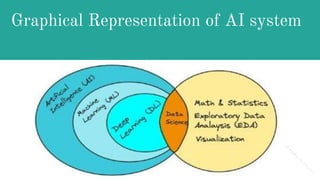
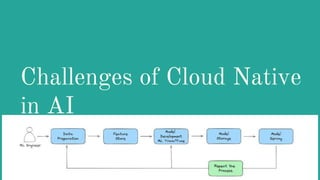
The document discusses Cloud Native Artificial Intelligence (CNAI), defining its key components and benefits while outlining significant challenges such as data management, processing efficiency, and architectural complexity. It presents a path forward that includes adopting flexible tools, sustainable practices, and unified terminology to enhance AI development. Additionally, it highlights solutions like Kubeflow for orchestration and vector databases to optimize AI capabilities in cloud environments.