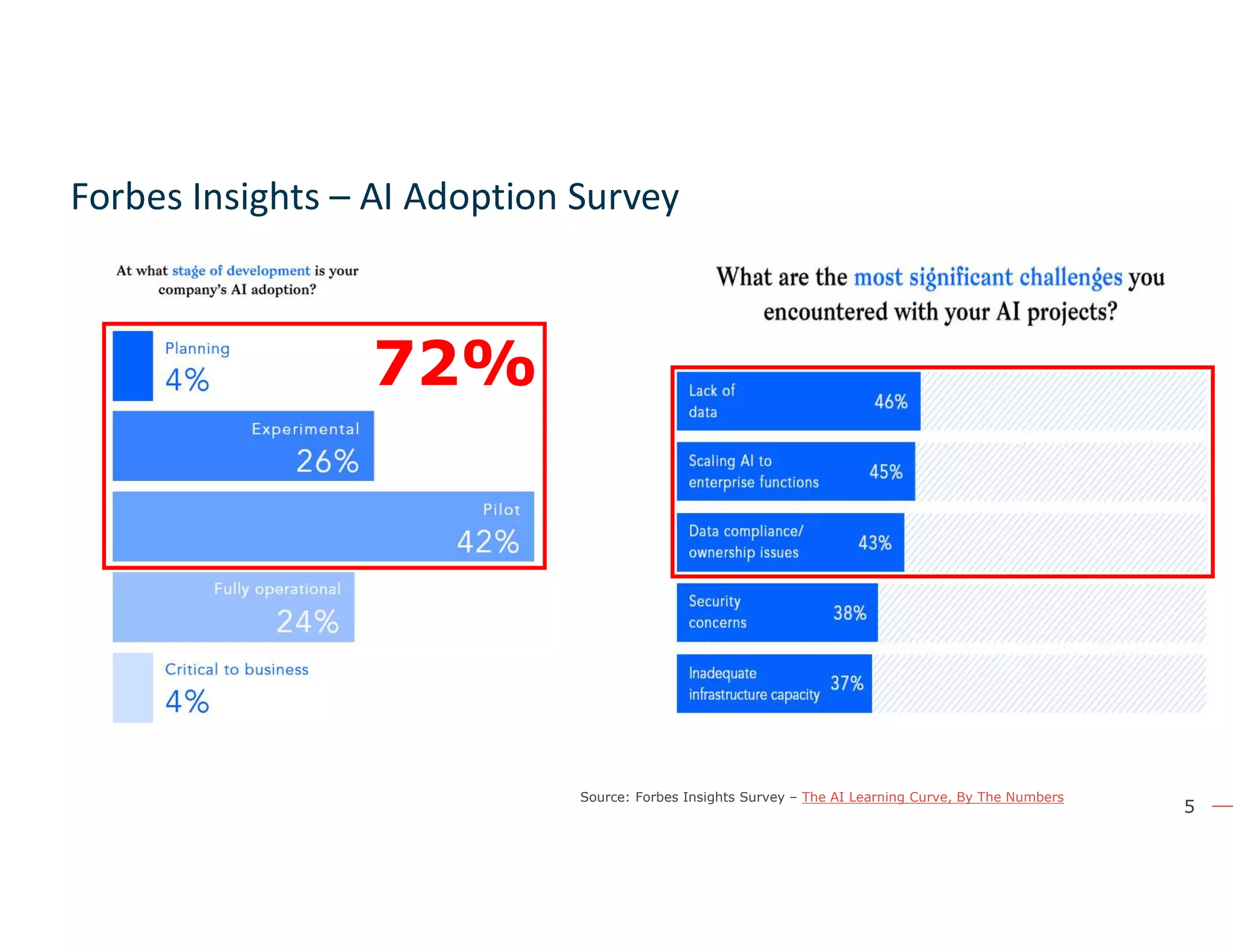
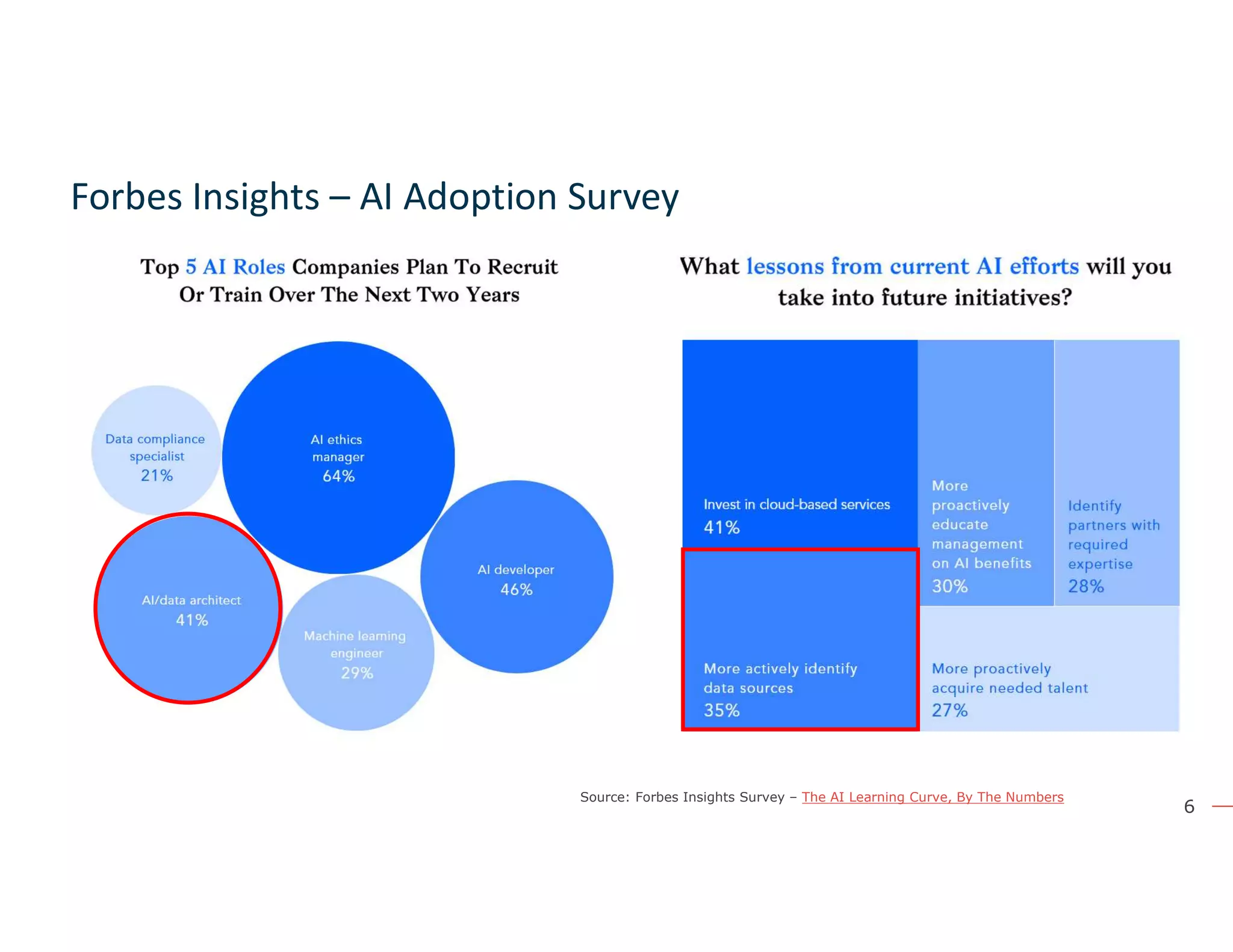
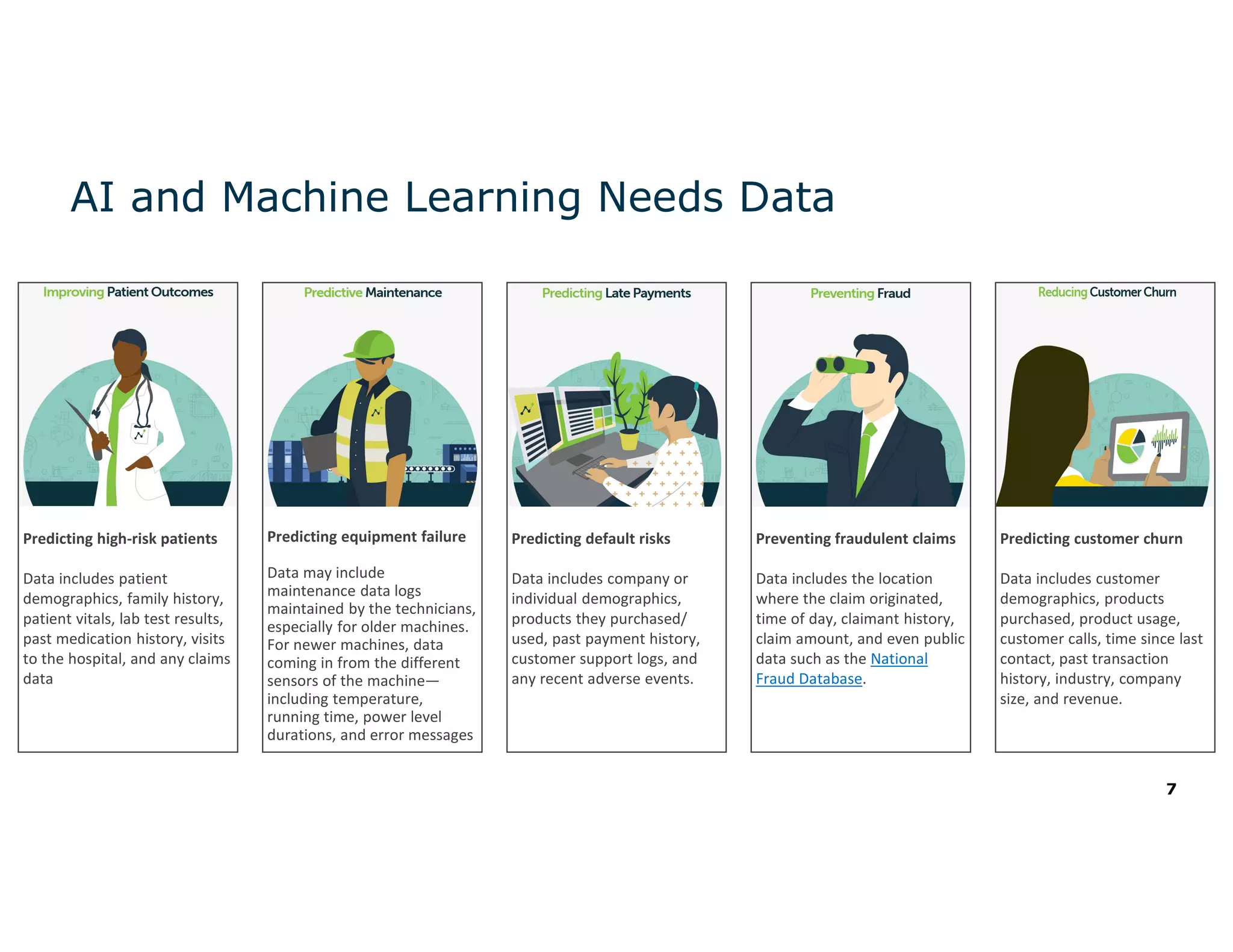
