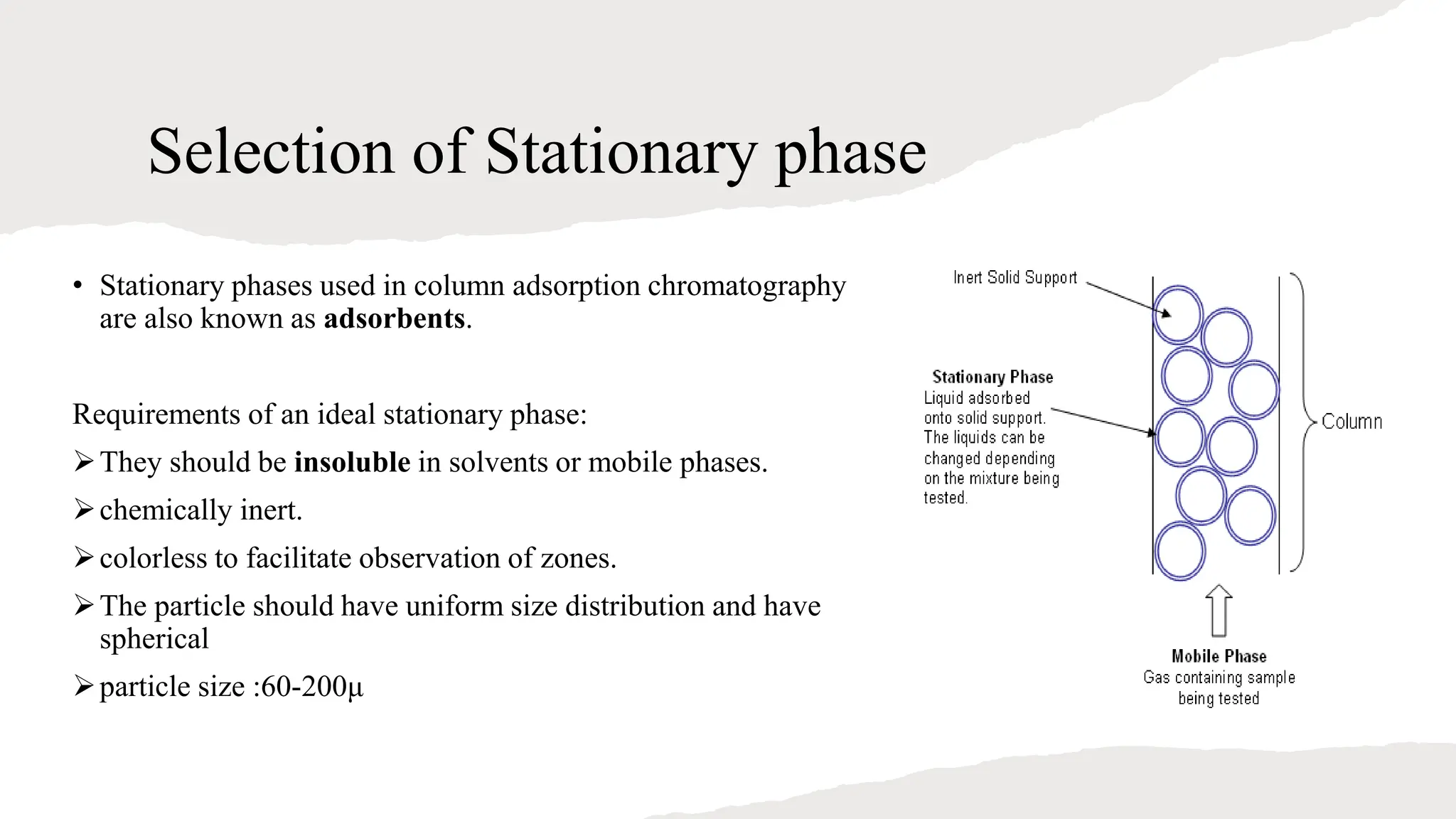
Column chromatography is a technique used to separate mixtures into individual components. It uses a column packed with a stationary phase (such as silica gel) and a mobile phase (liquid solvent) to separate the components. The mixture is dissolved in a mobile phase and passed through the column. Components are separated based on their differing interactions with and rates of migration through the stationary phase. Column chromatography is commonly used to purify organic compounds and separate inorganic ions.