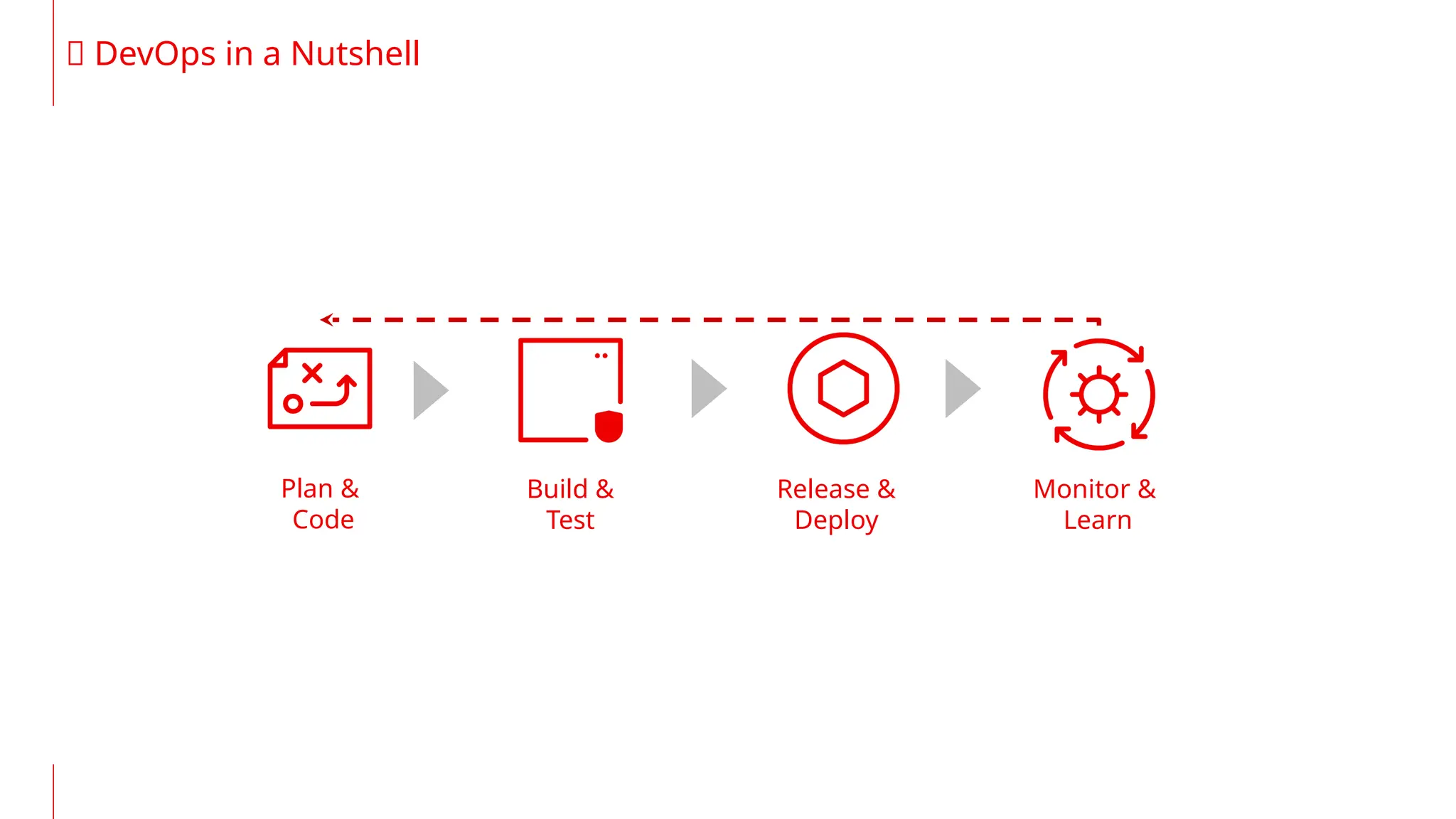
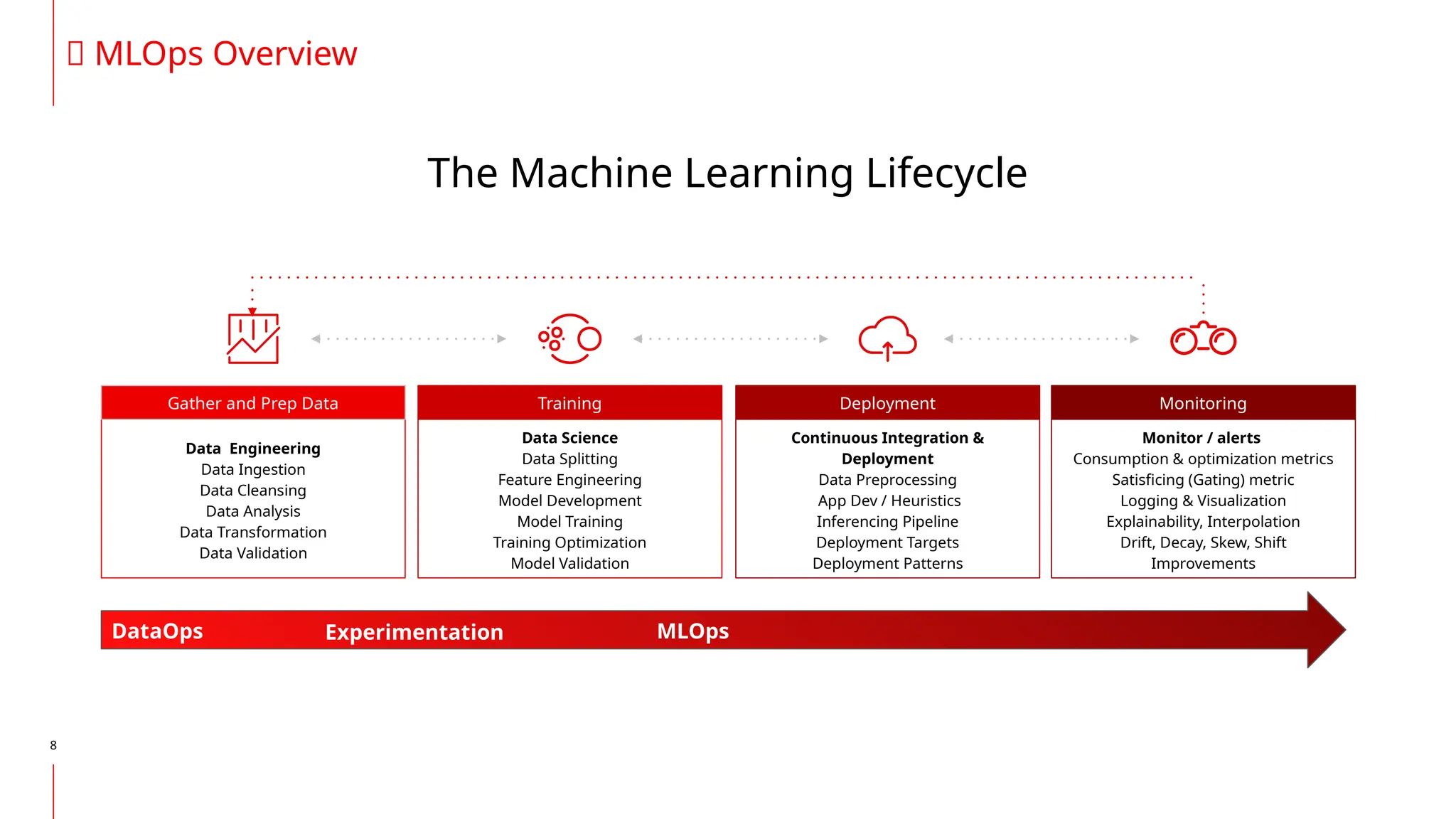
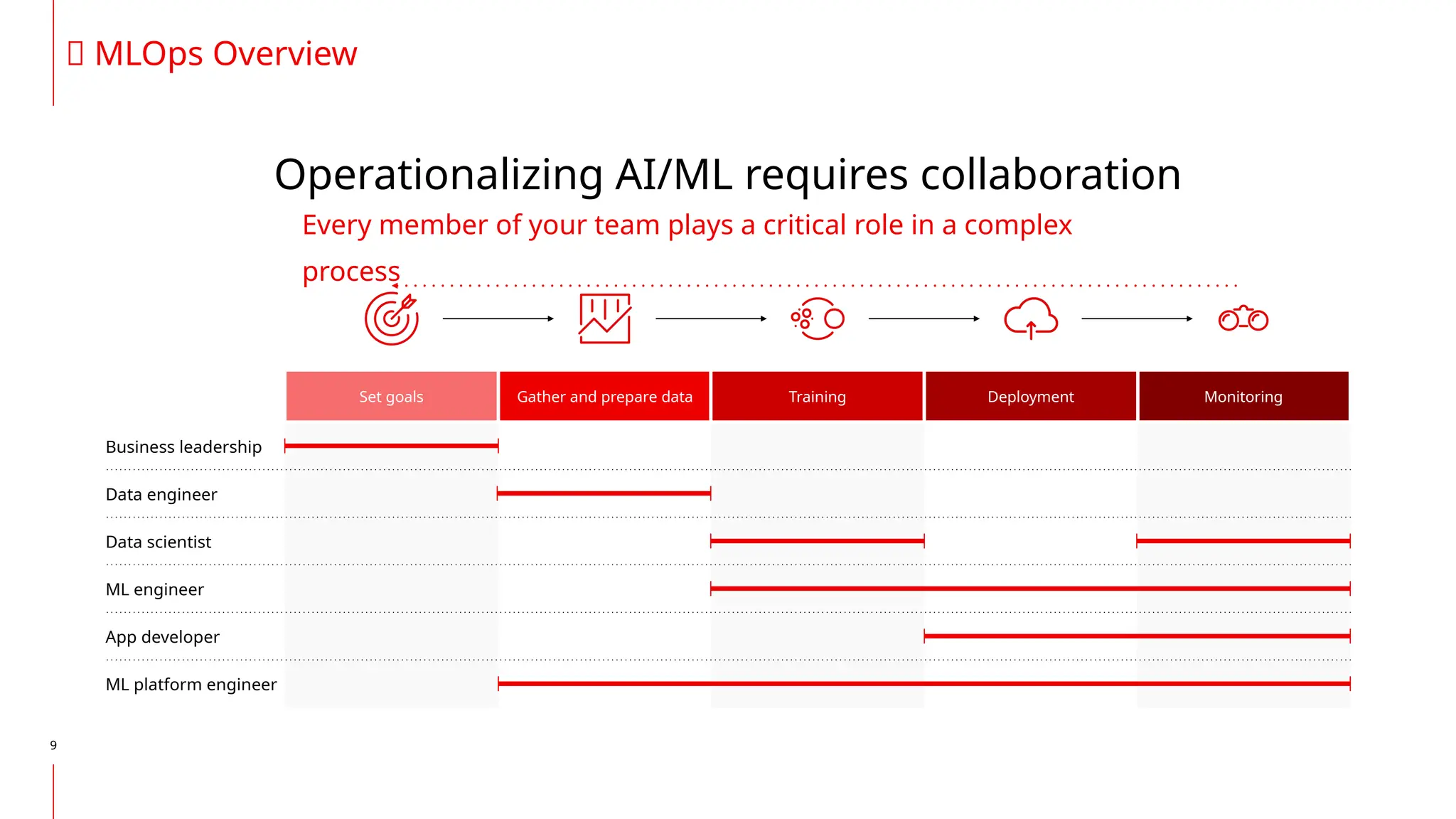
