1) Software parallelization is required to handle the increasing scale and complexity of high-energy physics (HEP) experiments, which produce vast amounts of data from particle collisions.
2) The authors developed a programming model called Communication Capability (CoCa) that allows parallelization at different levels of granularity and reduces software complexity.
3) CoCa is based on the database transaction paradigm and allows the results of components executing in parallel to be combined while ensuring consistency, as required for HEP event reconstruction.

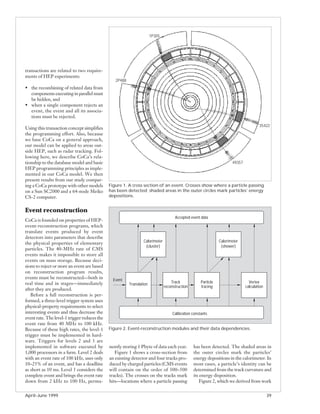




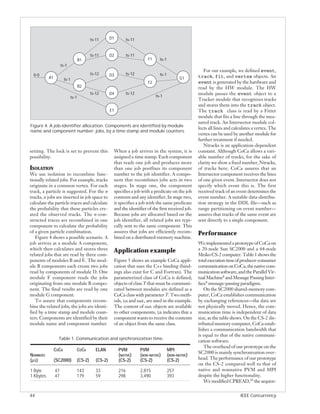
![// first module
void HW() {
CoCa<Event> event;
while(TRUE) {
equipment(&event); // get event data from equipment
event.out(); // store data in job space
tial event-reconstruction program of the }
CPLEAR experiment, to run on the }
SC2000 and CS-2 computers using CoCa
for communication between parallel // second module
parts. CoCa’s event generator creates void Tracker() {
events and stores them into job space. CoCa<Event> event;
CPREAD components then read the CoCa<Track> track;
events from job space, reconstruct the while(TRUE) {
event, and store an approved event into event.in(); // get an event from job space
job space. The reconstructed events are for(int i := 0; i< NTRACKS; i++) {
read by three components that store the event.find(&track);
events on disk. In the DDL file, we spec- track.out(); // track to job space
ified push mode with round robin. }
Figure 6 shows the results of the event }
reconstruction in relation to the number }
of processors on the CoCa-modified
CPREAD program, compared with a // third module
theoretical scale-up where the perfor- void Fitter() {
mance of one unmodified (“reference CoCa<Track> track;
scale-up”) and one CoCa-based (“CoCa CoCa<Line> line;
scale-up”) CPREAD program is multi- while(TRUE) {
plied by the number of processors. With track.in(); //get track from job space
relatively few modifications to the orig- track.fit(&line);
inal program, the production rate for this line.out(); // put line in job space
experiment was met on a distributed- }
memory machine with 28 processors, 23 }
of which were efficiently used.
// fourth module
void Intersector() {
ALTHOUGH MOTIVATED by proper- CoCa<line> line[NTRACKS];
ties of the HEP event-reconstruction CoCa<vertex> vertex;
programs, the generality of the CoCa while(TRUE) {
model makes it beneficial to other appli- for(int i := 0; i< NTRACKS; i++) {
cations that need parallelization. In ad- line[i].in();
dition, CoCa’s actual implementation } // got all associated lines
led to a surprisingly low communication vertex.intersect(line);
overhead, when compared with the // calculate intersection poin
overhead of PVM and MPI. vertex.out(); // Store vertex in job space
With CoCa we have clearly shown // for later reference
that fine-grain parallelization of HEP }
programs is a viable approach. The CoCa }
model combines a high level of abstrac-
tion and allows parallelization with very Figure 5. An example CoCa application using a C++ binding. The content of
out objects are available to other components; in indicates that a component
little overhead. Our approach, using
wants to receive the contents of an object from the same class.
application characteristics to arrive at a
low overhead programming model, has
produced a considerable payoff.
sity, Linköping, Sweden, for use of their SC2000; References
and Philippe Bloch for the use of the CPREAD 1. J. Zalewki, “Real-Time Data Acquisition in
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS program. The CERN CS-2 was funded by the High-Energy Physics Experiments,” Proc.
This work is jointly funded by CERN and the EU Esprit project P7255, GPMIMD2. We are IEEE Workshop on Real-Time Applications,
Eindhoven University of Technology. Results grateful to Martin Rem from EUT for support- IEEE Computer Society Press, Los Alamitos,
from our experiments are input for the Dutch ing this work and to several anonymous referees Calif., 1993, pp. 112–115.
Science Foundation’s project NFI33.3129, which for valuable comments on the article. Also, Con-
currency editor Keri Schreiner significantly con- 2. The Compact Muon Solenoid – Technical
focuses on construction and performance of real- Proposal, CMS Tech. Report CERN/LHCC
time transactions. We thank Linköping Univer- tributed to this article’s presentation.
April–June 1999 45](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coca1-120807115101-phpapp02/85/Coca1-8-320.jpg)
