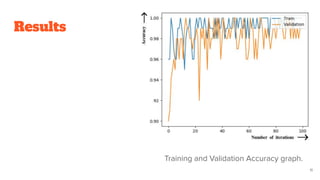
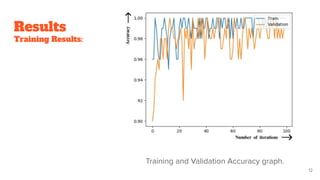
The document presents a CNN-based approach for handwritten signature recognition, emphasizing its importance in verifying legal documents to combat forgery. It discusses the methodology, which includes data preprocessing and the use of the GoogLeNet model for classification and feature extraction. The study outlines the experimental setup, data specifications, and mentions the training and validation process, highlighting the critical nature of signature validation.