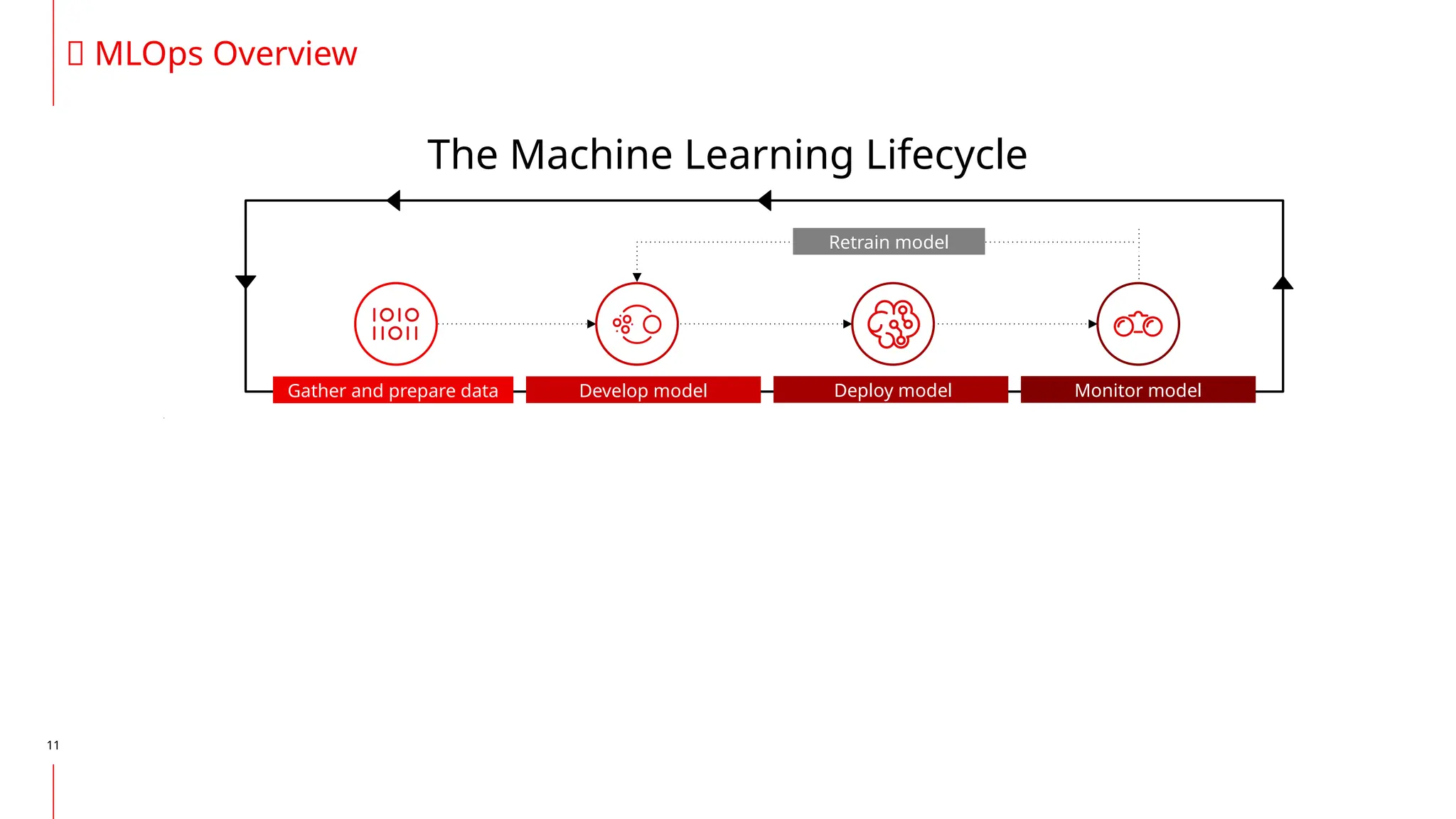
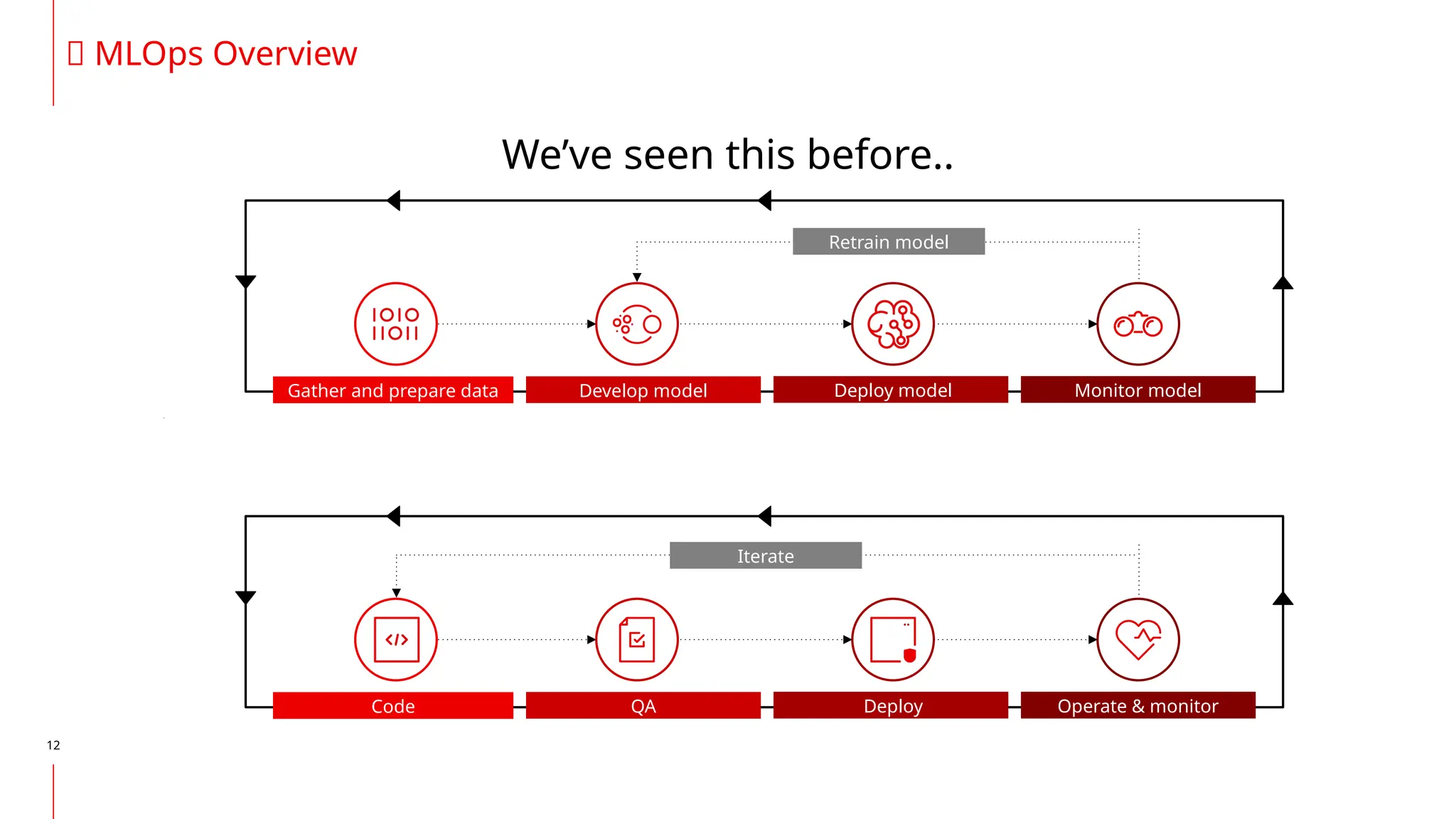
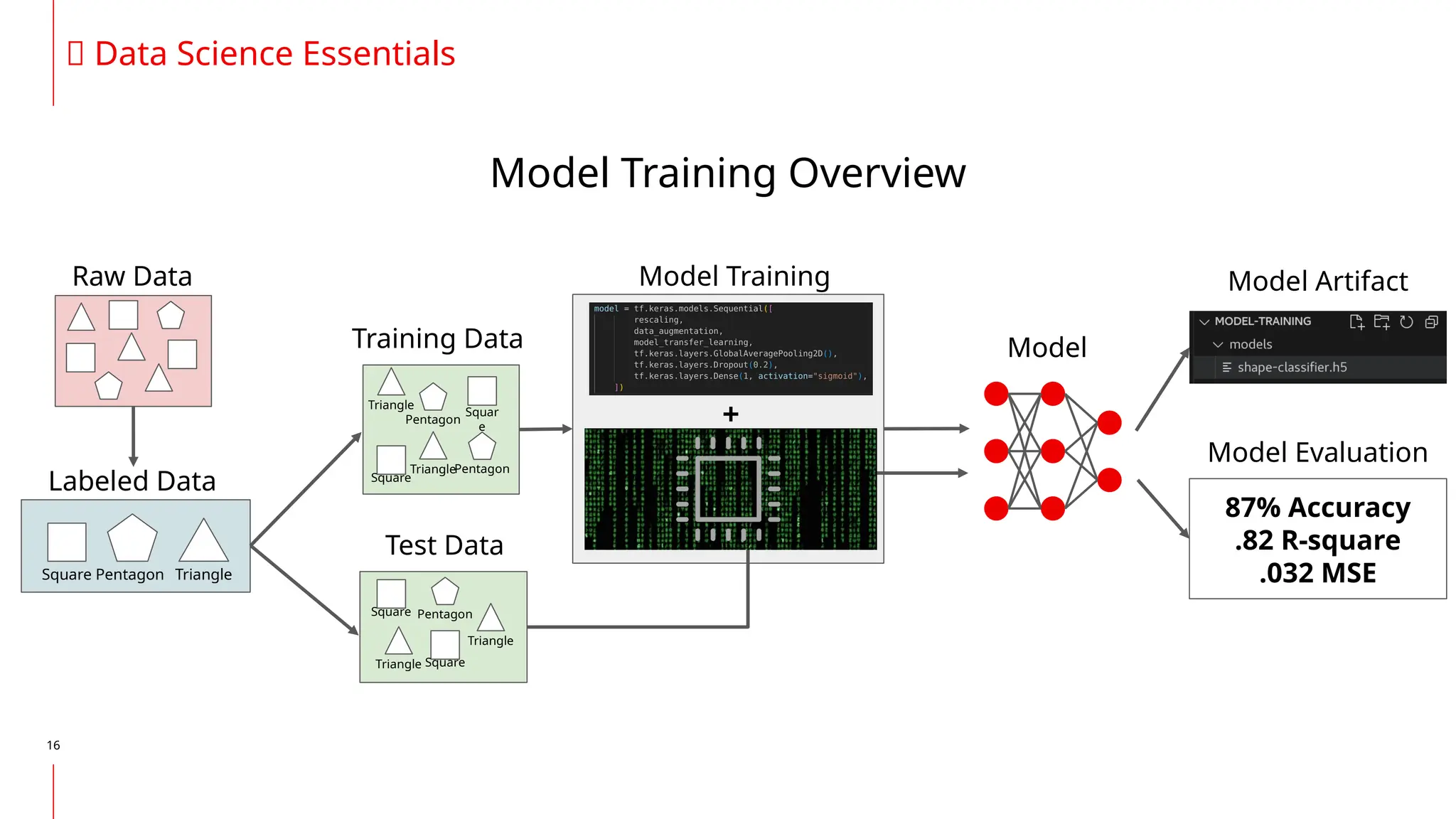
