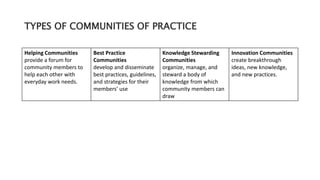
A community of practice (CoP) consists of individuals with shared interests who collaborate to achieve personal and group objectives, often through face-to-face and online interactions. CoPs can focus on various aspects including best practices, knowledge management, and innovation, and typically follow a natural life cycle from inception to conclusion. Members can be categorized into various roles, ranging from core team members to peripheral and transactional participants, each contributing at different levels to the community's goals.