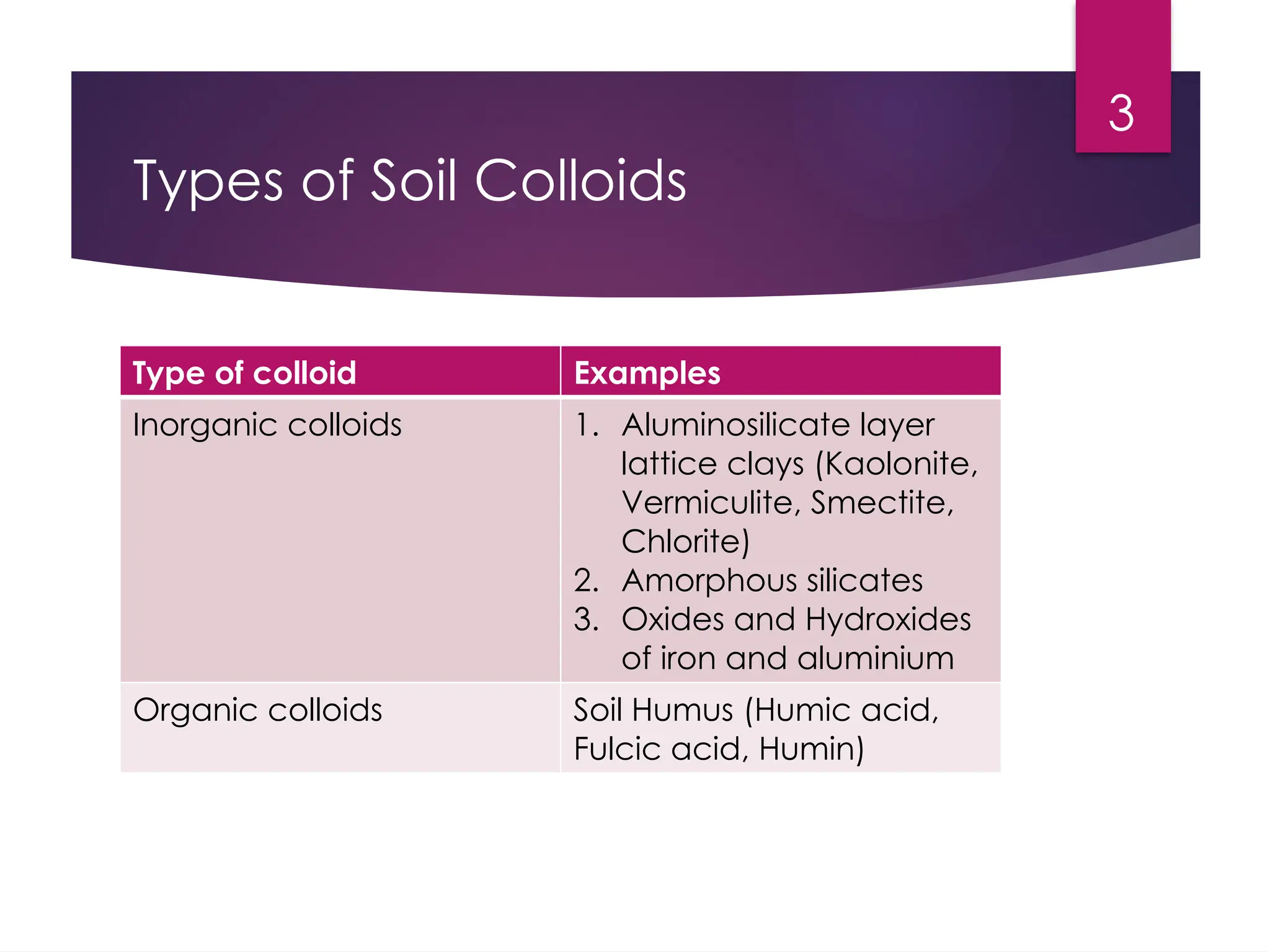
Soil colloids are heterogeneous mixtures characterized by small particle size, which makes them crucial for various soil properties. They possess unique properties such as high surface charge density, large interfacial surface area, and the ability to influence soil fertility through nutrient exchange. The zeta potential is an important measure of the stability of colloidal dispersions, affecting processes like flocculation and deflocculation.