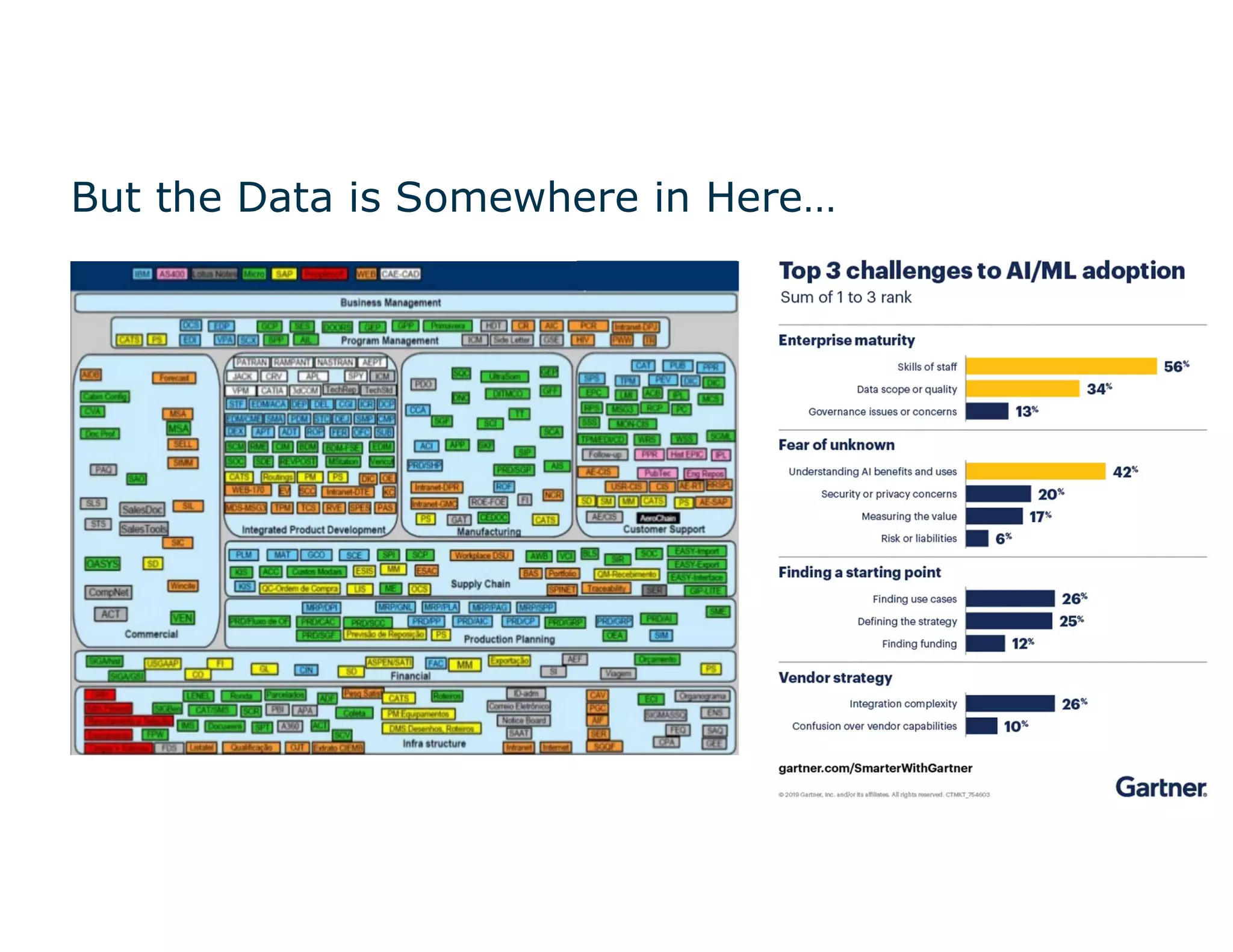
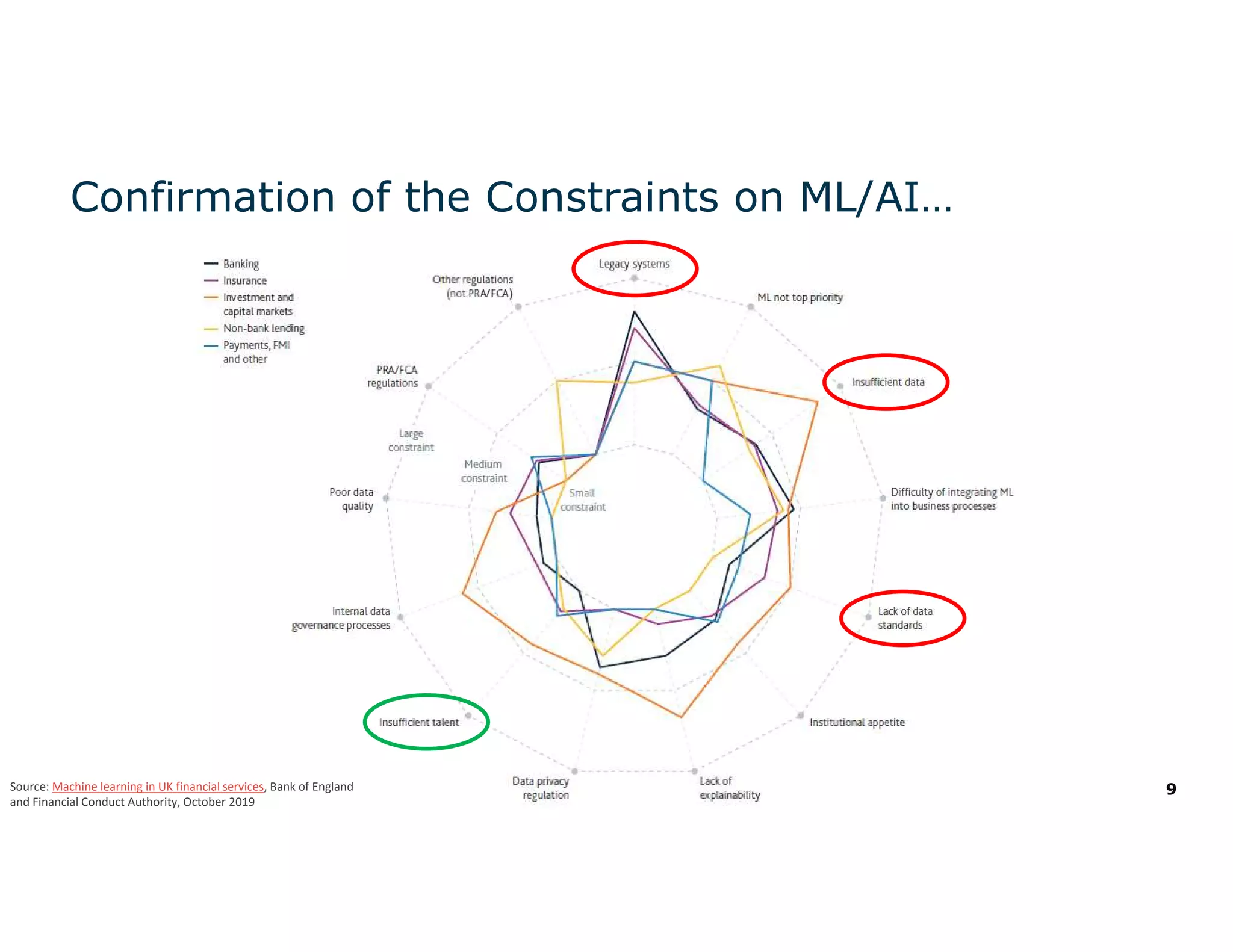
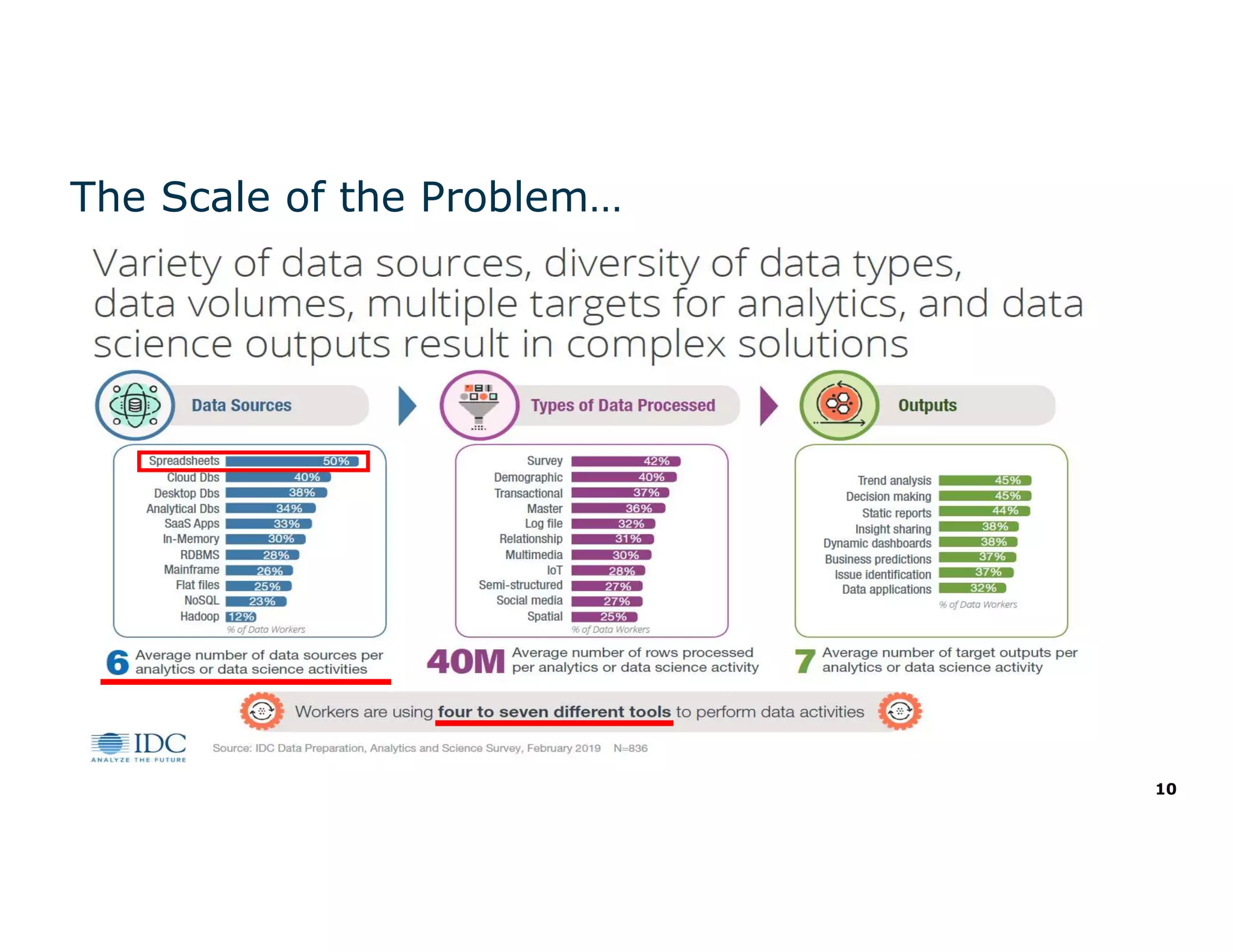
