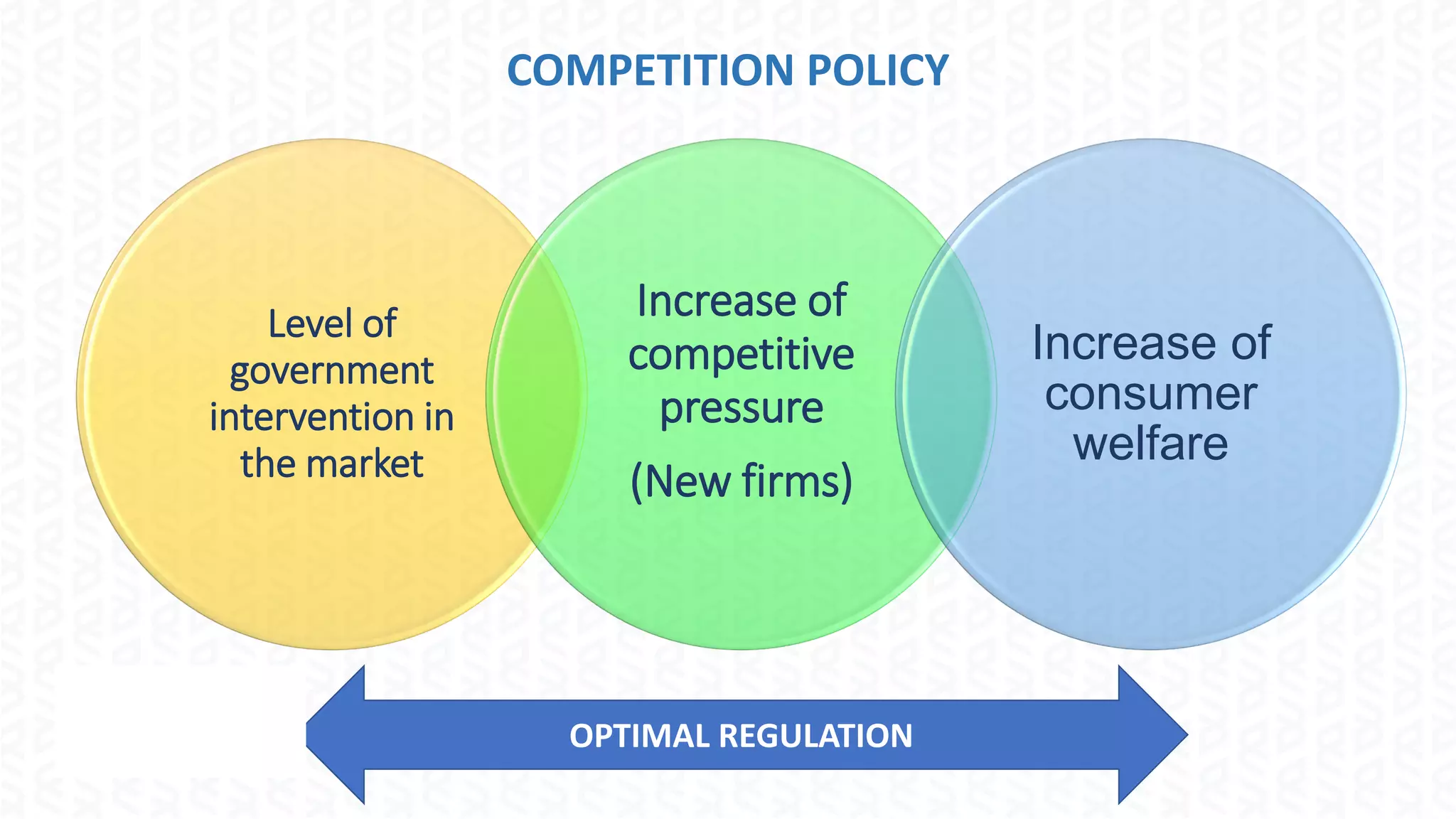


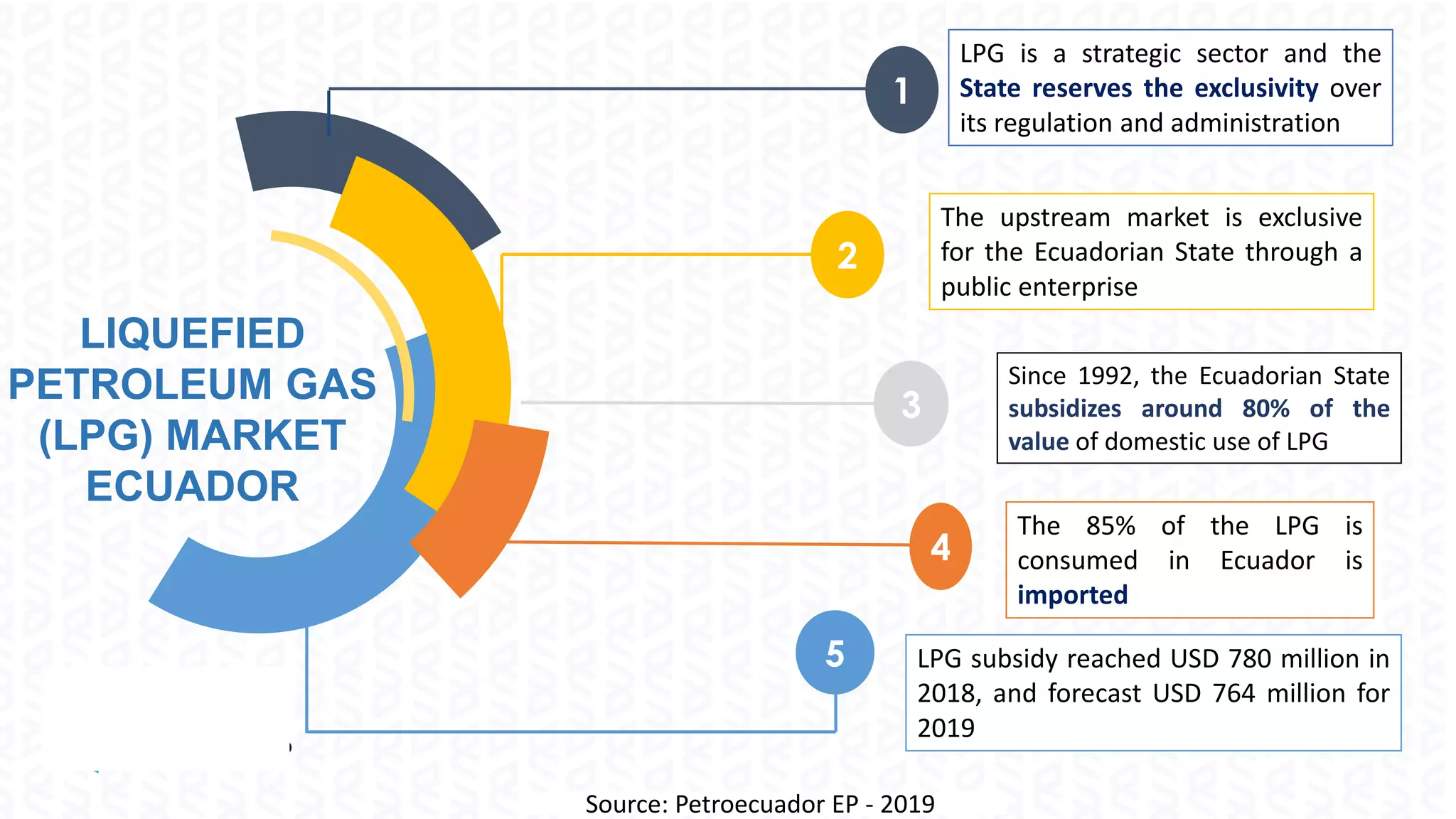
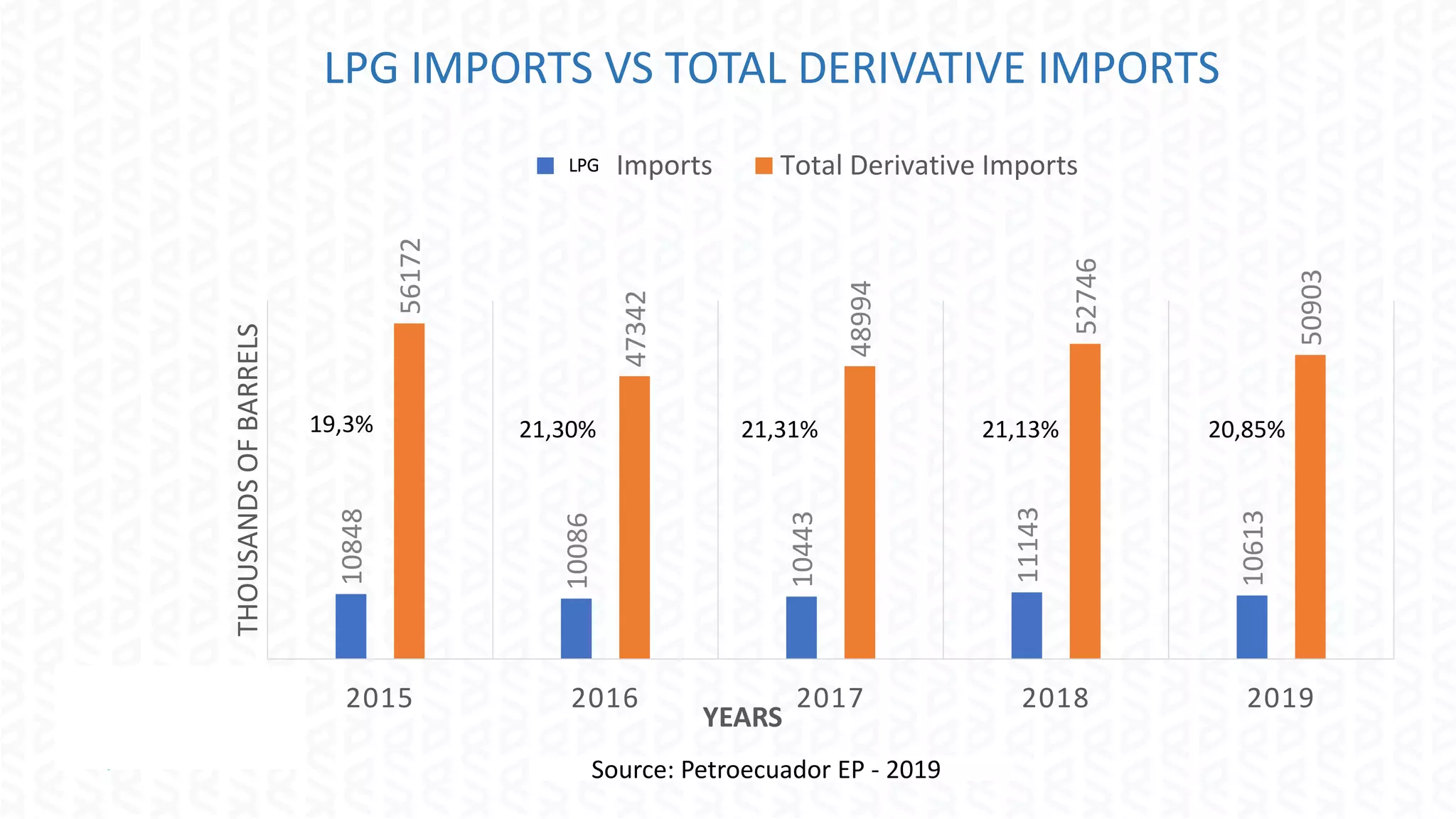

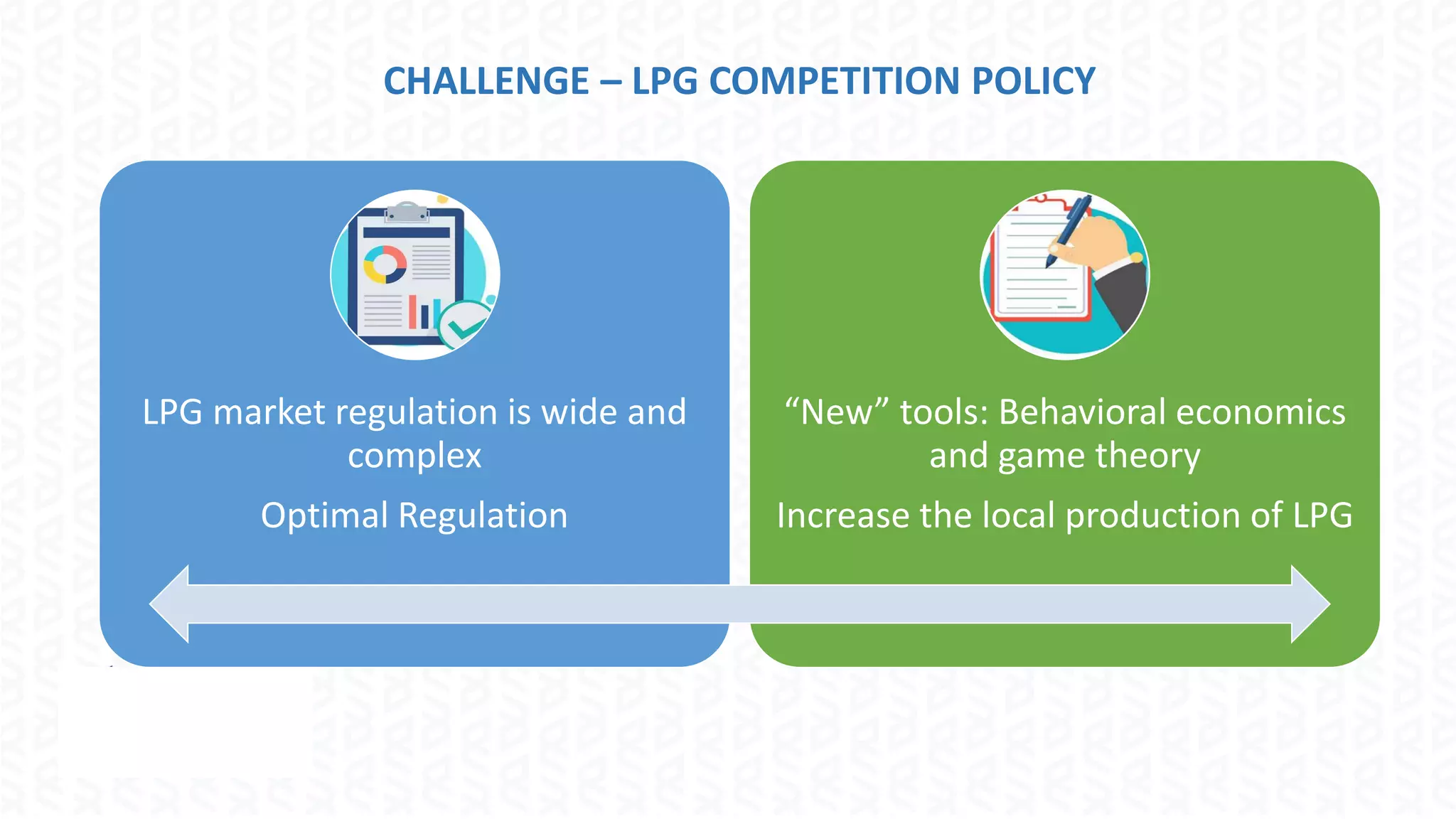


The document discusses the regulation of the liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) market in Ecuador, highlighting the need for optimal regulation in a natural monopoly context. It details the state's role in LPG, including the significant subsidies and the challenges posed by public enterprise inefficiencies. The document also emphasizes the importance of increasing local production and explores the application of behavioral economics and game theory in LPG market competition policy.









