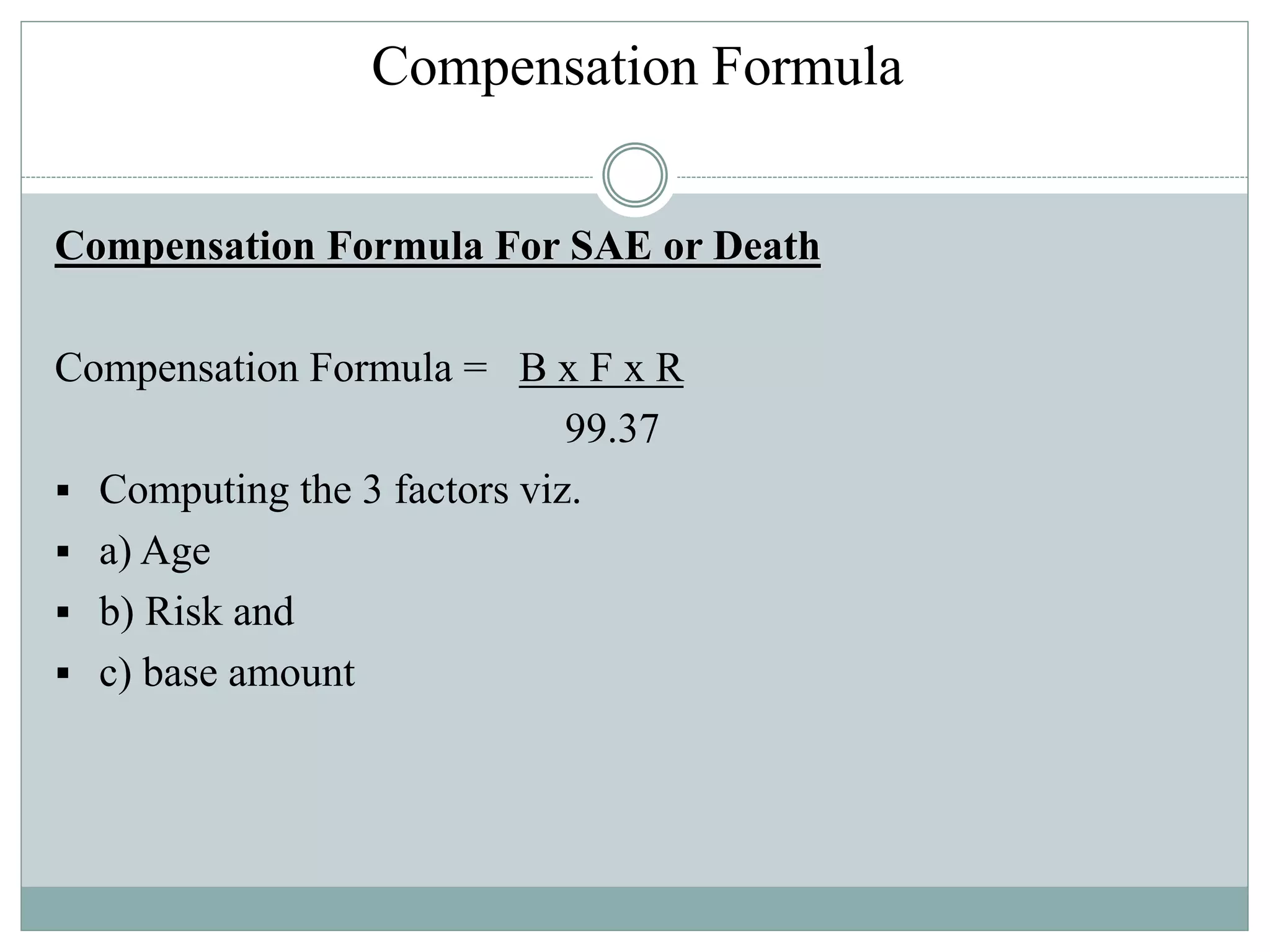
The document summarizes guidelines from the Drug Controller General of India regarding compensation for injuries or deaths related to clinical trials. It outlines that compensation is provided for trial-related injury, death, or serious adverse events. The procedures for determining compensation are described, including reports to ethics committees and expert panels. A compensation formula is provided based on a base amount, age factor, and risk factor. Limitations where compensation is not provided are also stated.