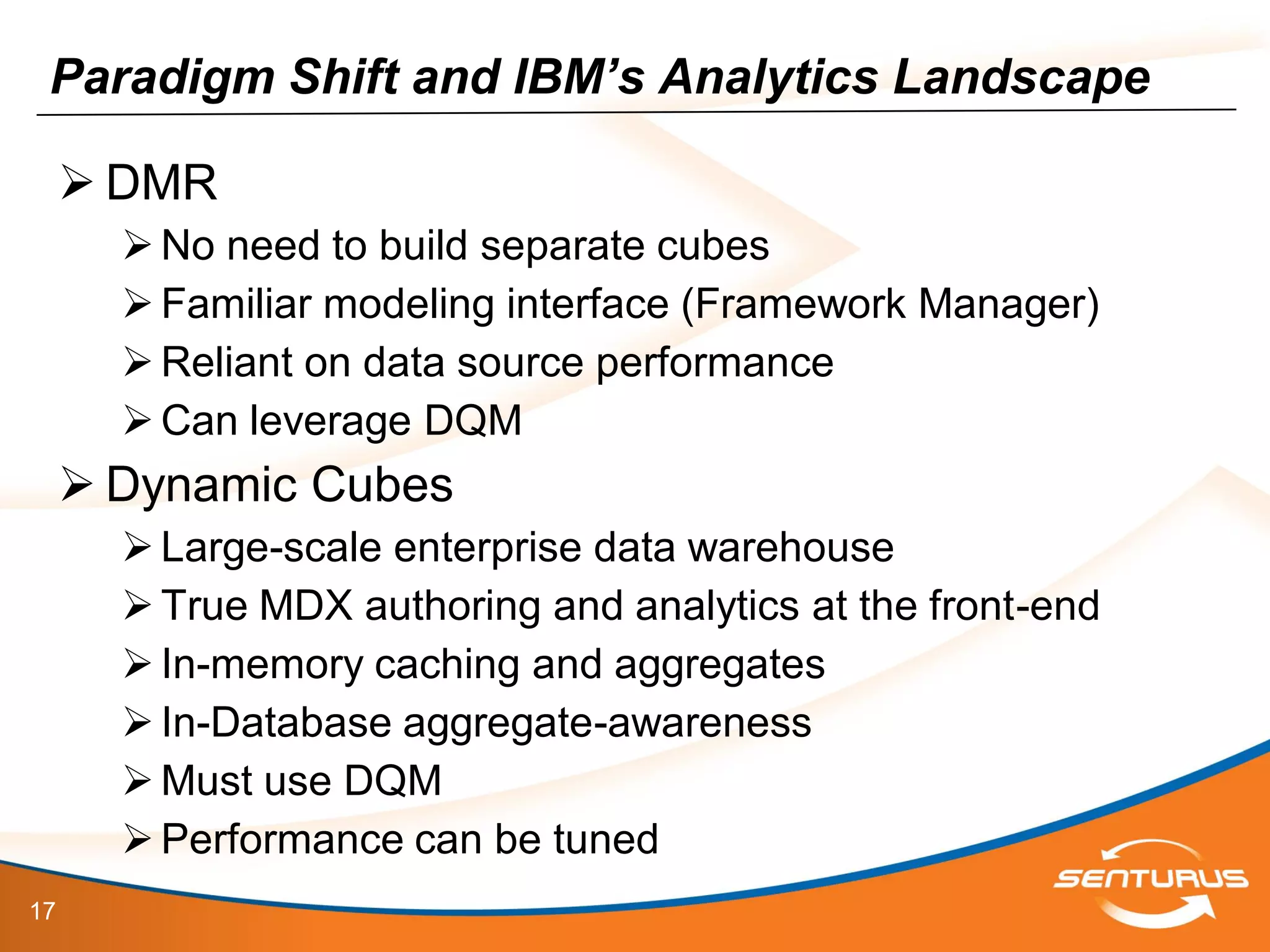
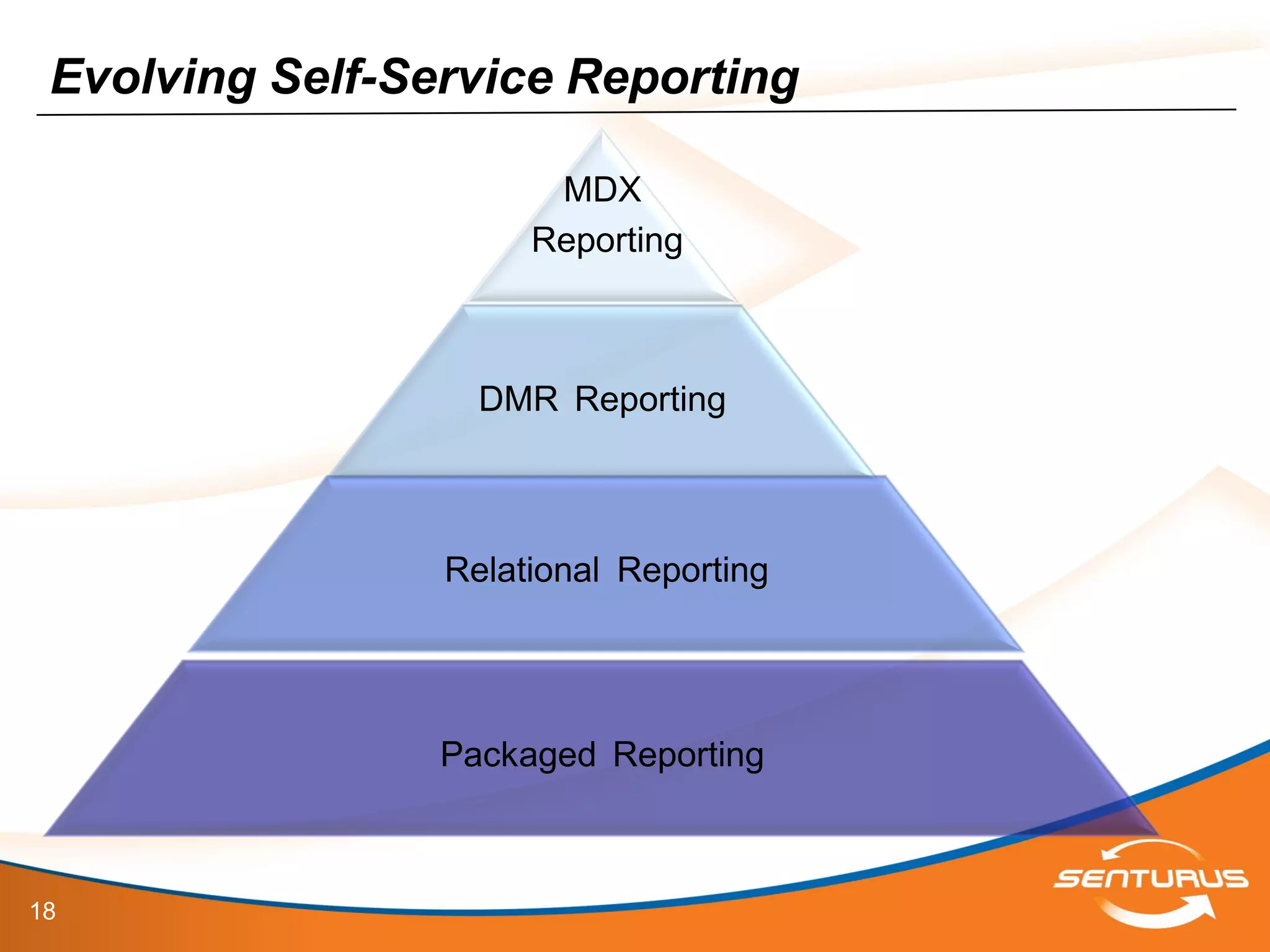
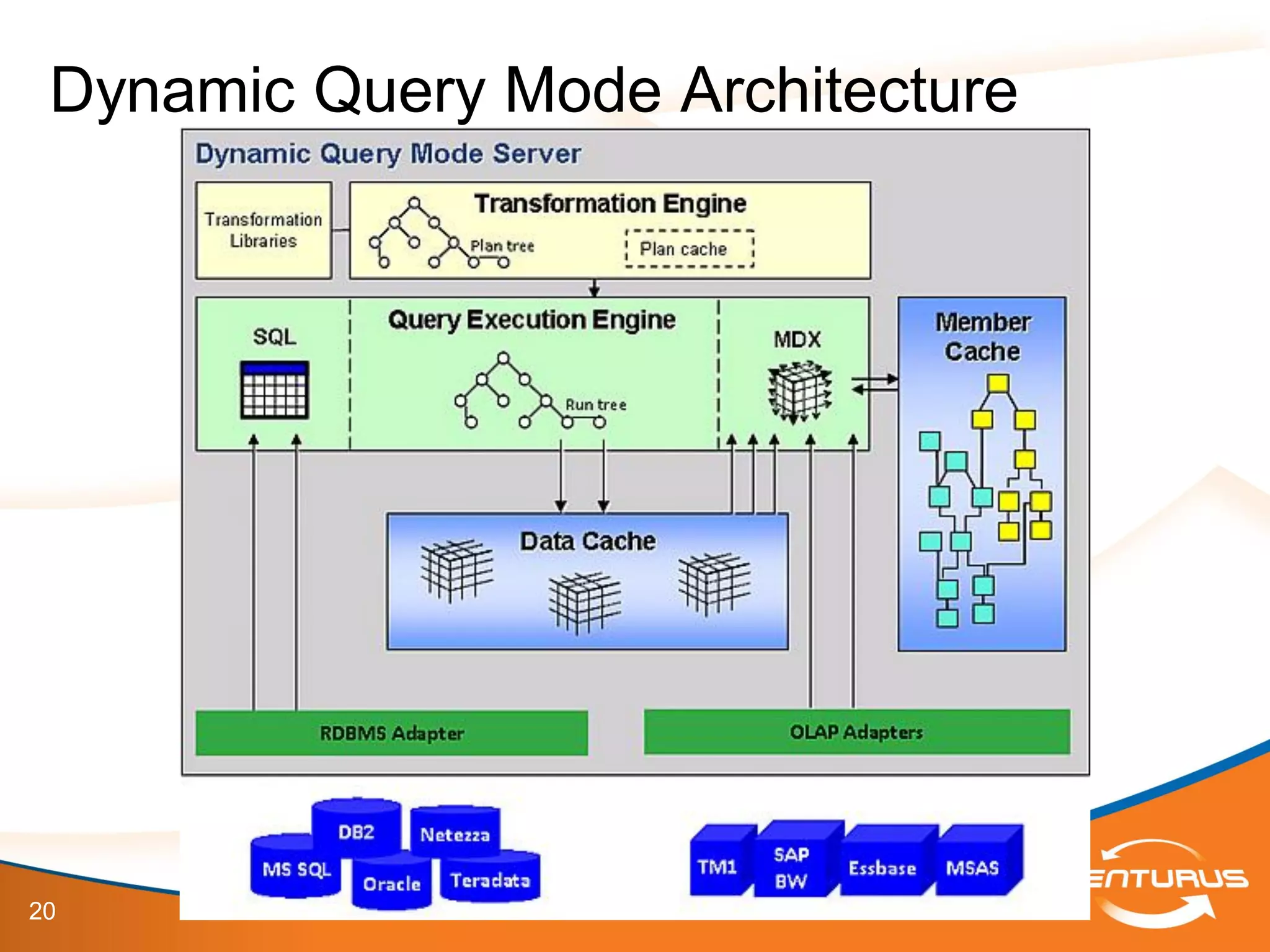
