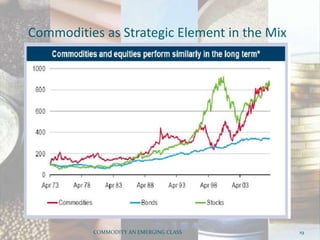
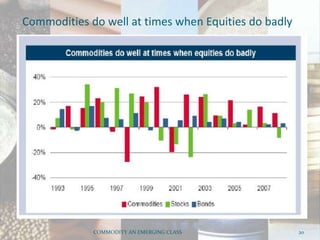
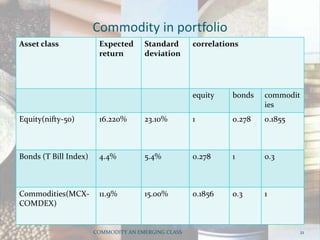
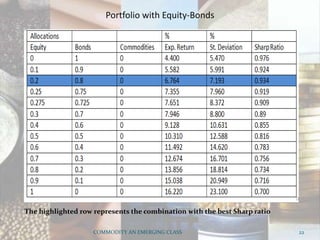
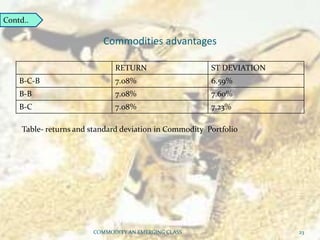
This document discusses how commodities have emerged as a distinct asset class with the advent of commodity futures markets. It notes that commodity futures allow individual investors to participate in commodities through leverage. Commodities offer advantages like leverage, liquidity, returns, diversification, and inflation hedging which make them an attractive asset class. However, commodities in India are still highly correlated with equities, contradicting their diversification benefits in developed markets. Overall, the document analyzes how commodity futures have simplified participation in commodities and the characteristics that establish them as a distinct investment class.