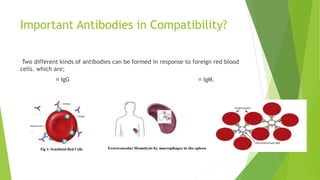
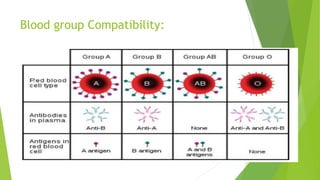
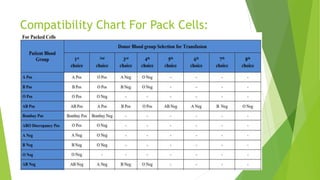
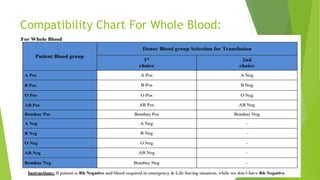
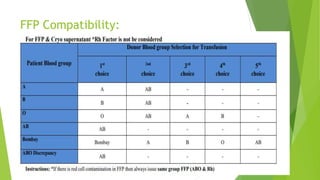
Compatibility testing is performed before blood transfusions to ensure the donor blood will (1) not harm the recipient, (2) function properly within the recipient, and (3) survive adequately in the recipient. The main compatibility factors considered are the ABO blood type antigens (A, B, and H) found on red blood cells and in bodily secretions, as well as antibodies that form in response to foreign antigens. A cross-match test is done to directly mix the recipient's serum with donor red blood cells to check for any antibodies that could cause the donor cells to be destroyed.