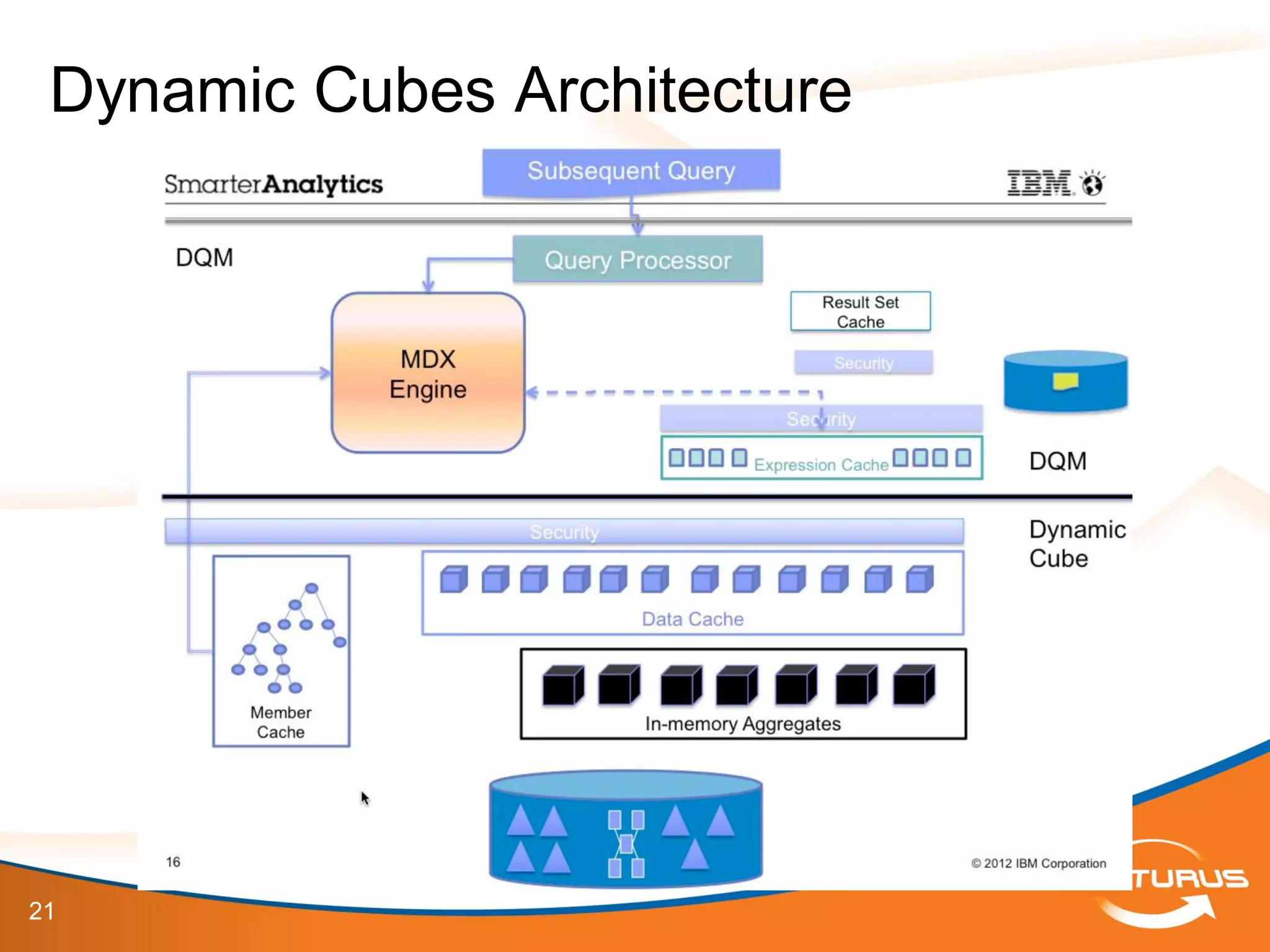
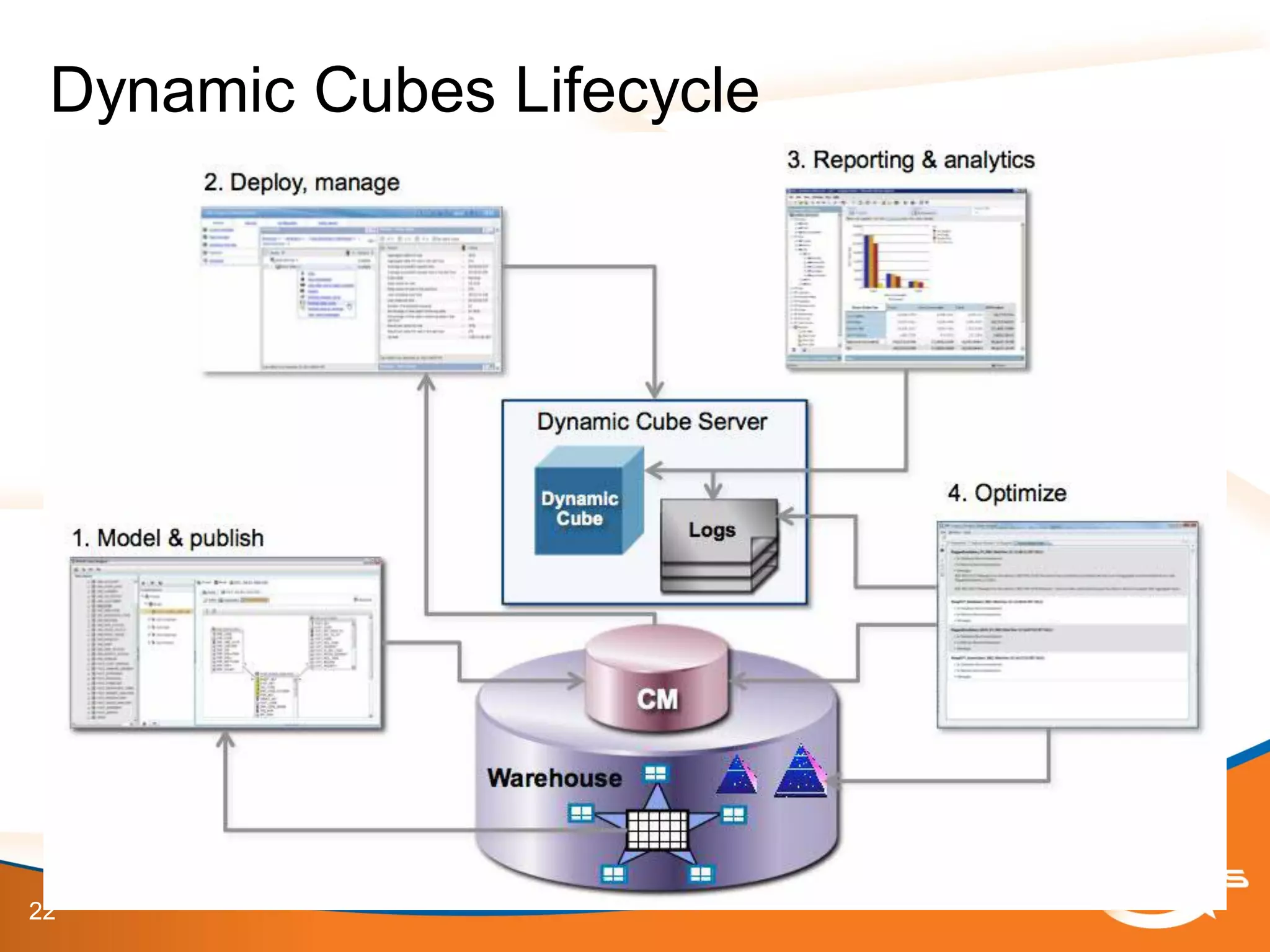
