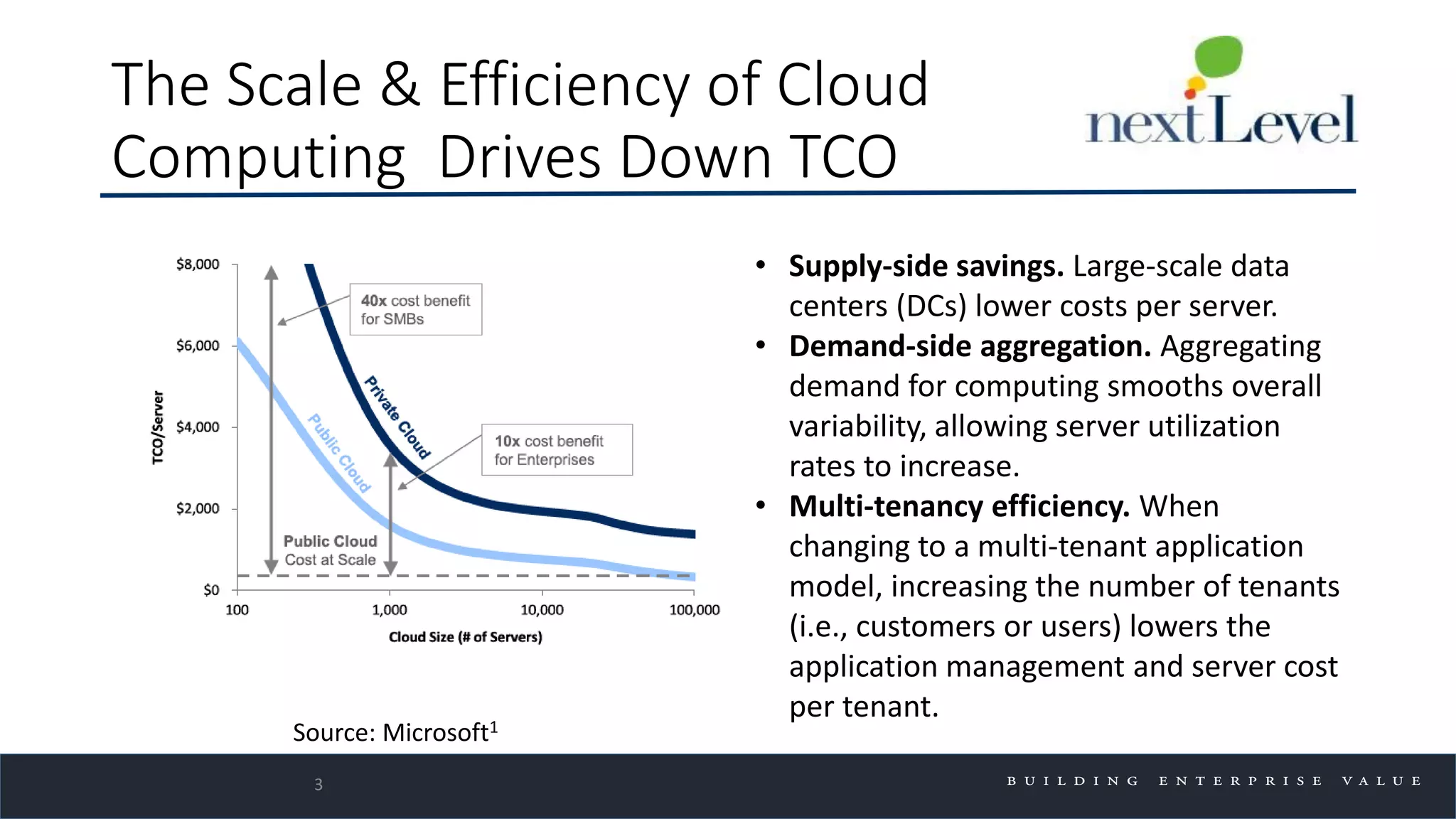
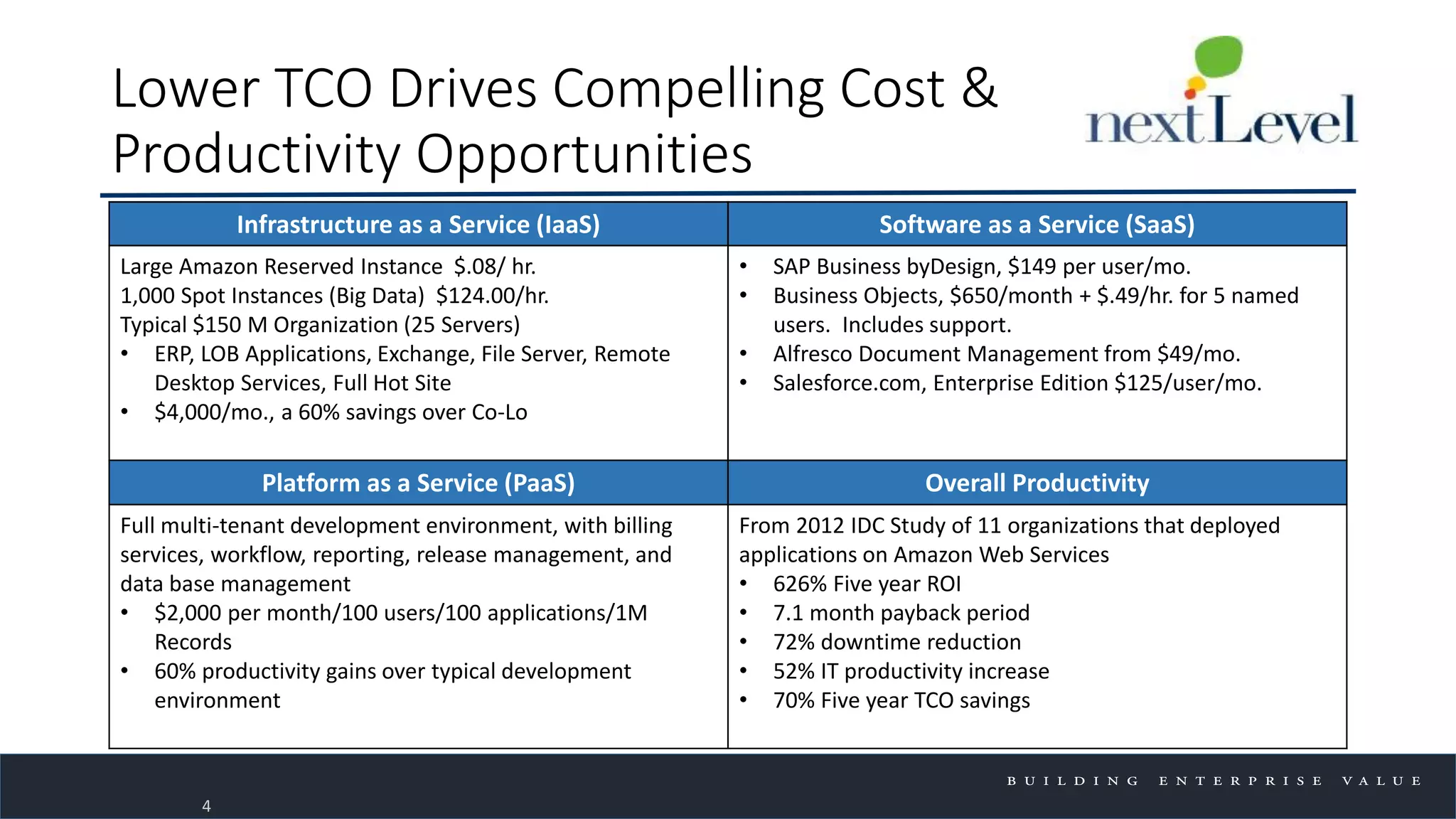
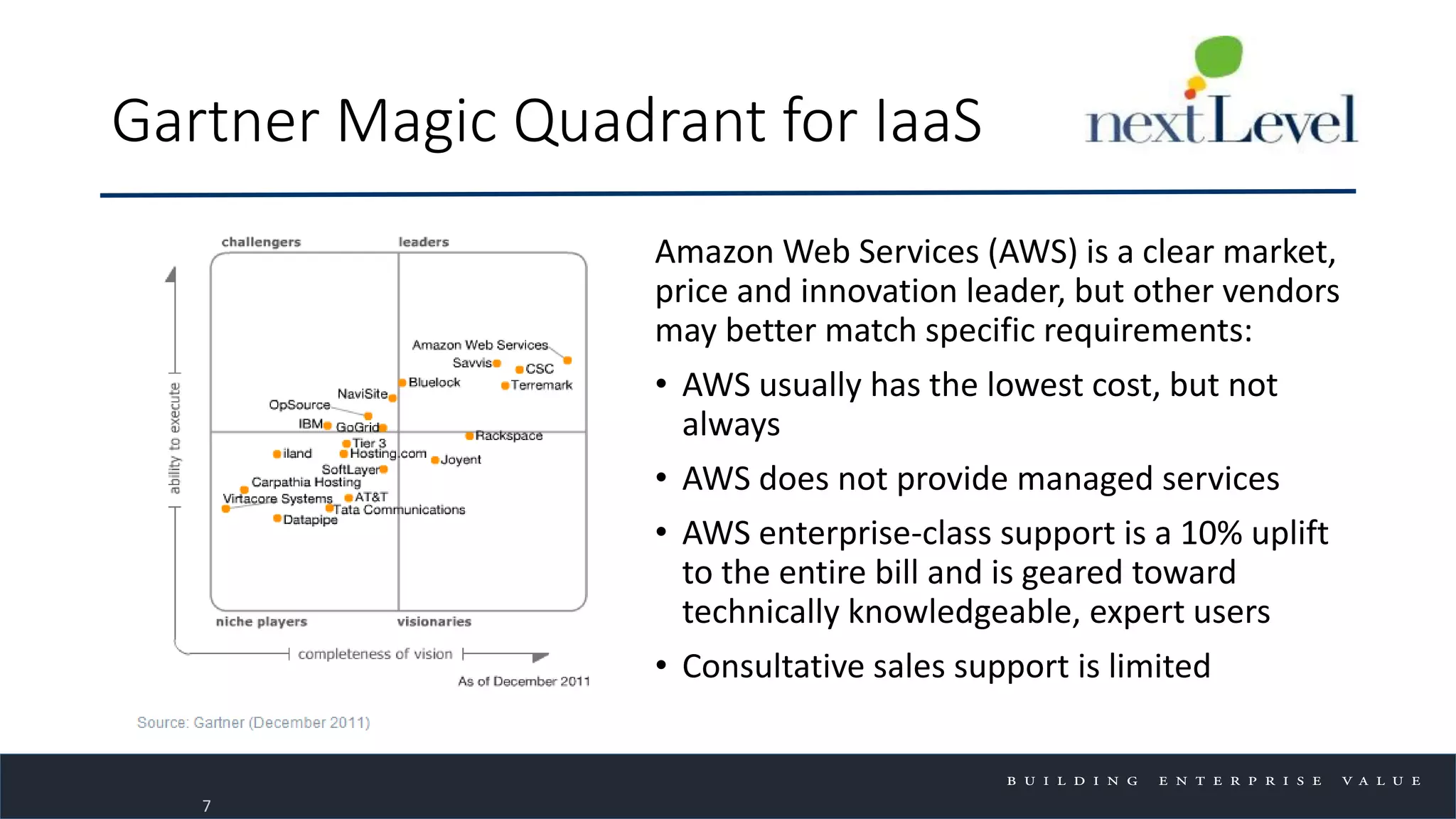
