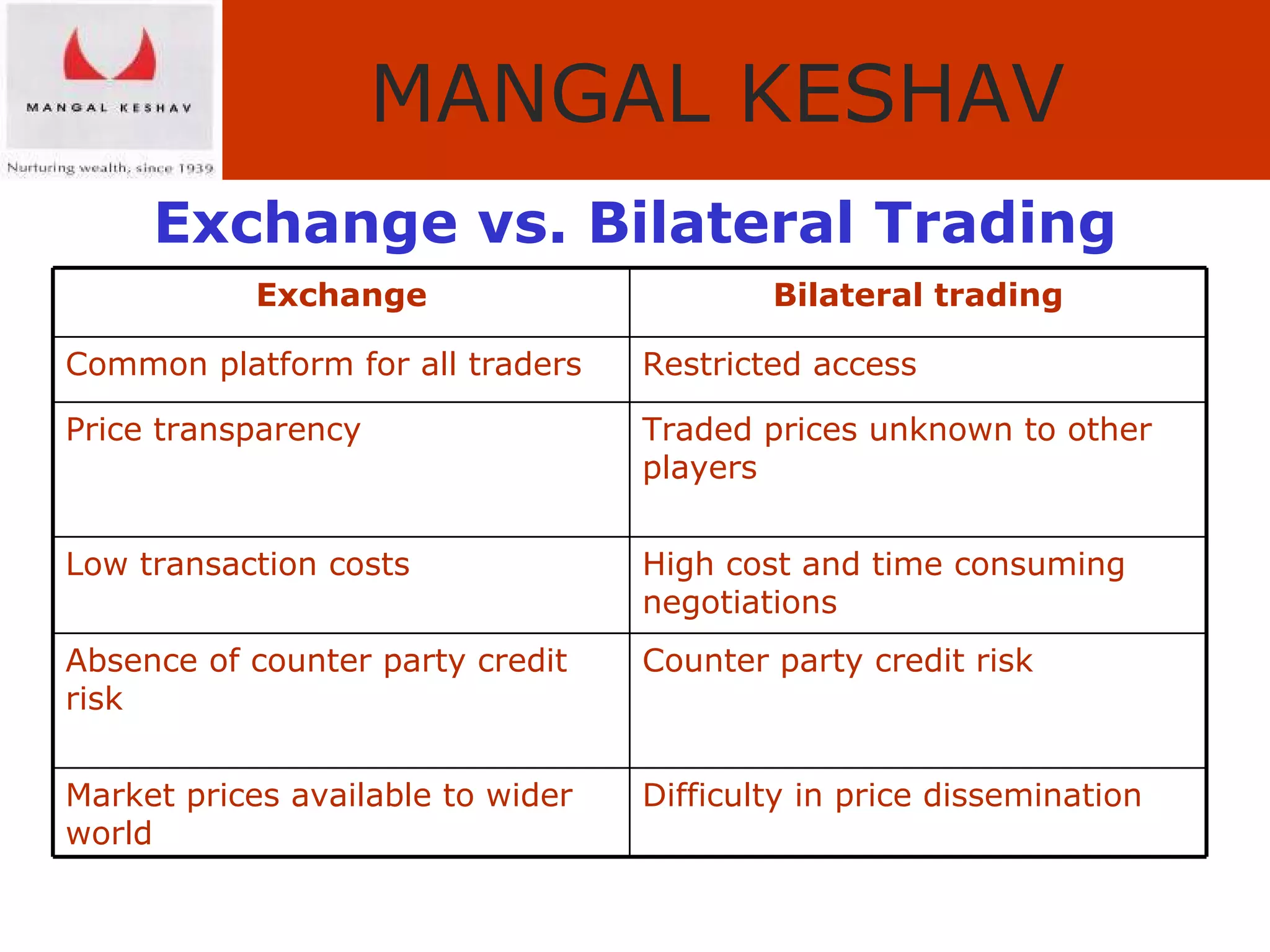
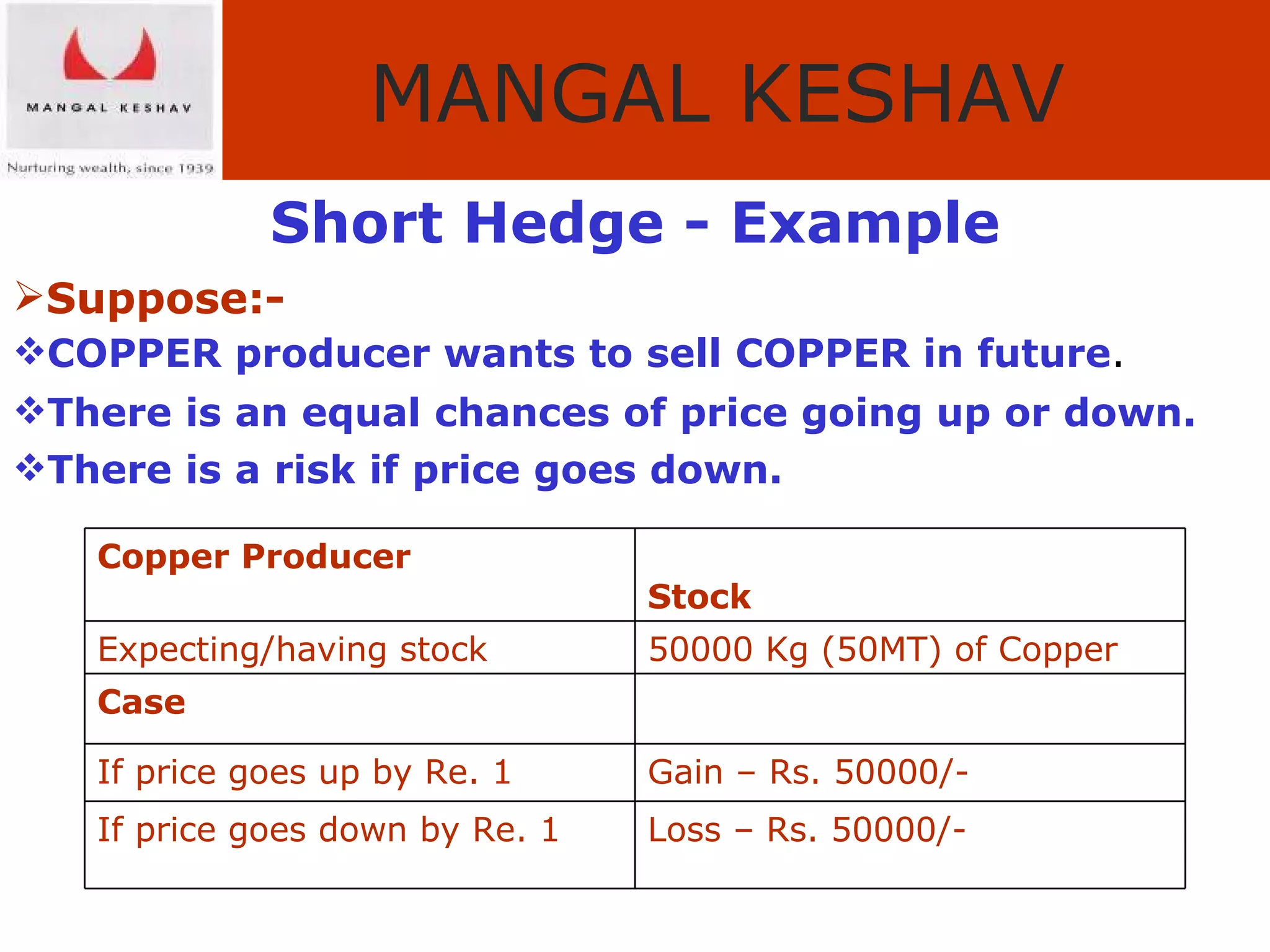
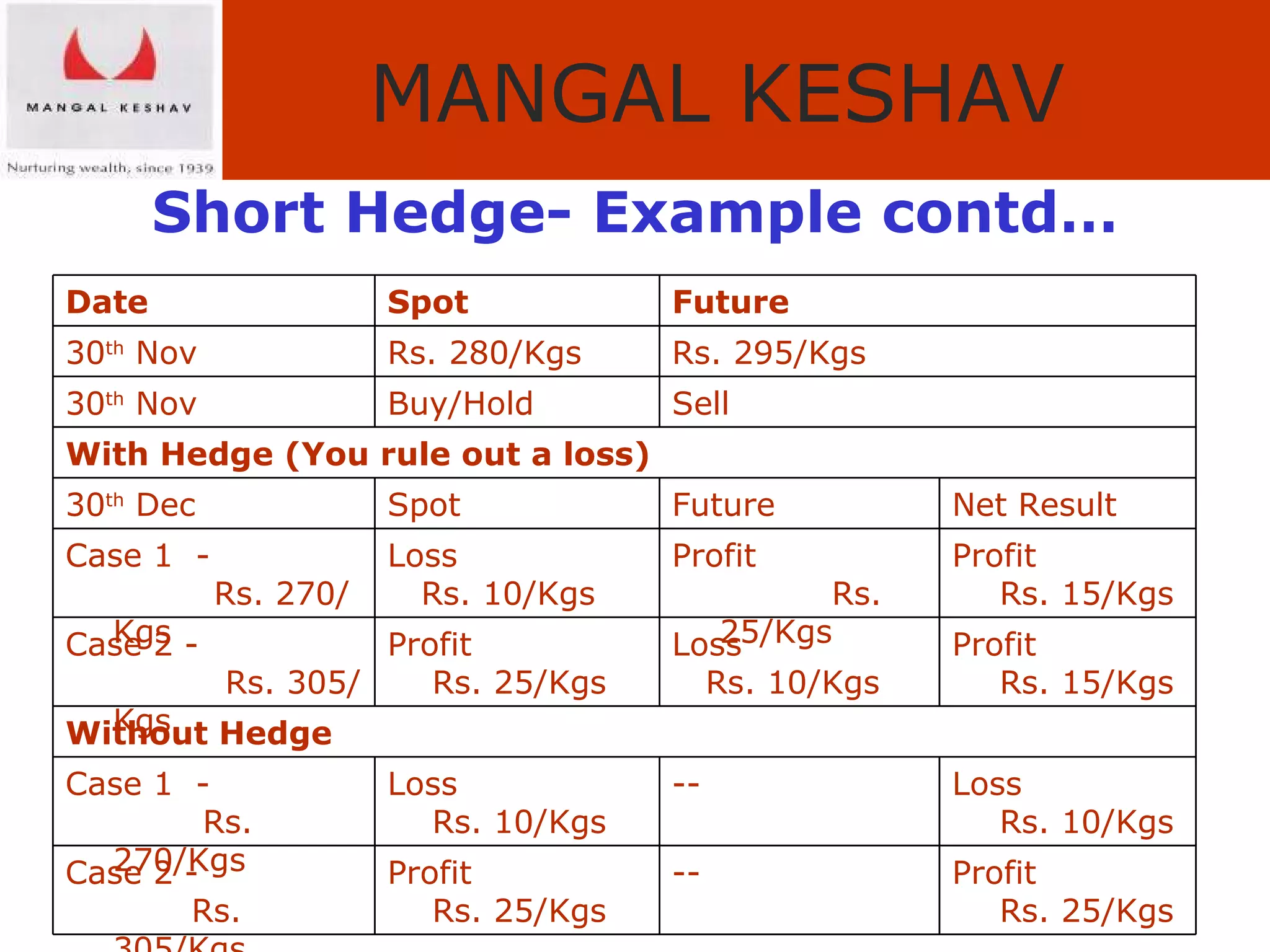
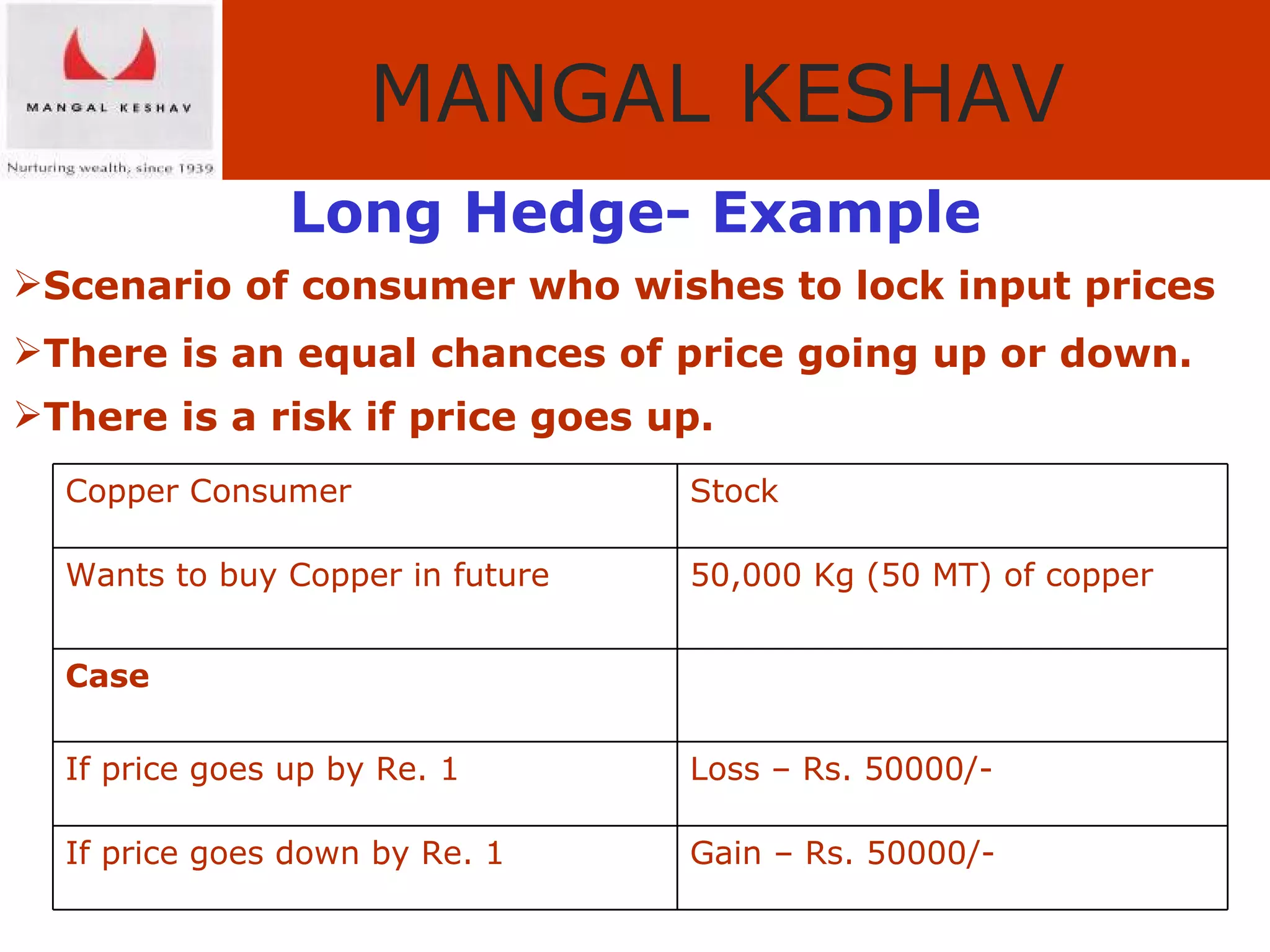
