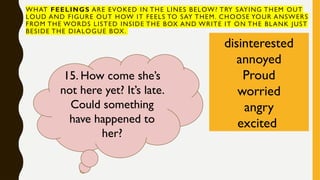
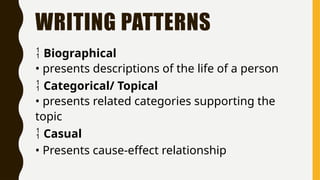
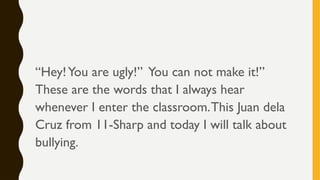
The document outlines the nature and process of communication, emphasizing its importance as a fundamental human need for exchanging ideas and understanding each other. It explains various models of communication, including linear, interactive, and transactional, and identifies barriers that can hinder effective communication, such as physical, language, and emotional barriers. Furthermore, it highlights the significance of intercultural communication in fostering understanding and respect among diverse groups.