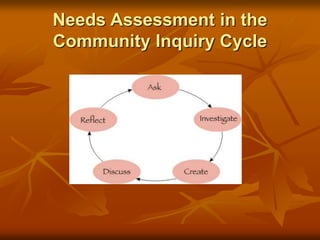
A community needs assessment identifies gaps in services for citizens through gathering information directly from community members, evaluates current programs, and determines priorities and resource allocation to better serve community needs. The case study describes a needs assessment initiated in Lorain County, Ohio to understand service utilization and needs of elderly residents which found needs for increased access to mental health and social support services in addition to physical health programs.