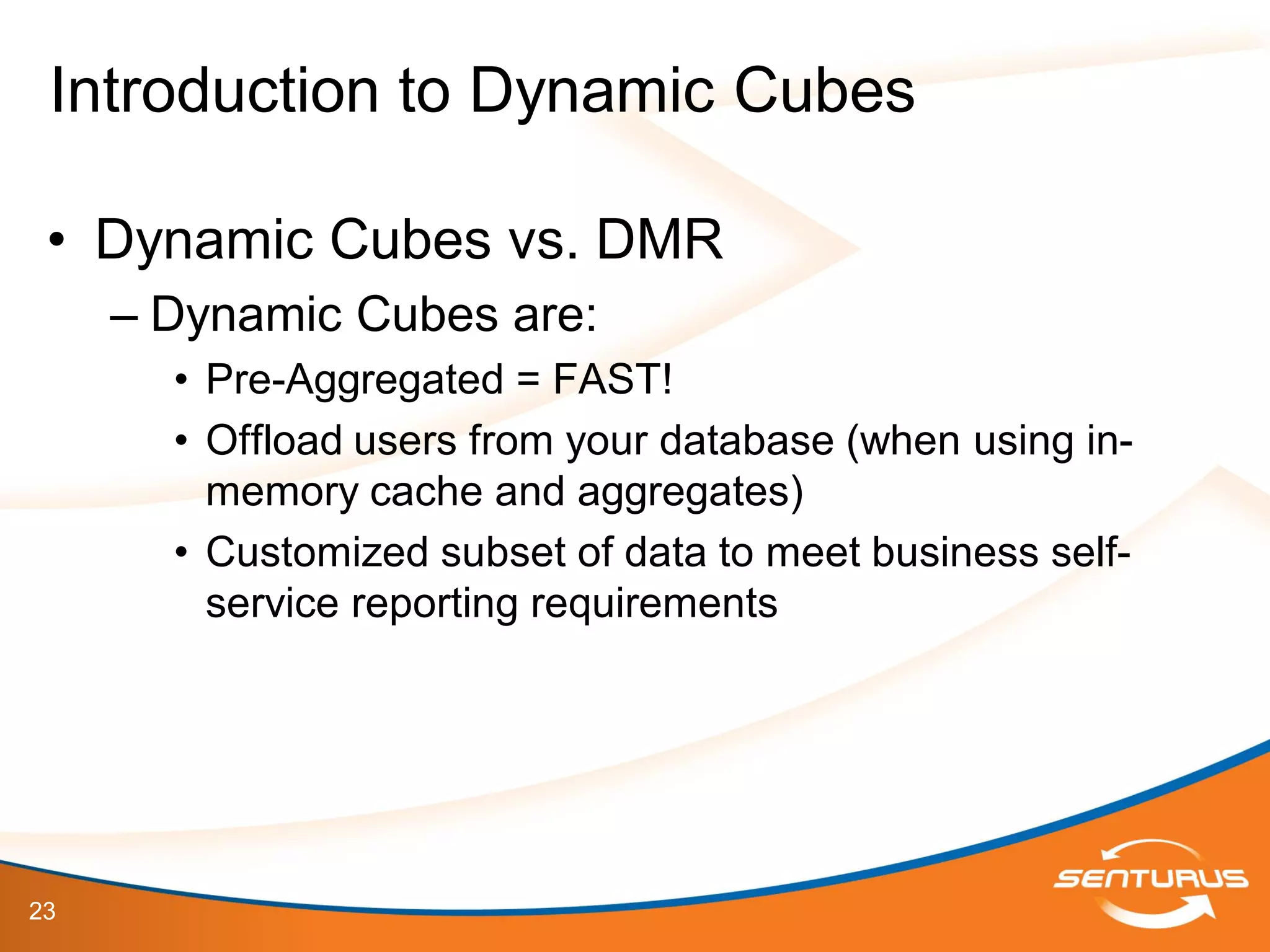
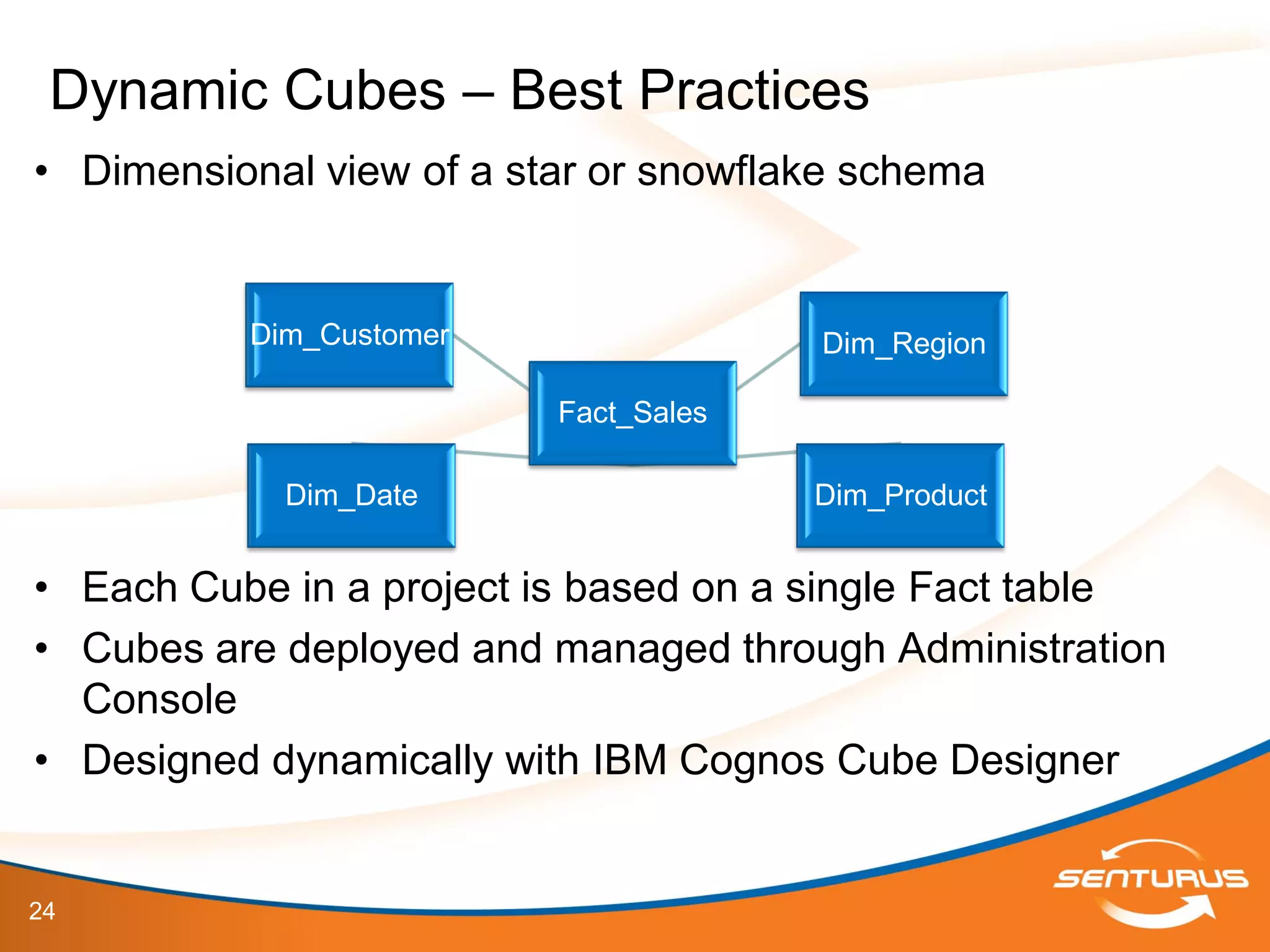
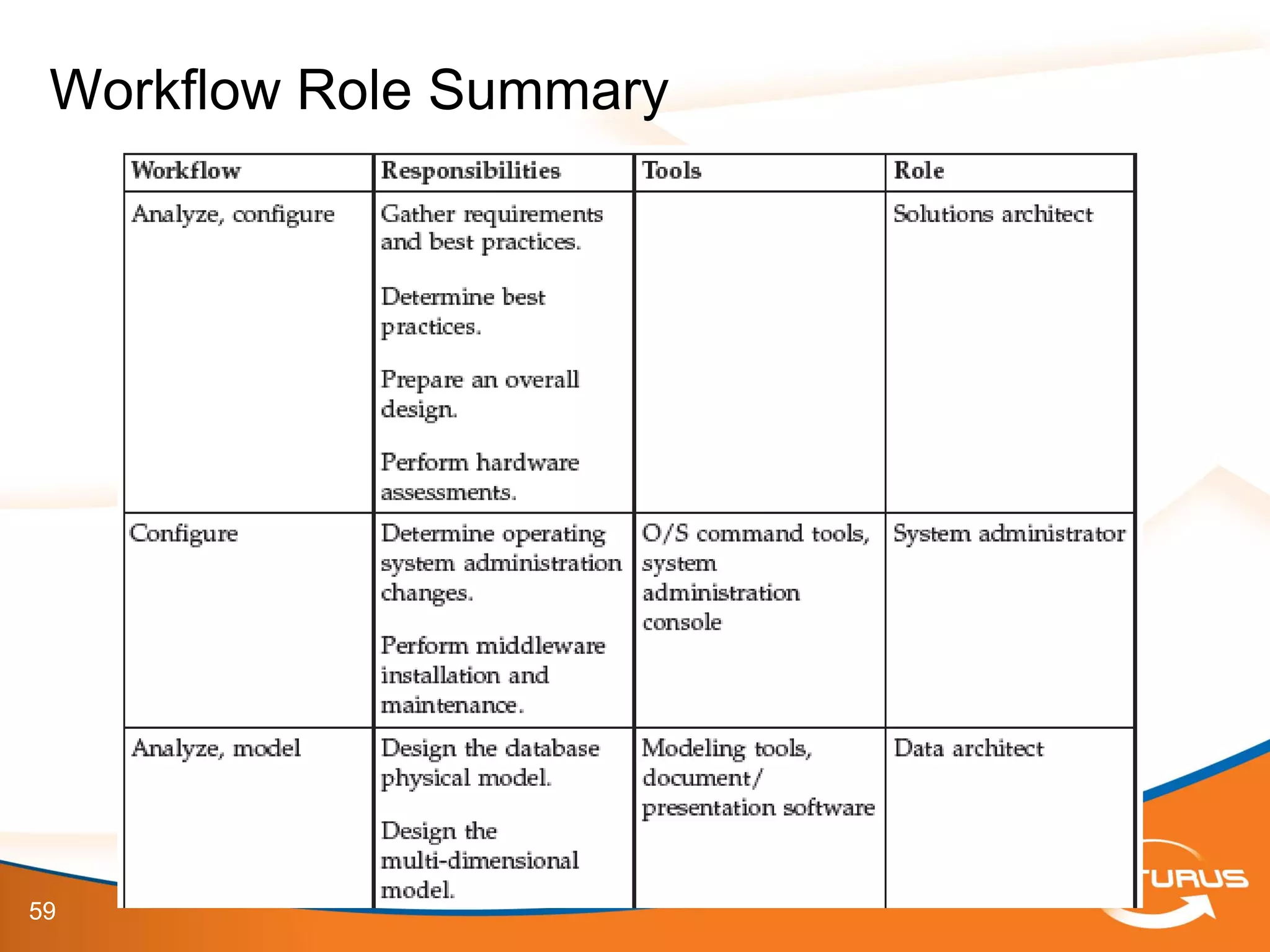
