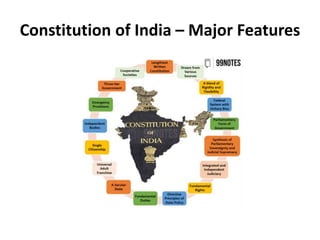
The Indian Constitution is the longest in the world, containing 395 articles and 12 schedules. It draws from multiple sources like the Government of India Act of 1935. The constitution establishes a federal system with both unitary and federal features, including a strong central government and all-India administrative services. It implements a parliamentary form of government with an executive branch drawn from the legislature. The constitution also balances parliamentary sovereignty and judicial supremacy through the power of judicial review. It creates an independent and integrated judicial system with the Supreme Court at the top.