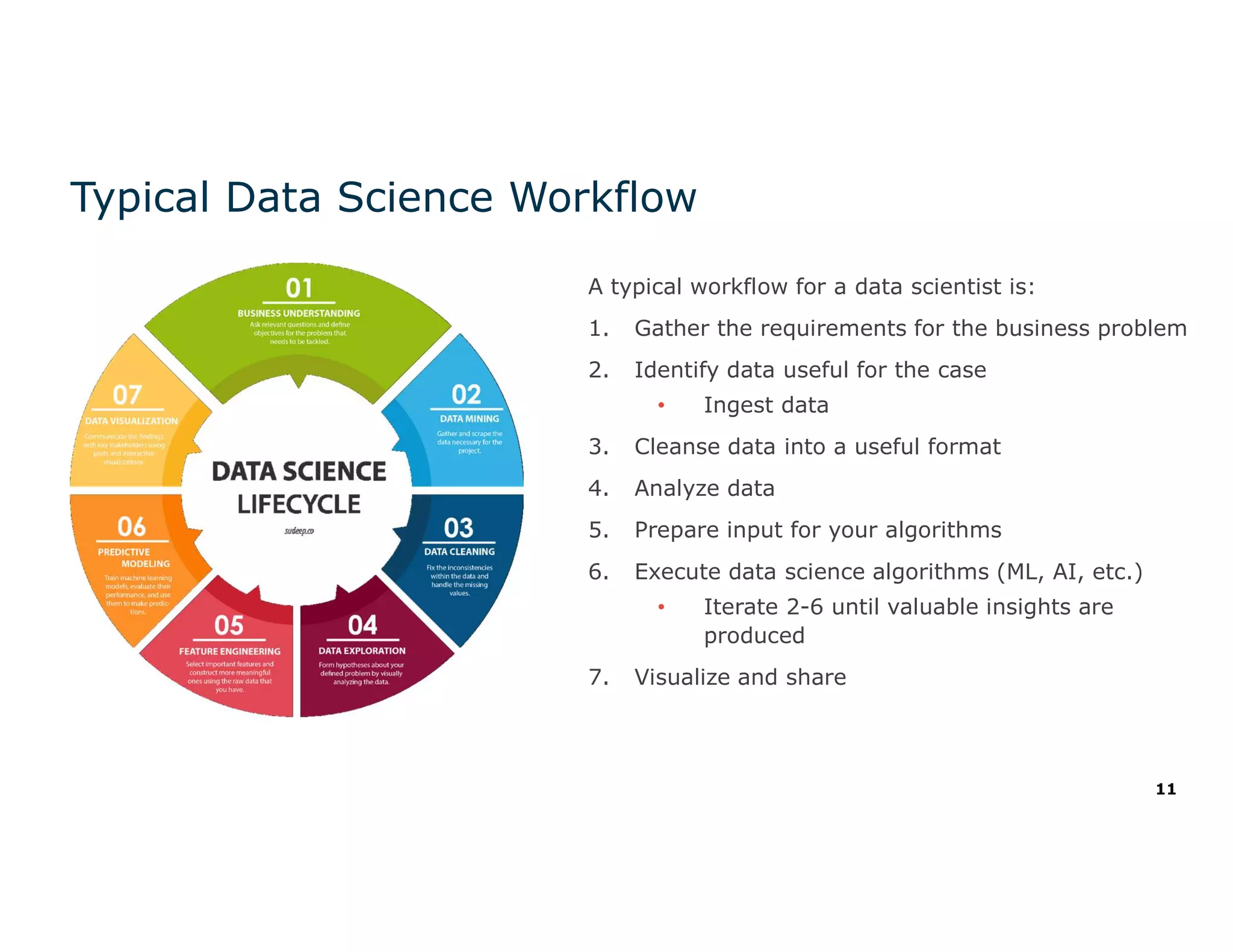
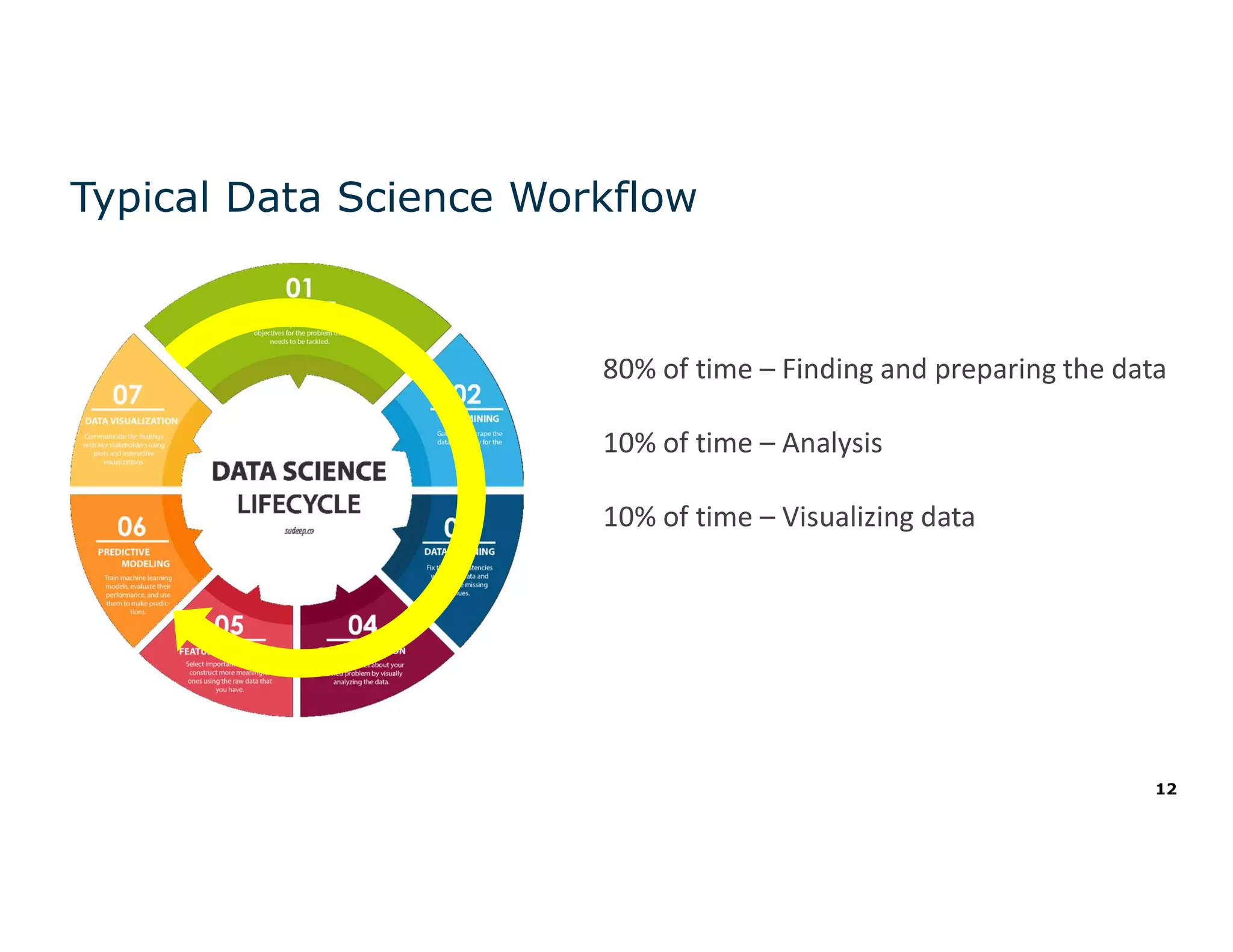
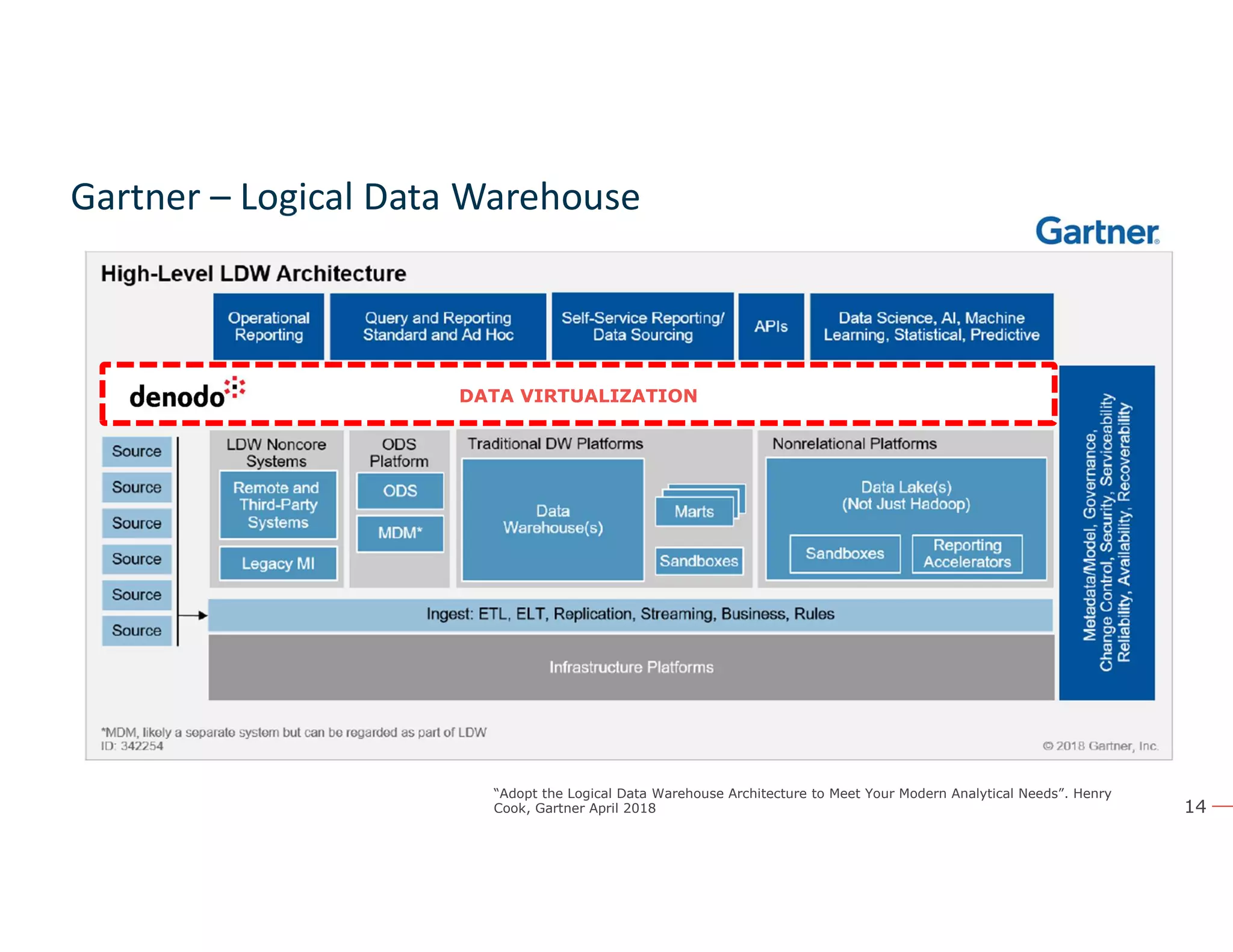