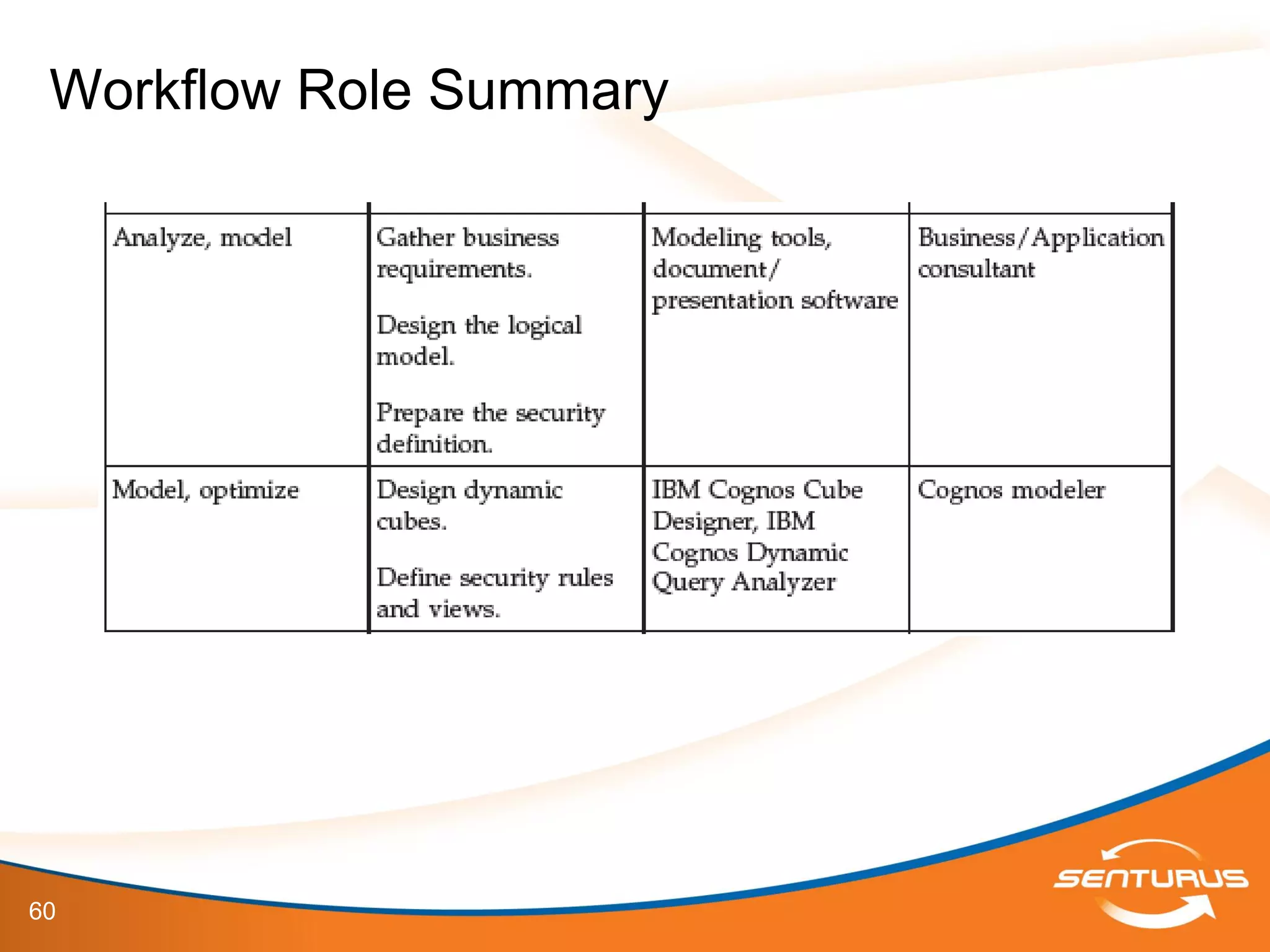
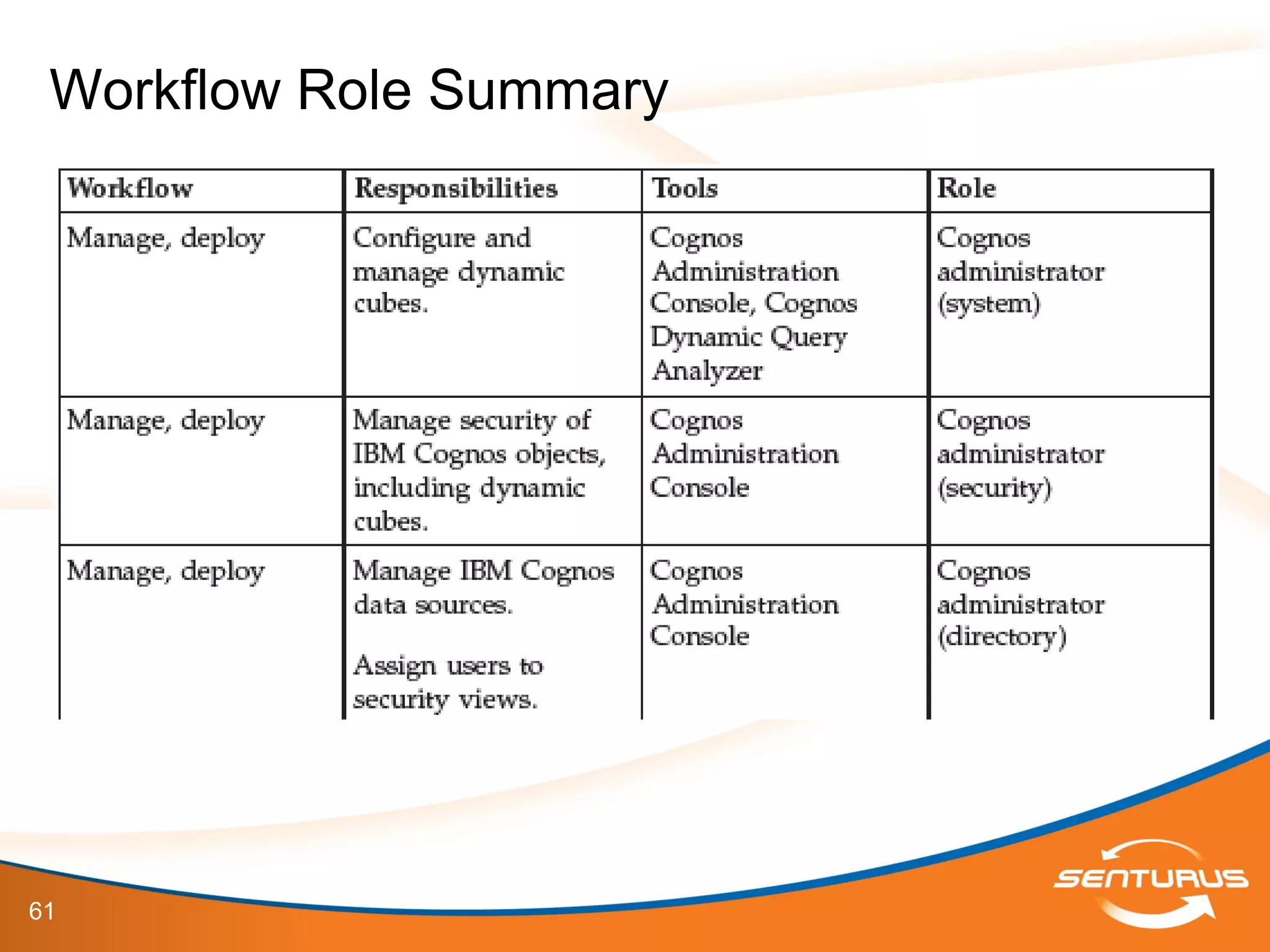
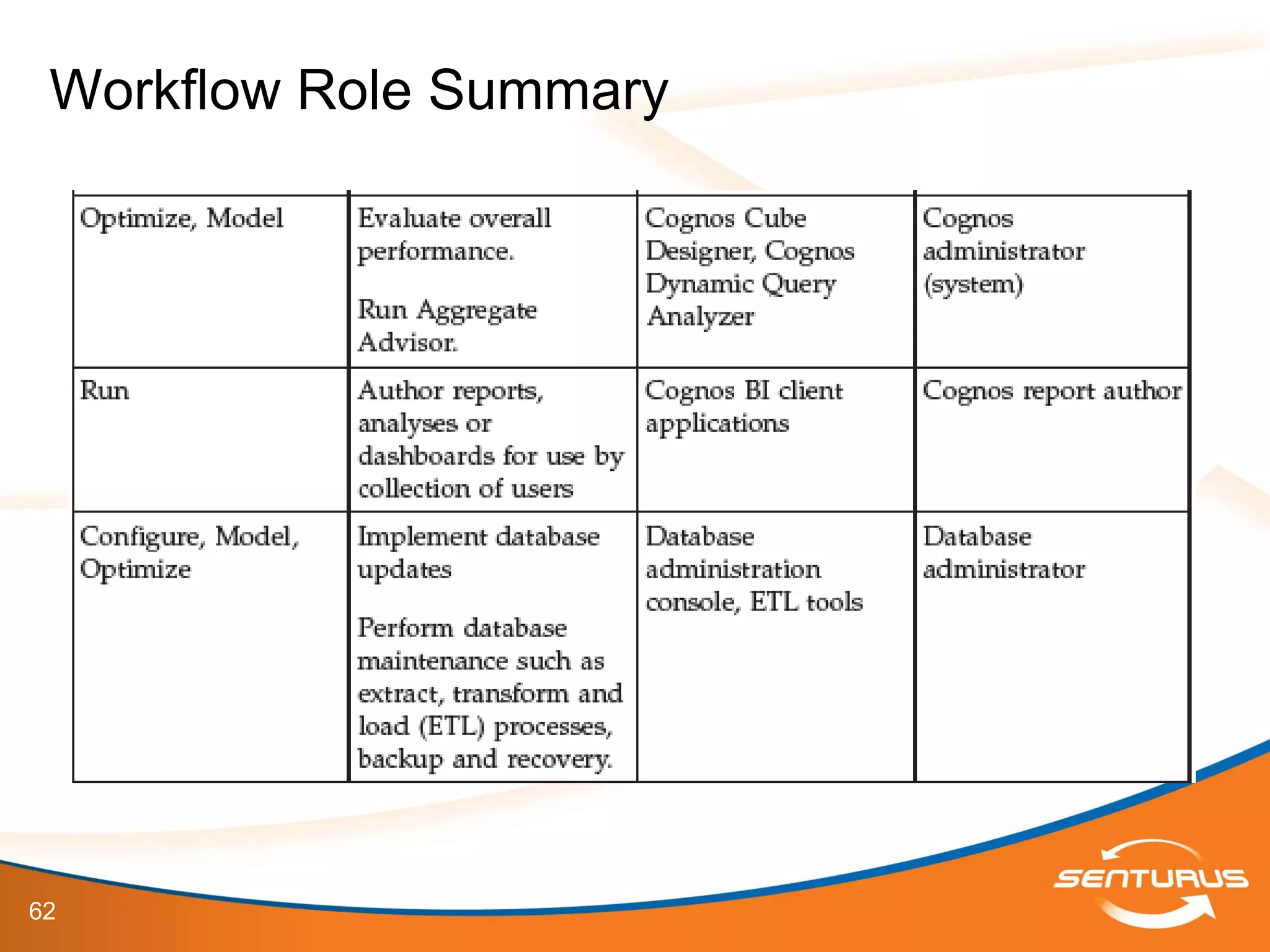
The document provides an overview of IBM Cognos 10.2 Dynamic Cubes, highlighting its features such as improved OLAP capabilities, expanded data sources, and enhanced reporting functions. It introduces cube design best practices and the importance of using a star schema for optimal performance. Additionally, it emphasizes the role of stakeholders in the dynamic cube deployment process and includes resources for further training and documentation.