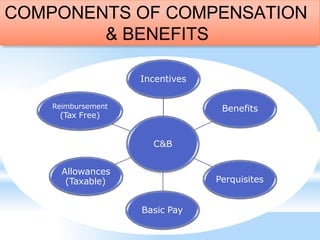
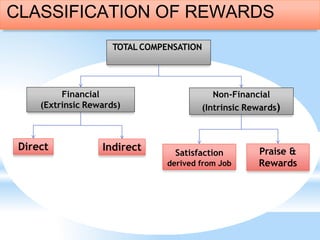
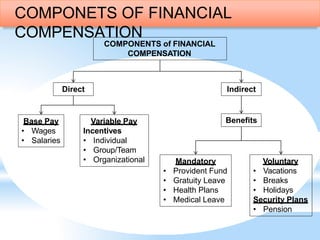
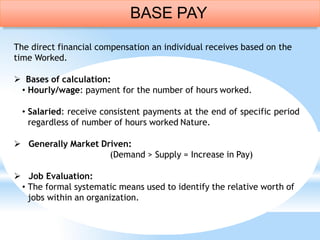
This document discusses compensation and benefits management. It defines key terms like salary, wages, and compensation. Salary refers to regular money received by an employee on a weekly, biweekly or monthly basis including benefits. Wages refer to payment for labor, especially on an hourly, daily or weekly basis. Compensation is the total payment and rewards provided to employees for their work, including pay, incentives and benefits. The document also outlines the components of an effective compensation strategy, and discusses different types of financial and non-financial compensation.