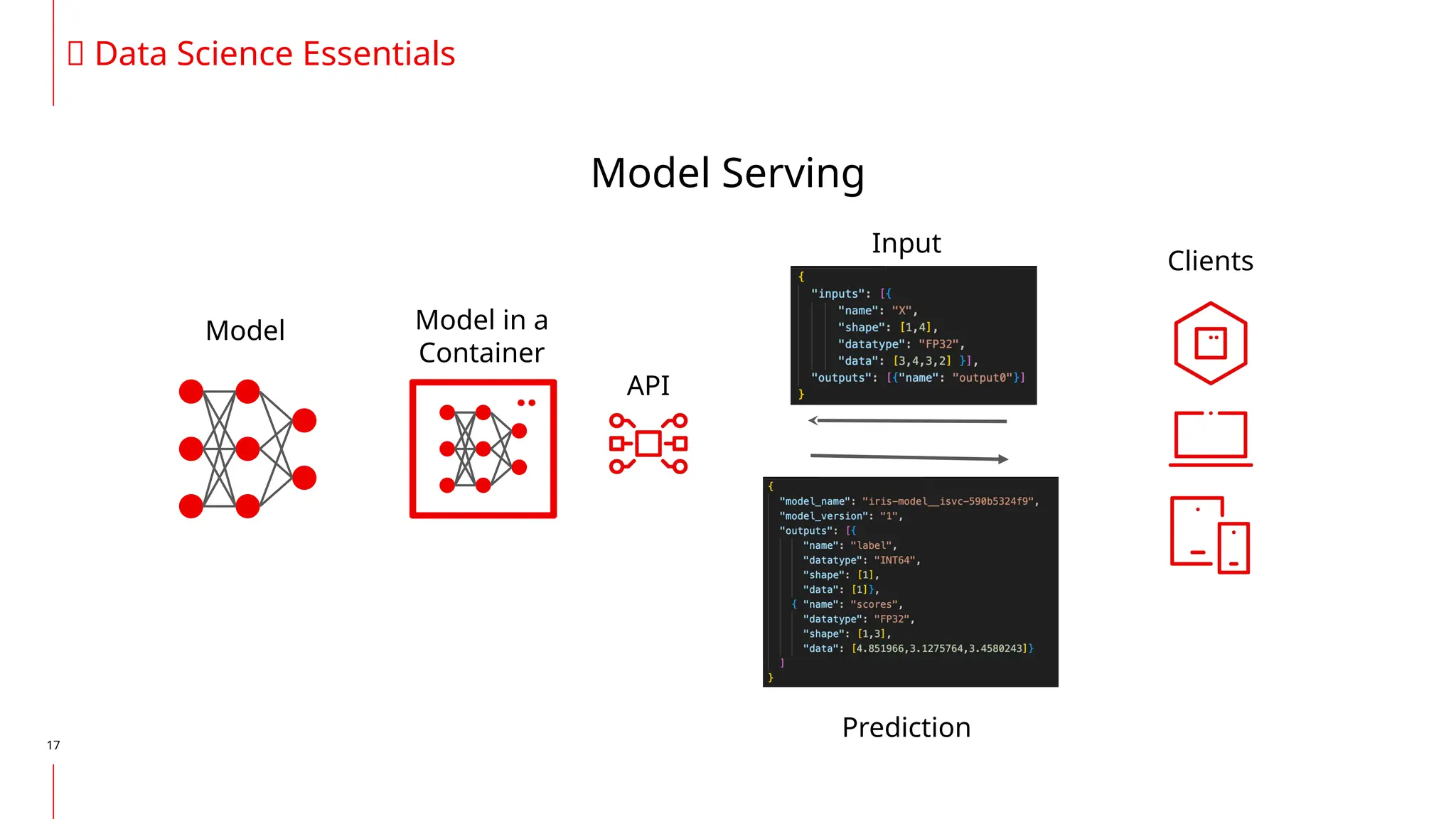
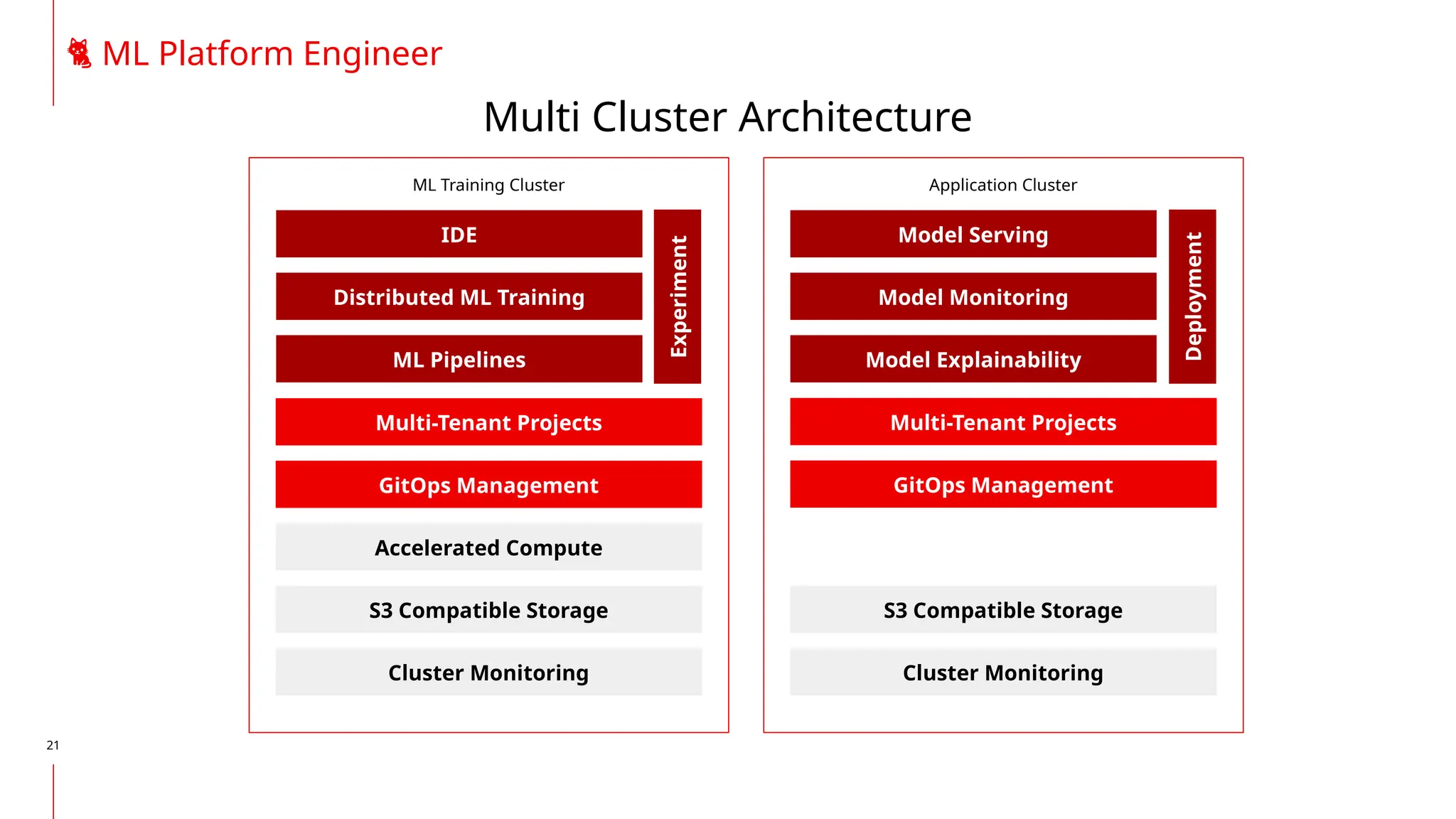
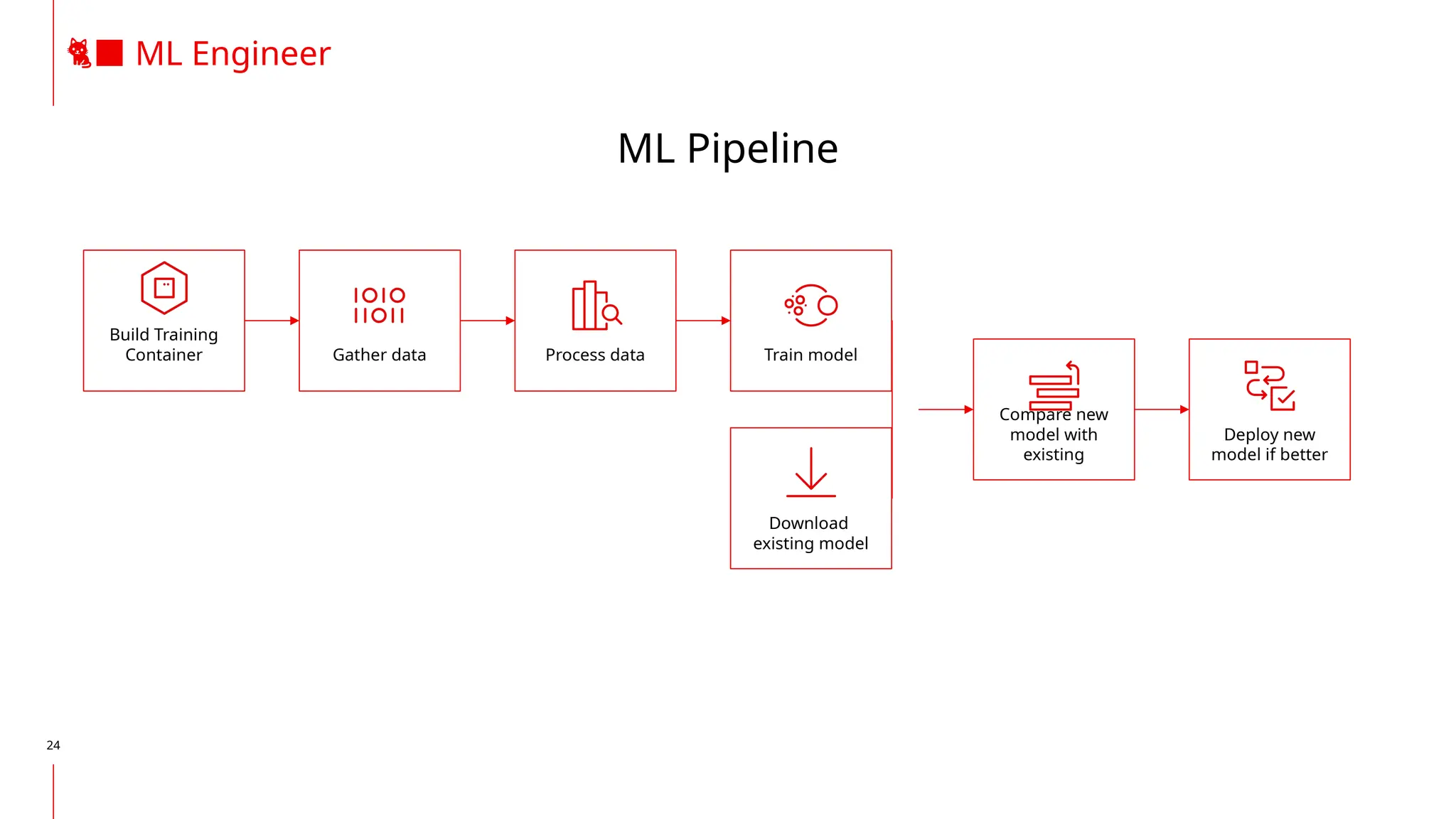