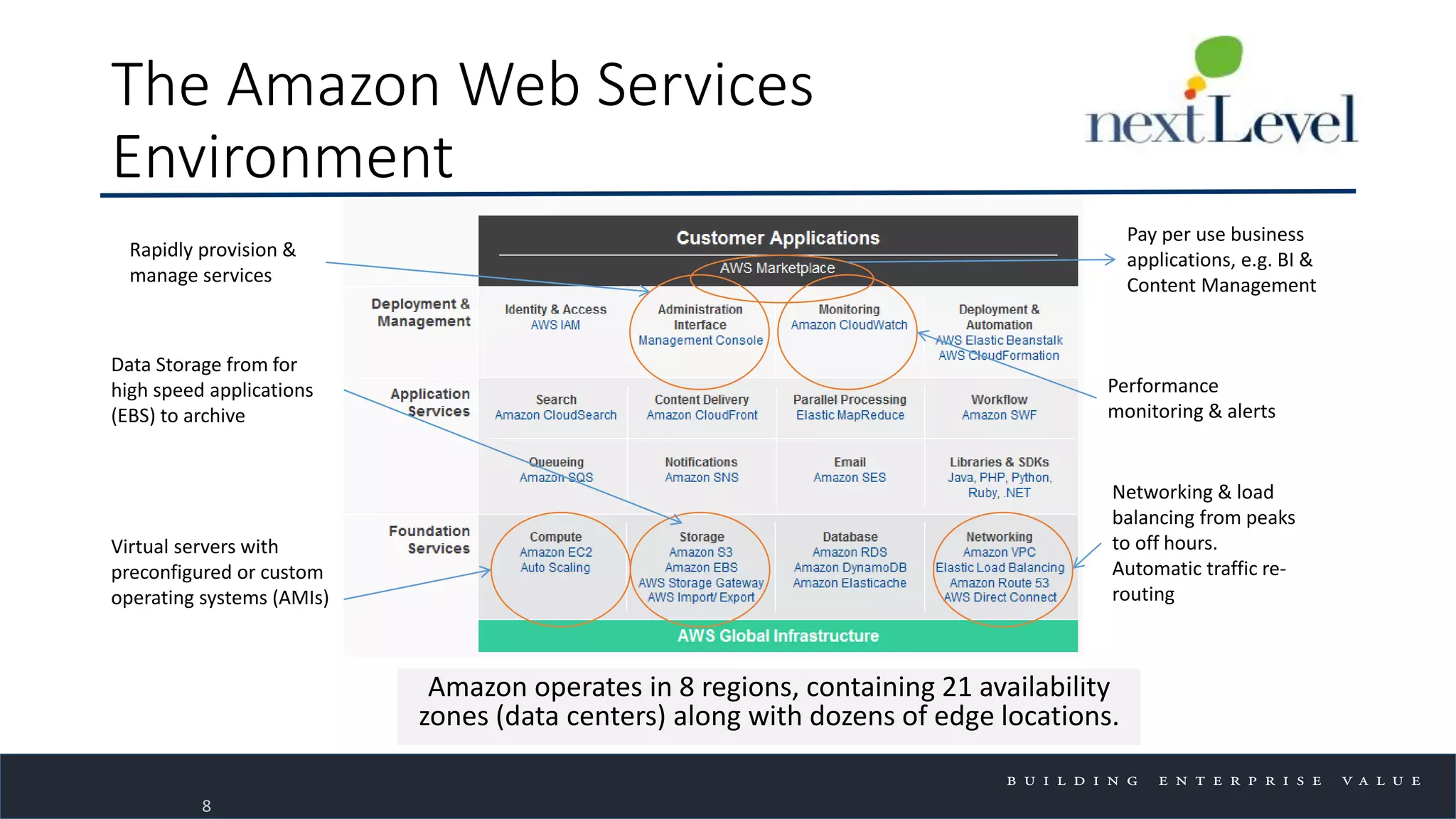
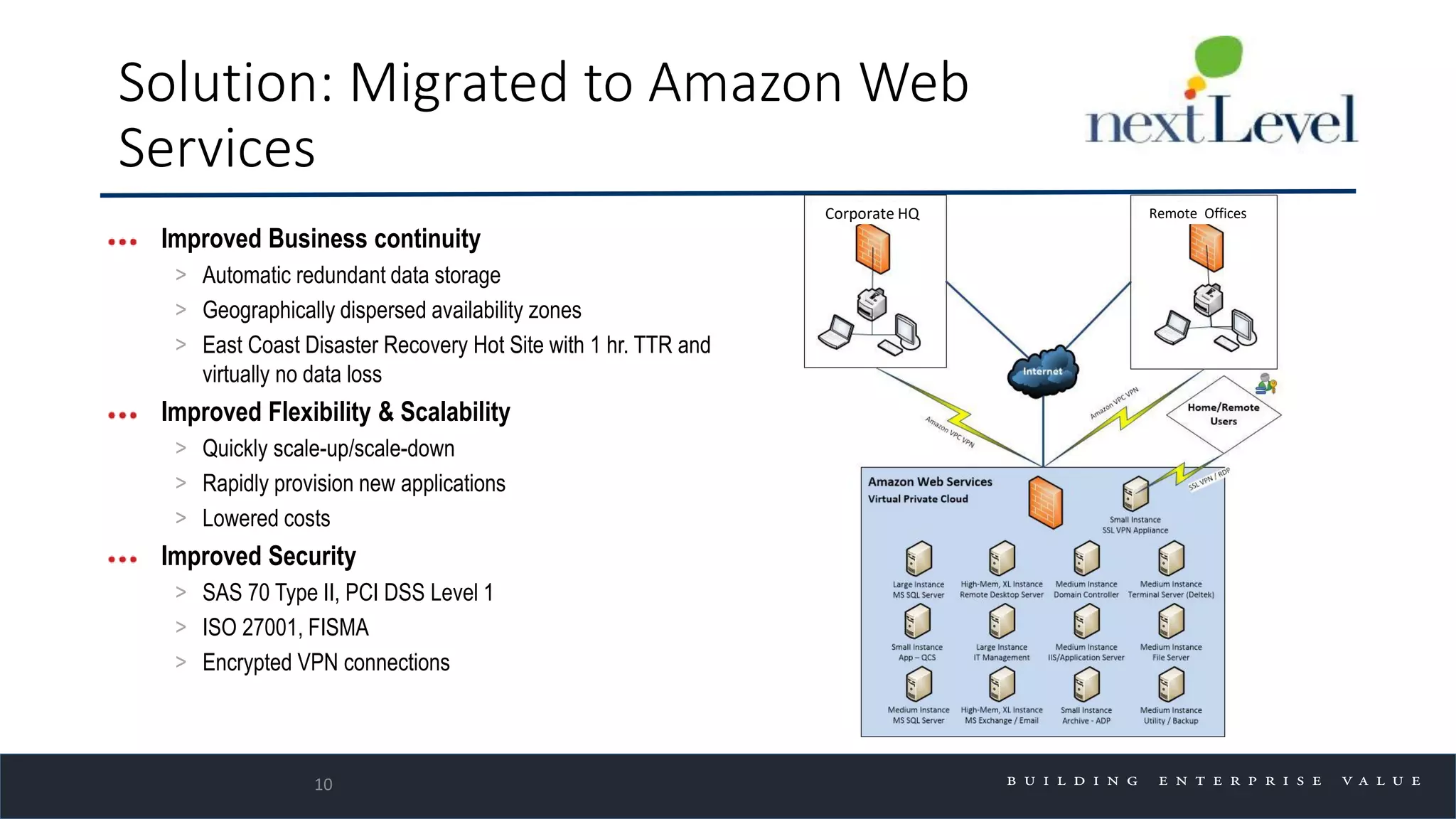
