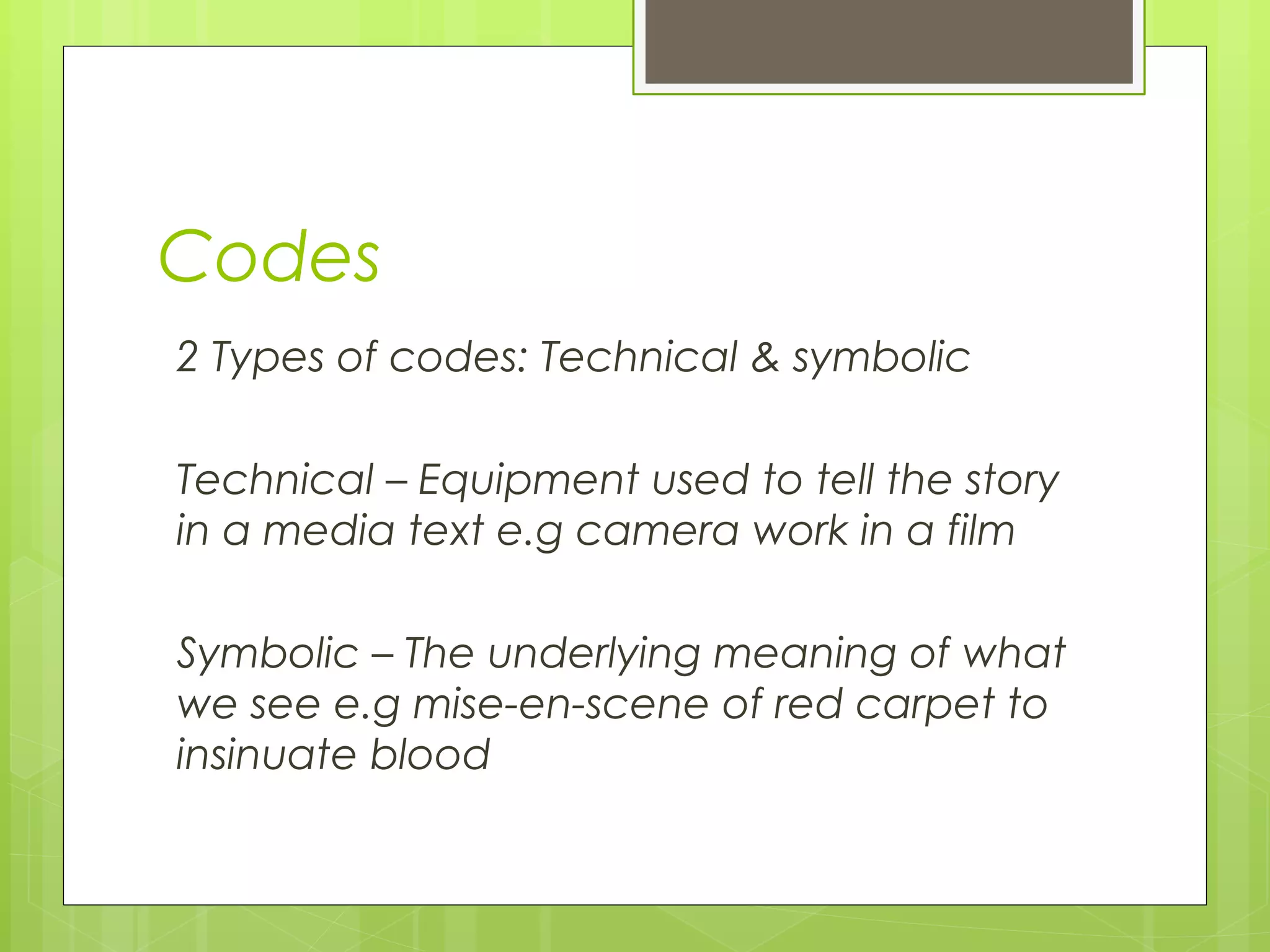
The document discusses several common codes and conventions used in documentaries. It explains that conventions are generally accepted techniques like using upbeat music in horror films. It also discusses two types of codes: technical codes involving equipment and symbolic codes that convey underlying meanings. Some key conventions mentioned include using voiceovers to narrate, documenting truth, conducting interviews, incorporating relevant sounds, and selective editing.