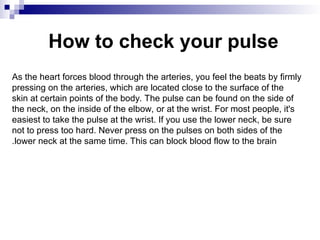
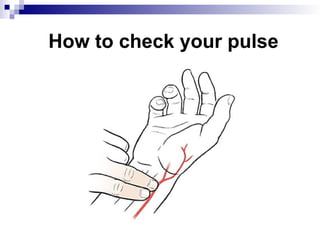
Vital signs are crucial indicators of a patient's health, including temperature, pulse, respiration rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation. Abnormal readings in these vital signs can indicate medical conditions such as fever, hypertension, or low oxygen levels. Accurate measurement techniques and understanding normal ranges are essential for effective health monitoring.