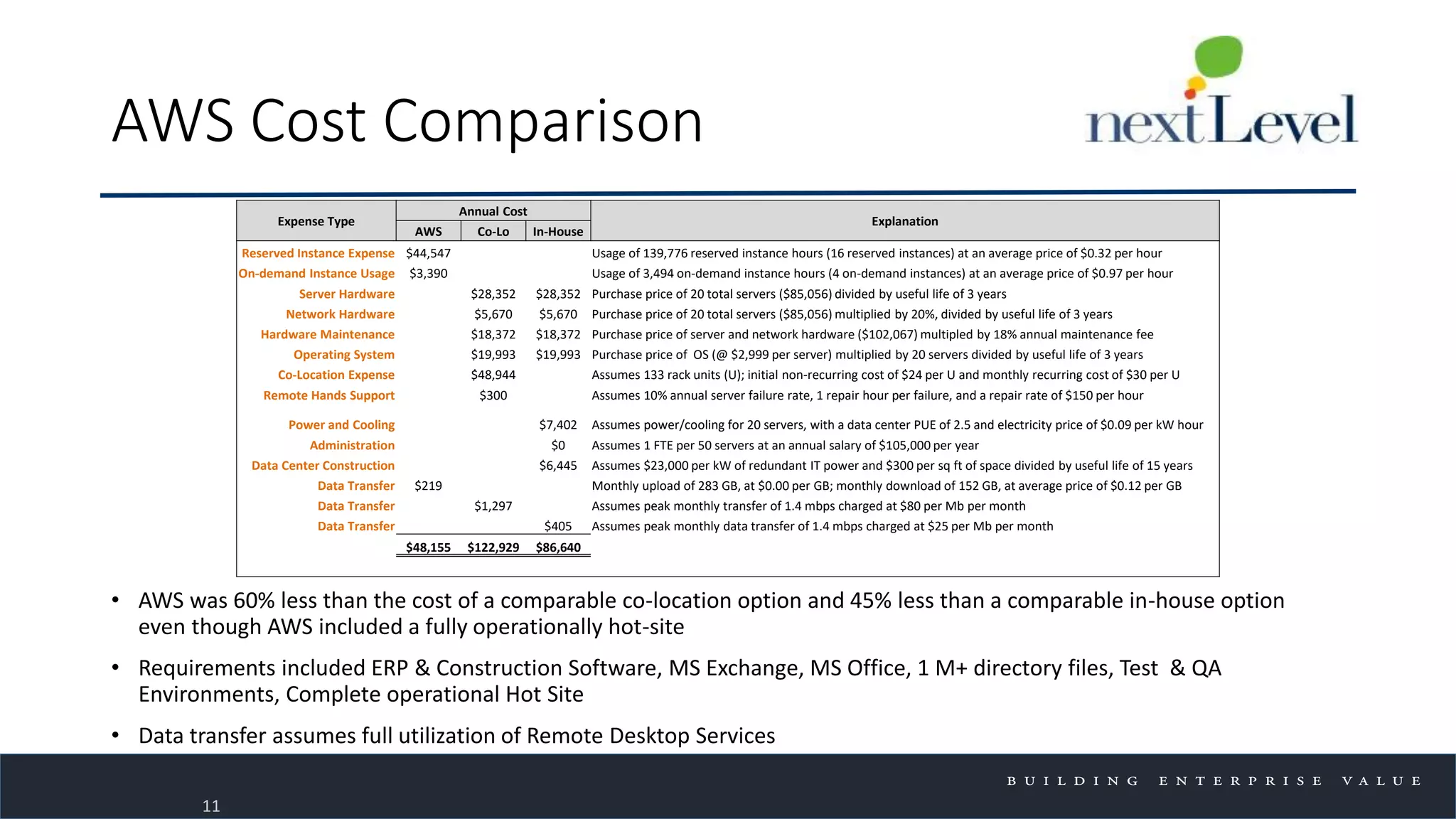
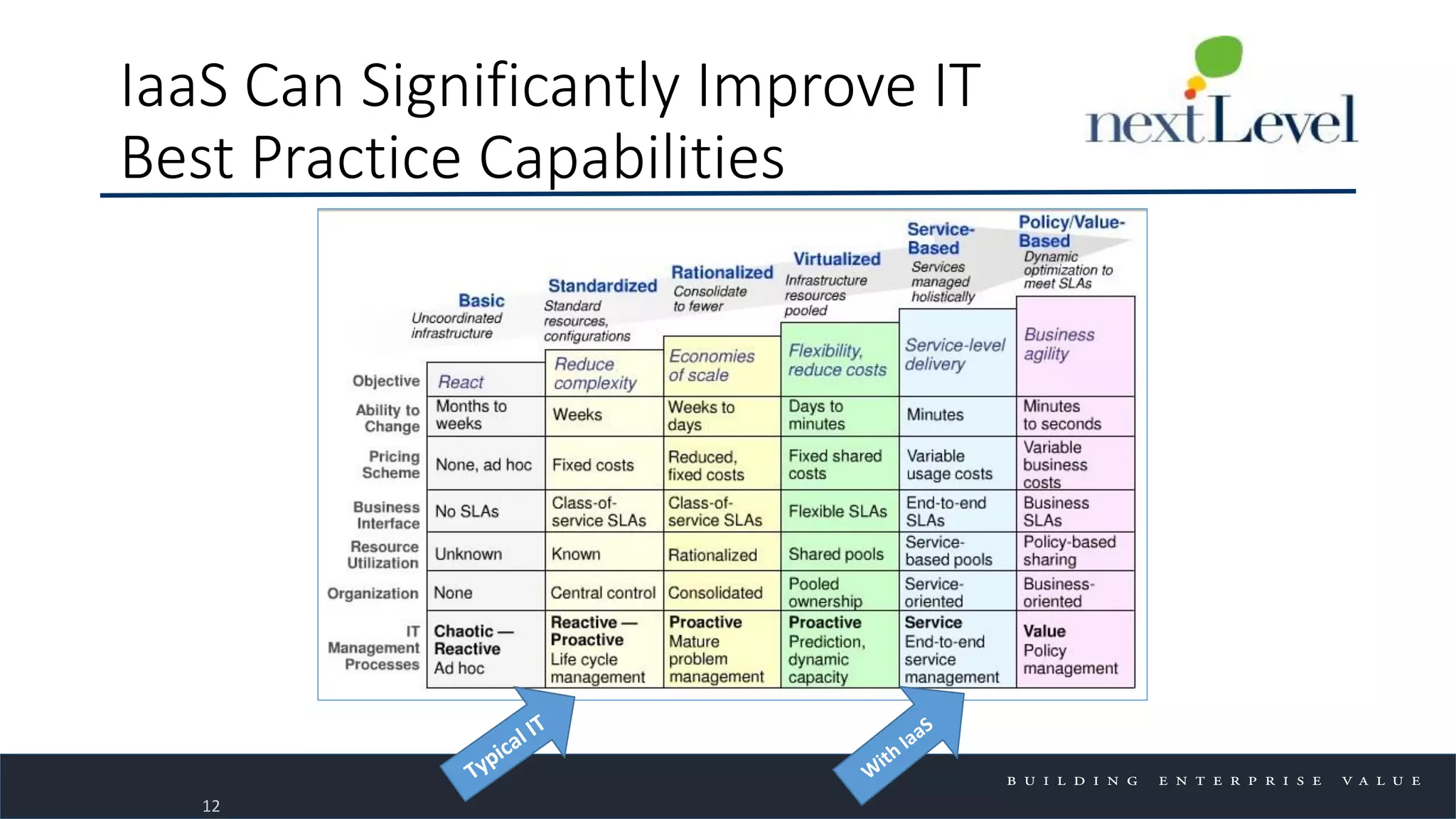
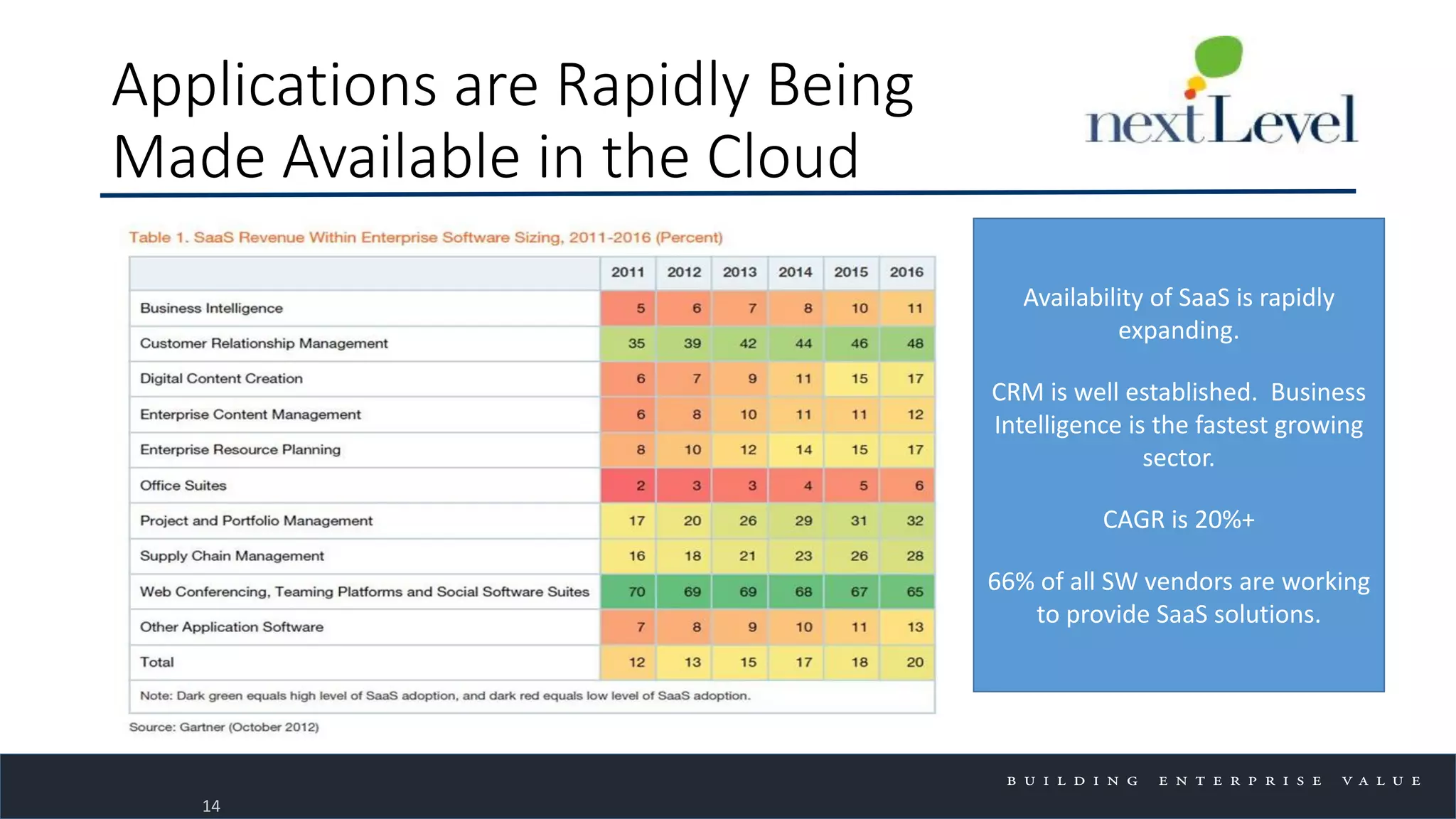