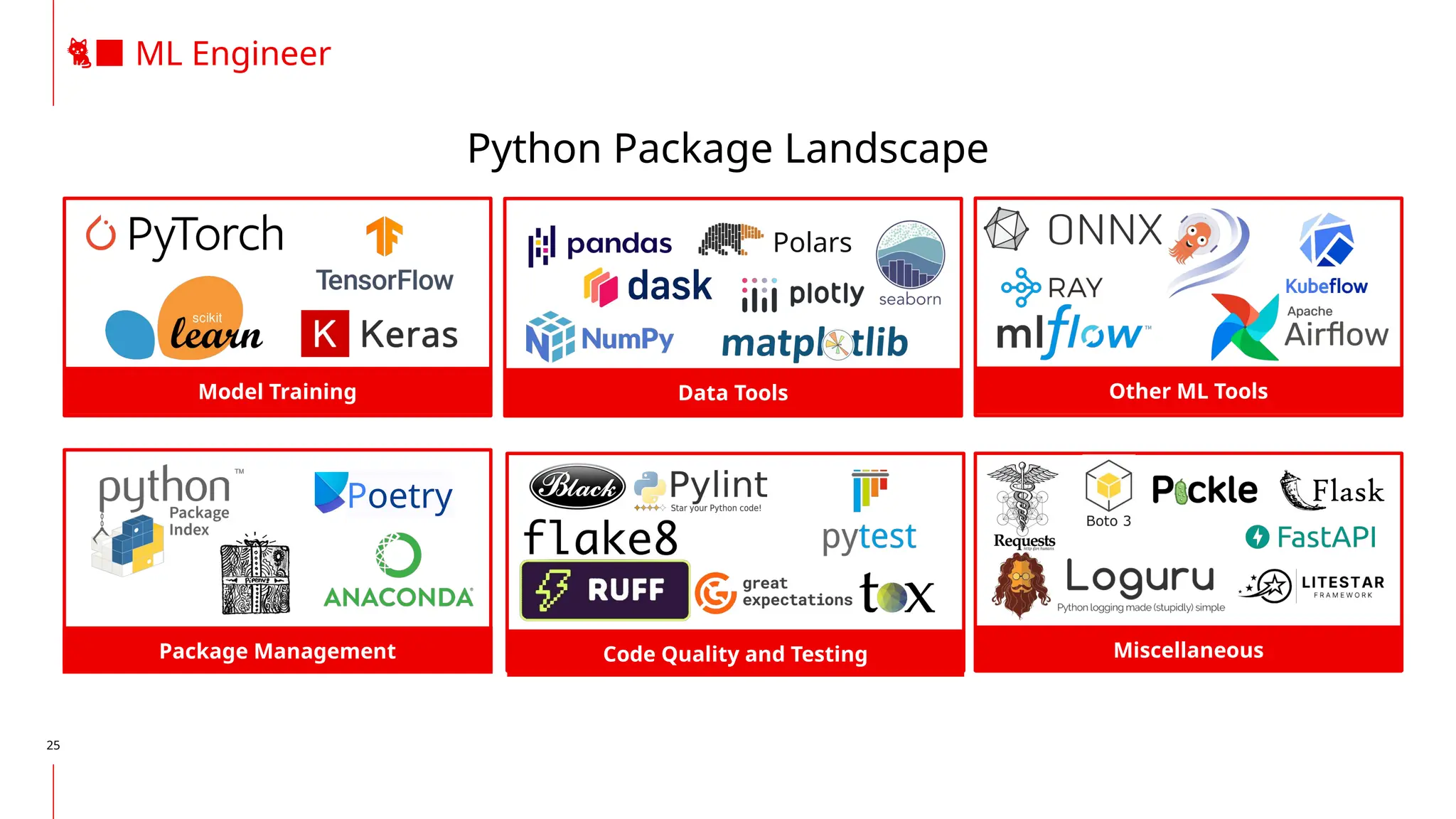
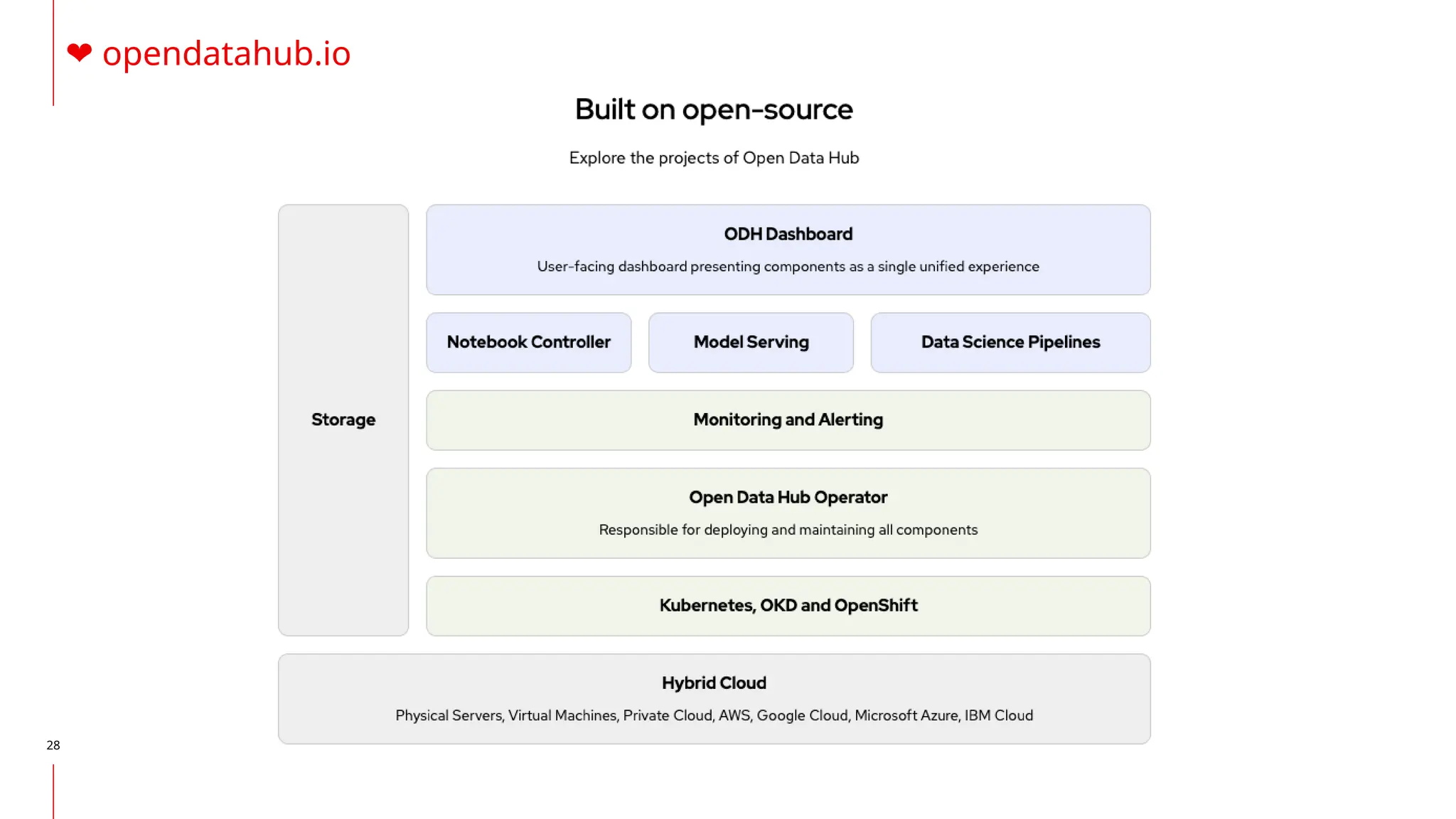
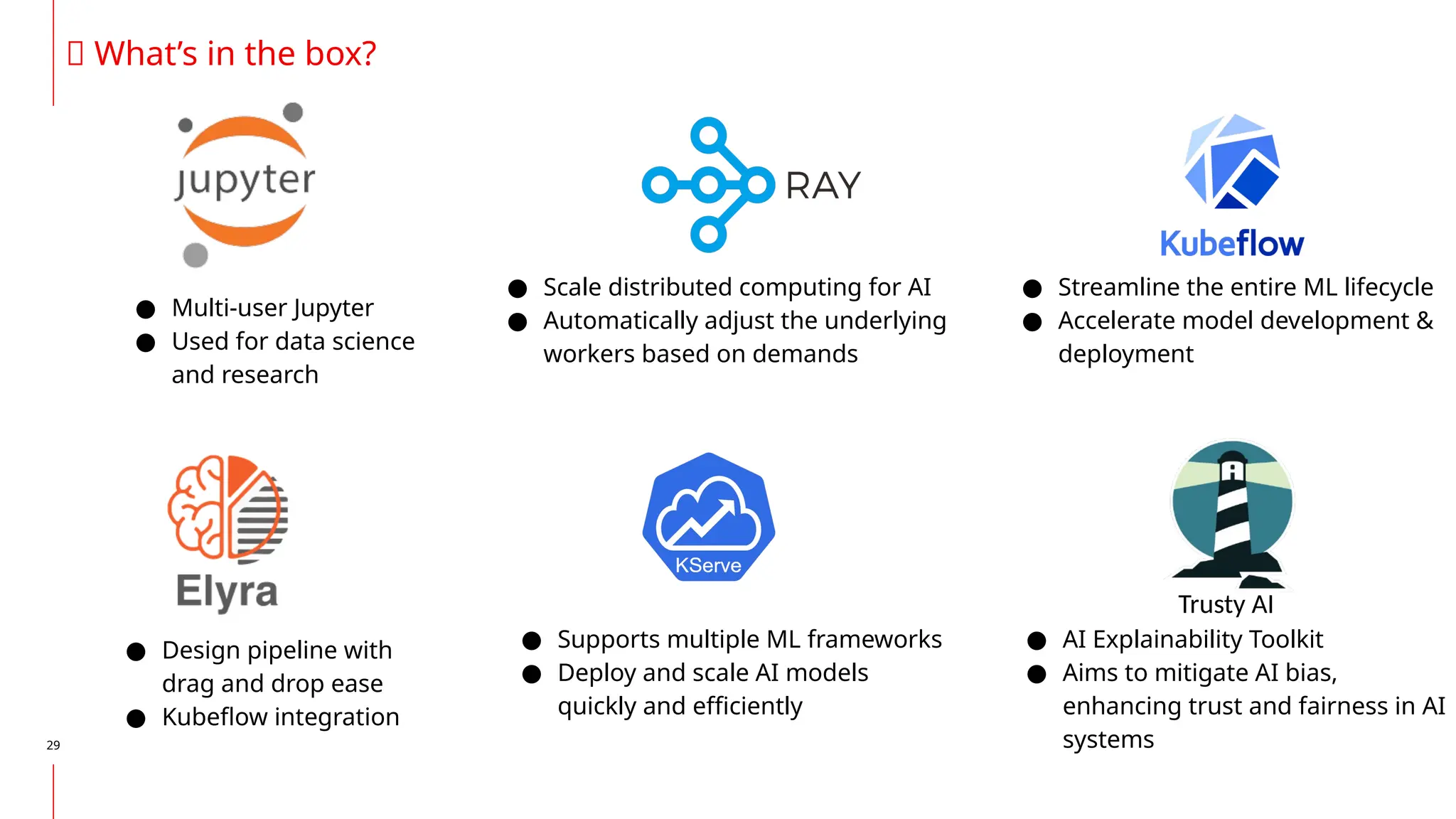
The document discusses the integration of DevOps and MLOps, focusing on the operationalization of machine learning models in production environments. It highlights the challenges faced by organizations, such as poor communication and the need for reproducibility and traceability in machine learning processes. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of collaboration among various roles in the machine learning lifecycle to ensure effective model deployment and monitoring.