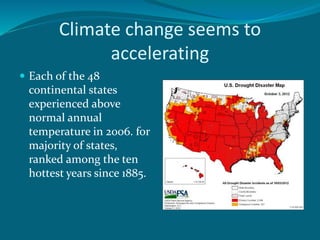
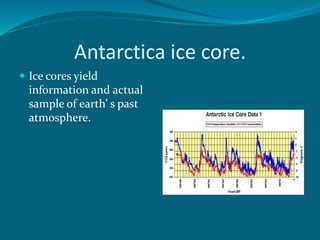
The document explains the differences between weather and climate, highlighting that weather is short-term and localized, while climate is a long-term, averaged observation of weather patterns. It discusses the effects of greenhouse gases on planetary temperatures, emphasizing the accelerating impacts of climate change due to human activity. The document also suggests lifestyle changes to mitigate climate change, including energy conservation and water-saving measures.