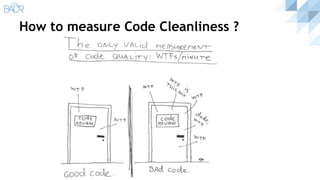
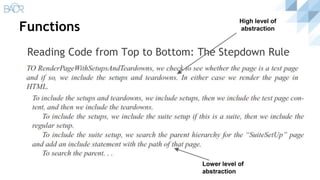
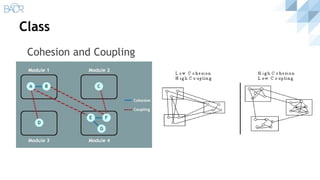
The document discusses principles of clean code, beginning with definitions of clean code from various authors. It outlines key principles like the single responsibility principle and open/closed principle. It then covers sections on meaningful naming, functions, and classes. For functions, it recommends they be small, do one thing, avoid flag arguments, and have no side effects. For classes, it advocates for small size, encapsulation, high cohesion and low coupling following the single responsibility principle.