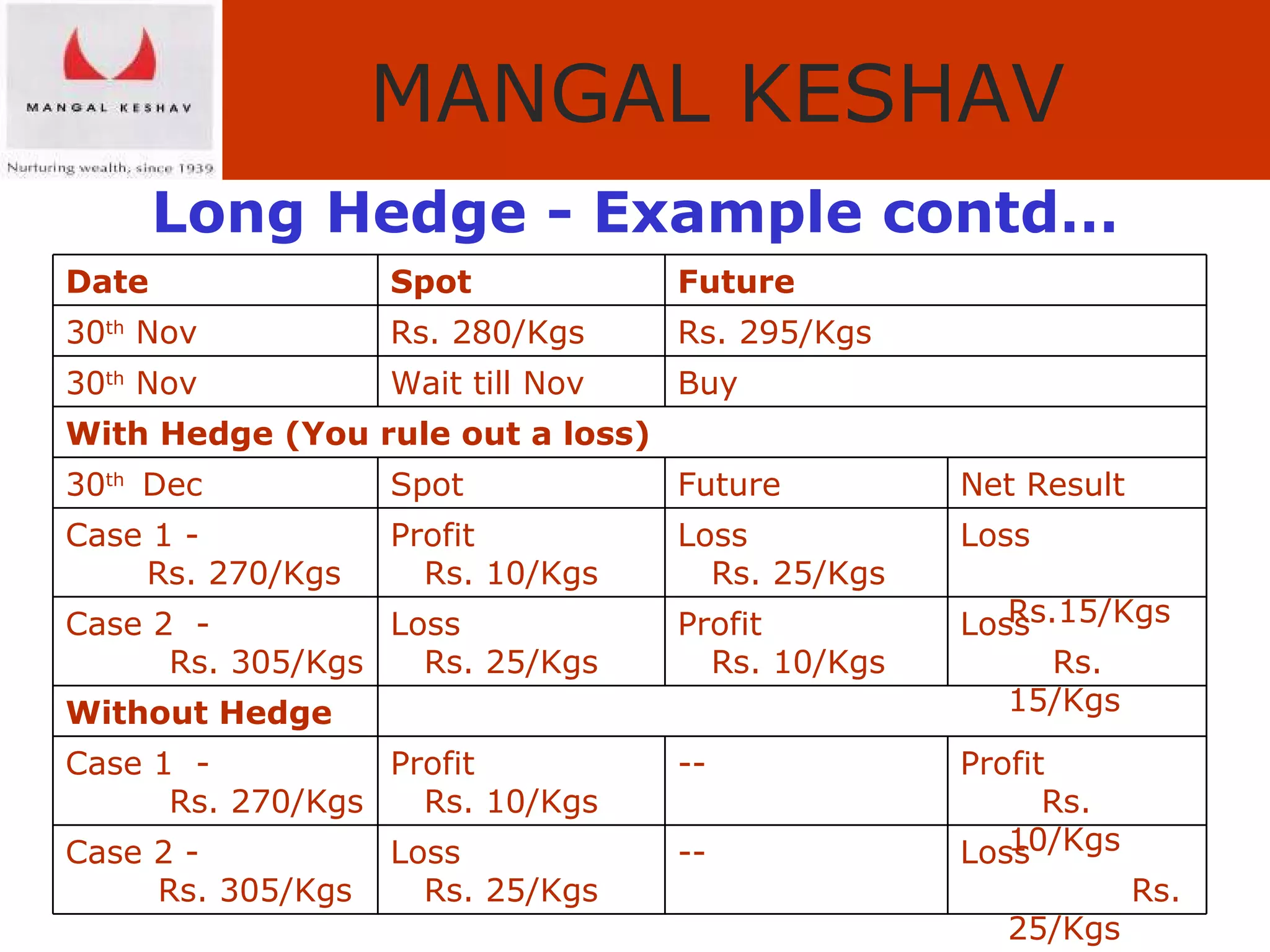
The document provides an overview of the Indian commodity market, including the two major commodity exchanges - MCX and NCDEX. It discusses the various commodities traded on the exchanges like agricultural products, precious metals, base metals and energy. It also provides details about commodity futures contracts, their purpose and participants. The benefits of hedging and different hedging strategies like long hedge and short hedge are explained with examples. Lastly, it summarizes the advantages of trading commodities with MK Commodity Brokers like their research, online trading platform and round-the-clock operations.