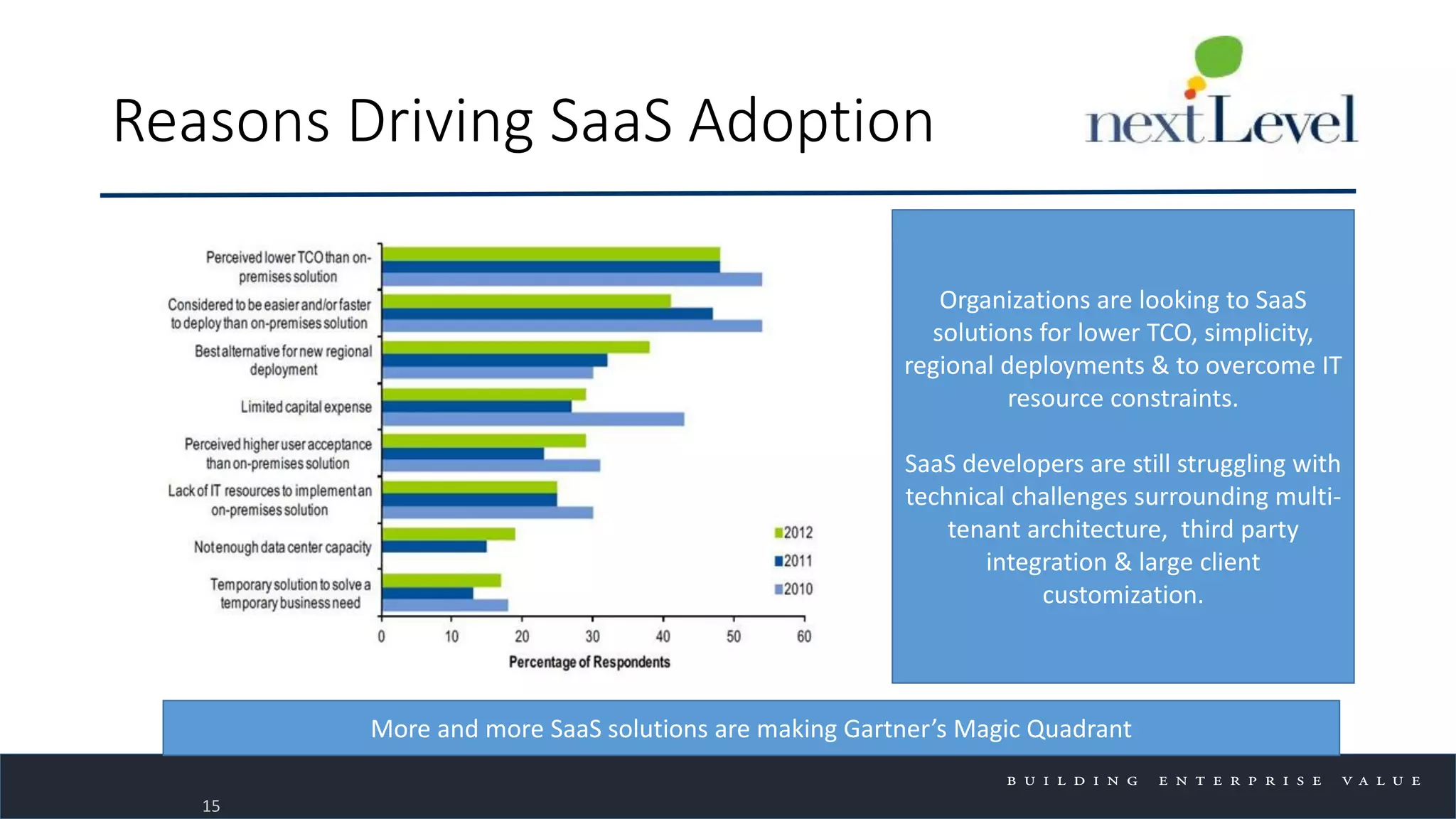
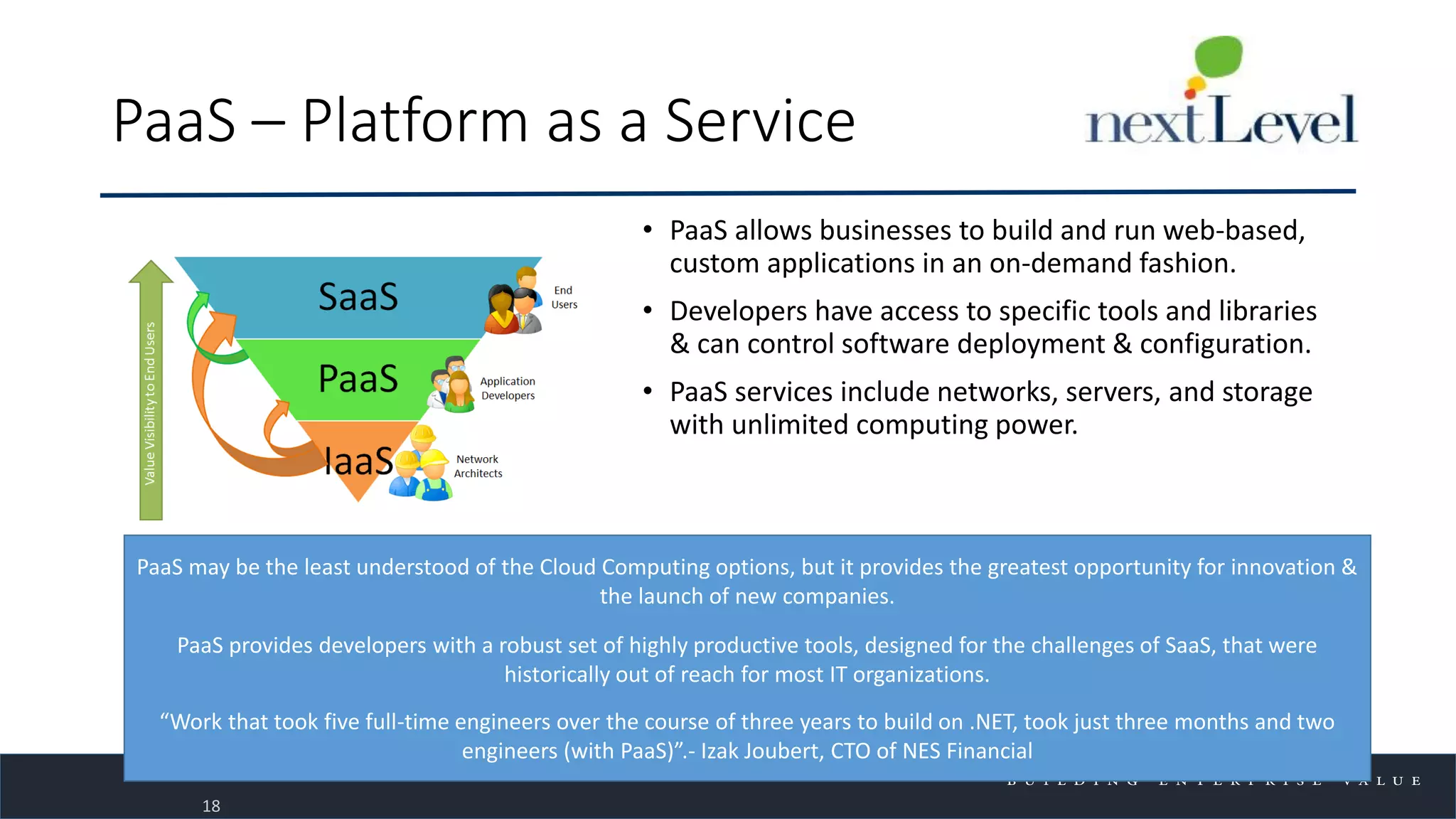
The document discusses key trends in cloud computing, emphasizing its capacity to reduce costs and improve productivity across organizations. It highlights the benefits of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS), detailing how they can enhance business operations and flexibility. However, it also notes the need for careful evaluation and management to fully realize the advantages of cloud solutions.