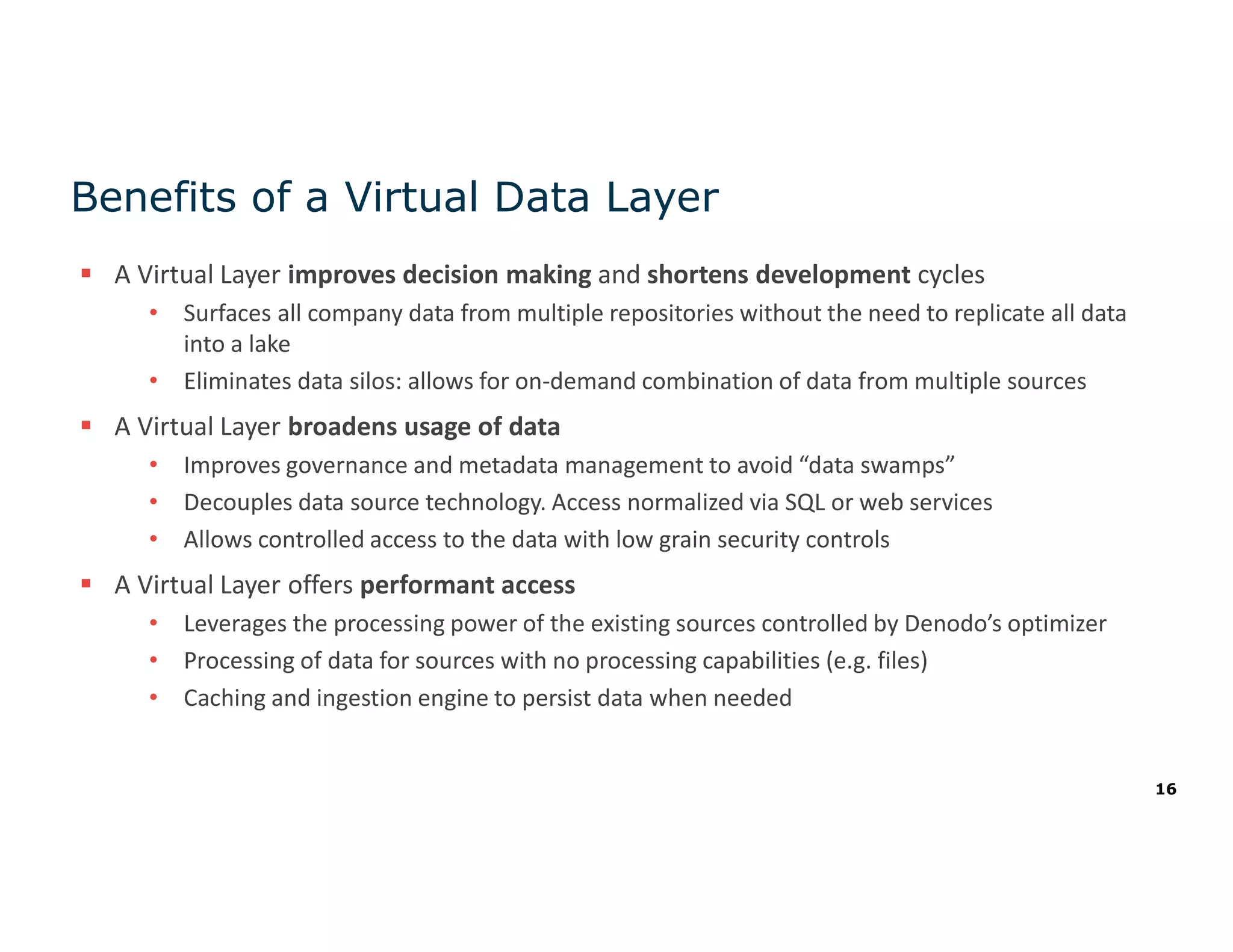
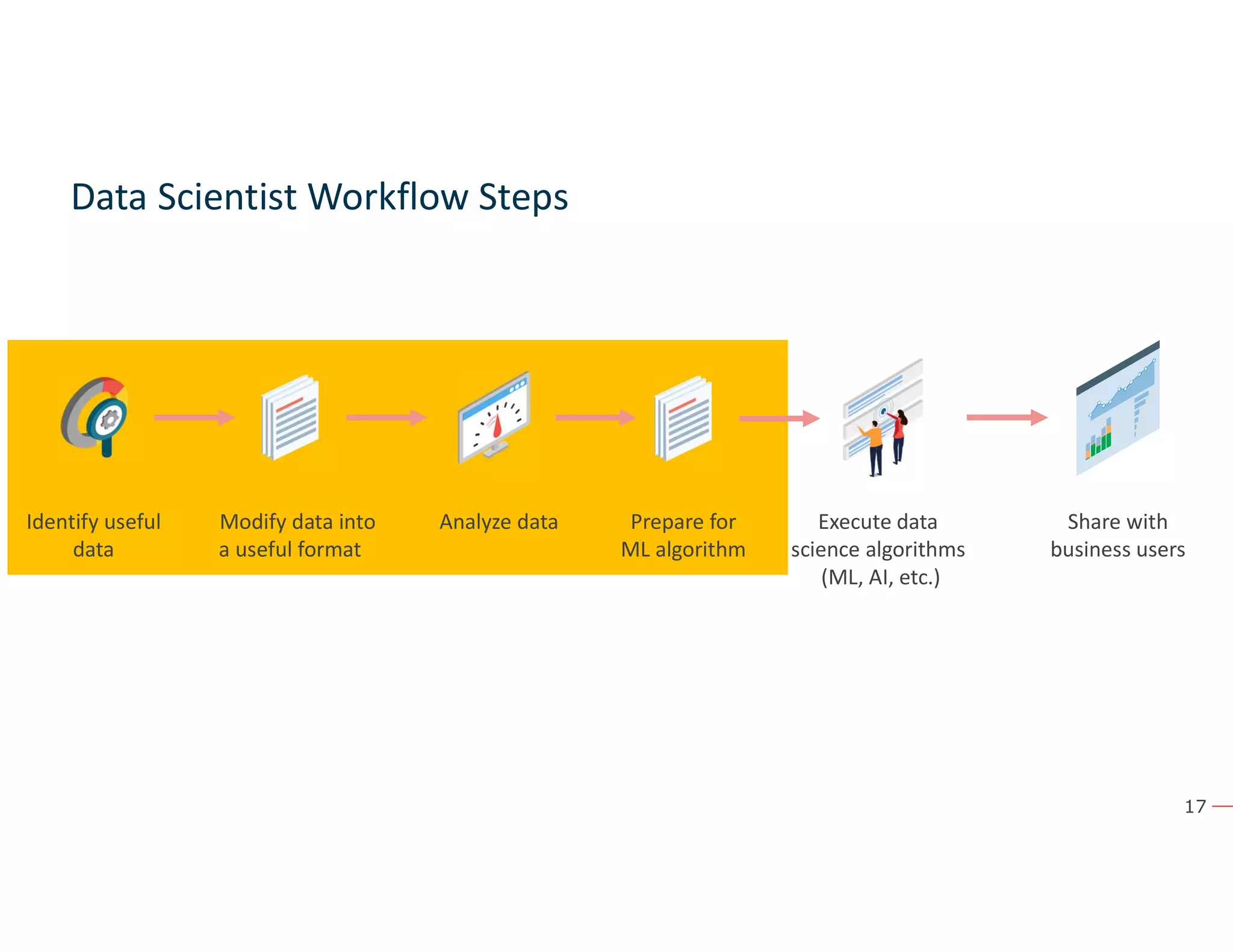
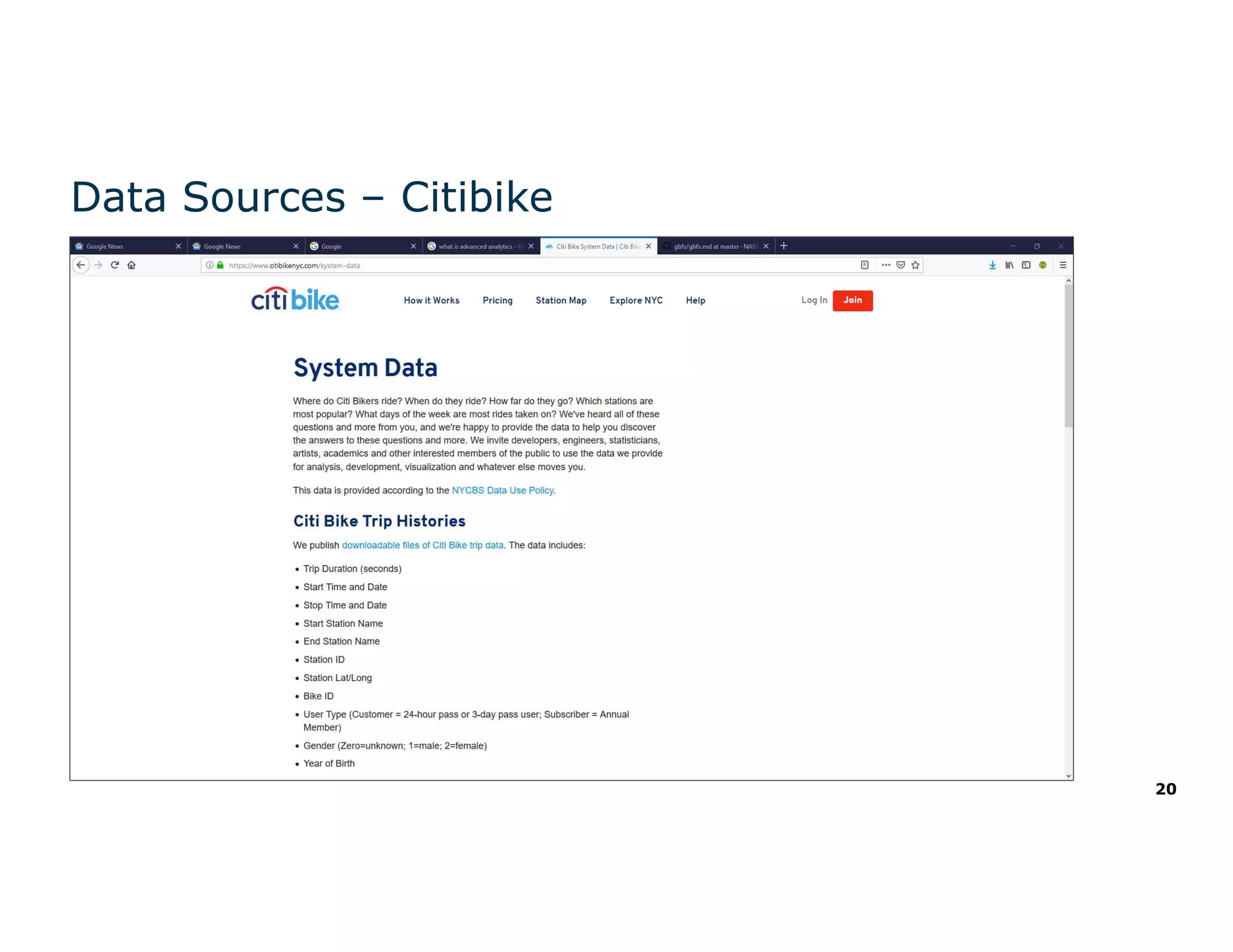
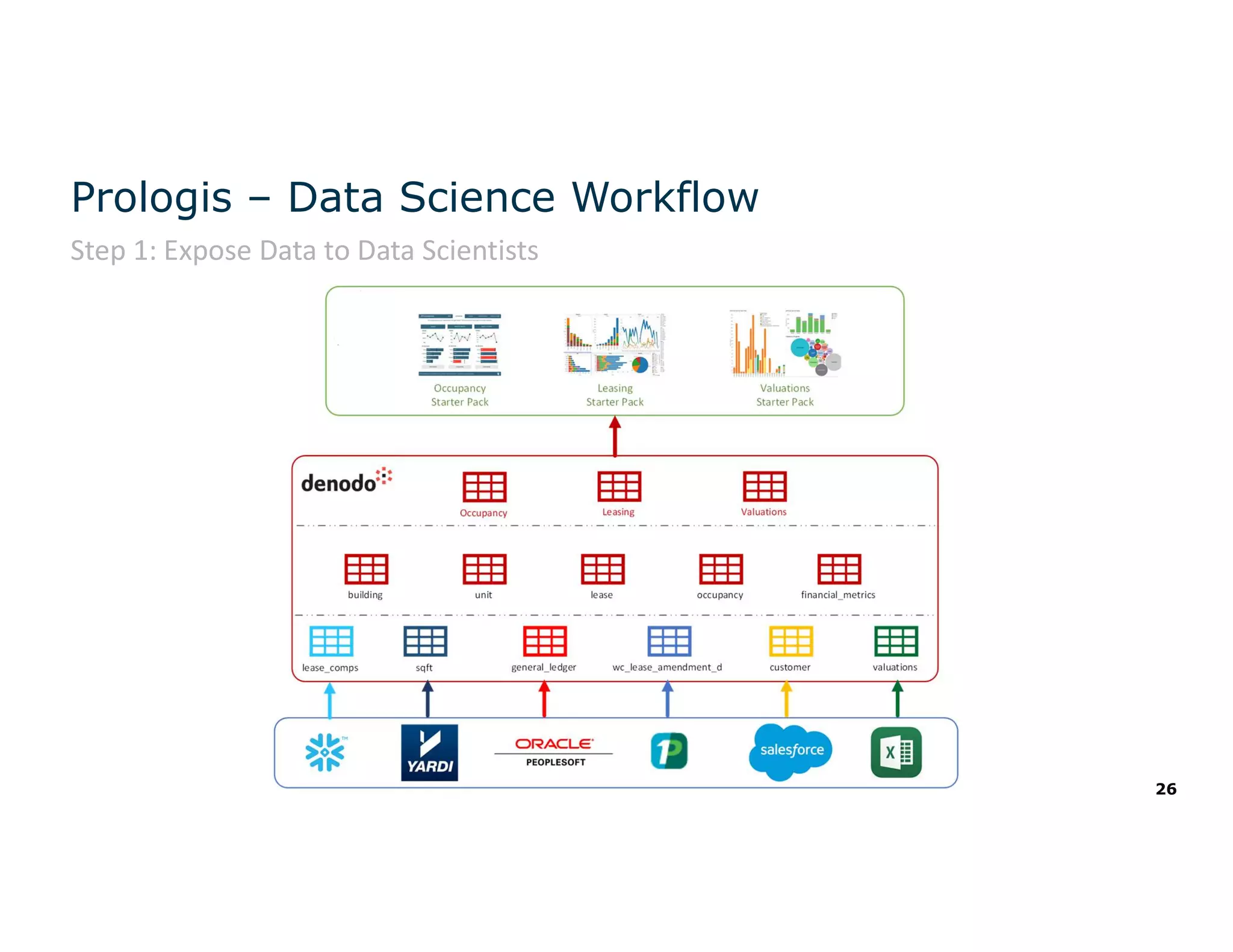
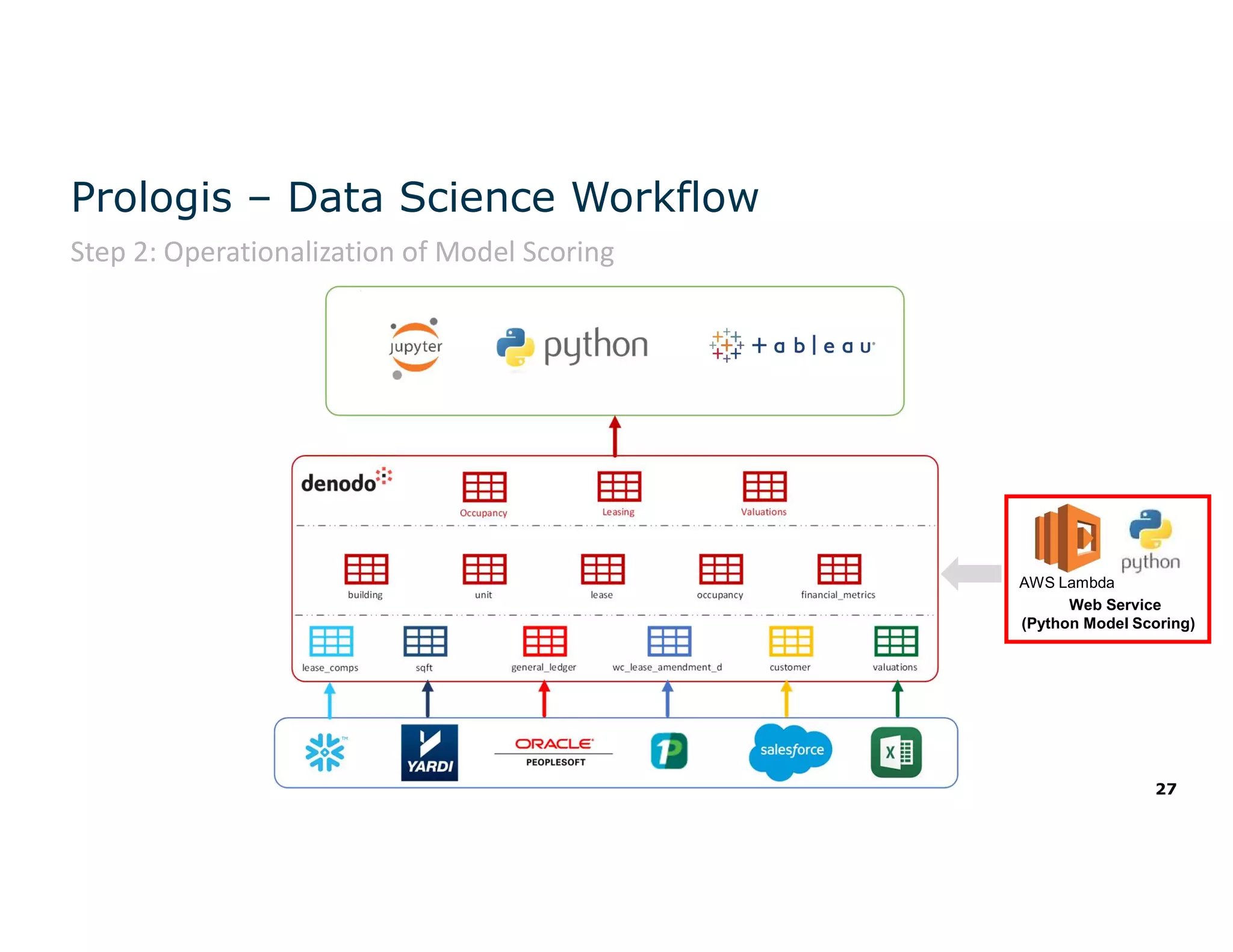
The document discusses the value and challenges of data virtualization, highlighting its role in integrating data for advanced analytics and machine learning. It outlines a typical data science workflow and emphasizes how data virtualization can streamline processes, reduce latency, and improve data governance. Key takeaways include the ease of accessing varied data sources and the platform's potential to simplify analytics and machine learning projects.