Embed presentation
Download to read offline


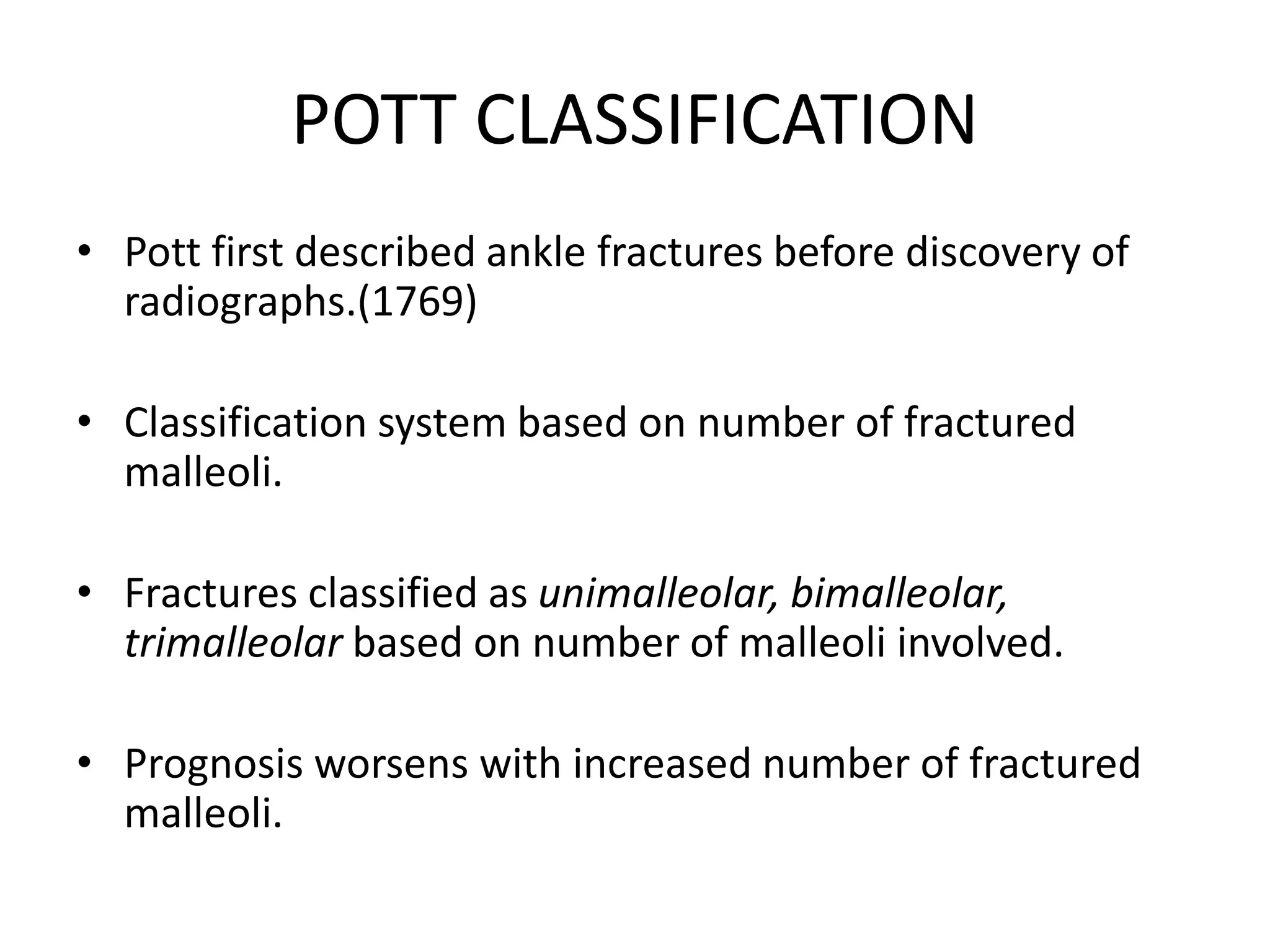
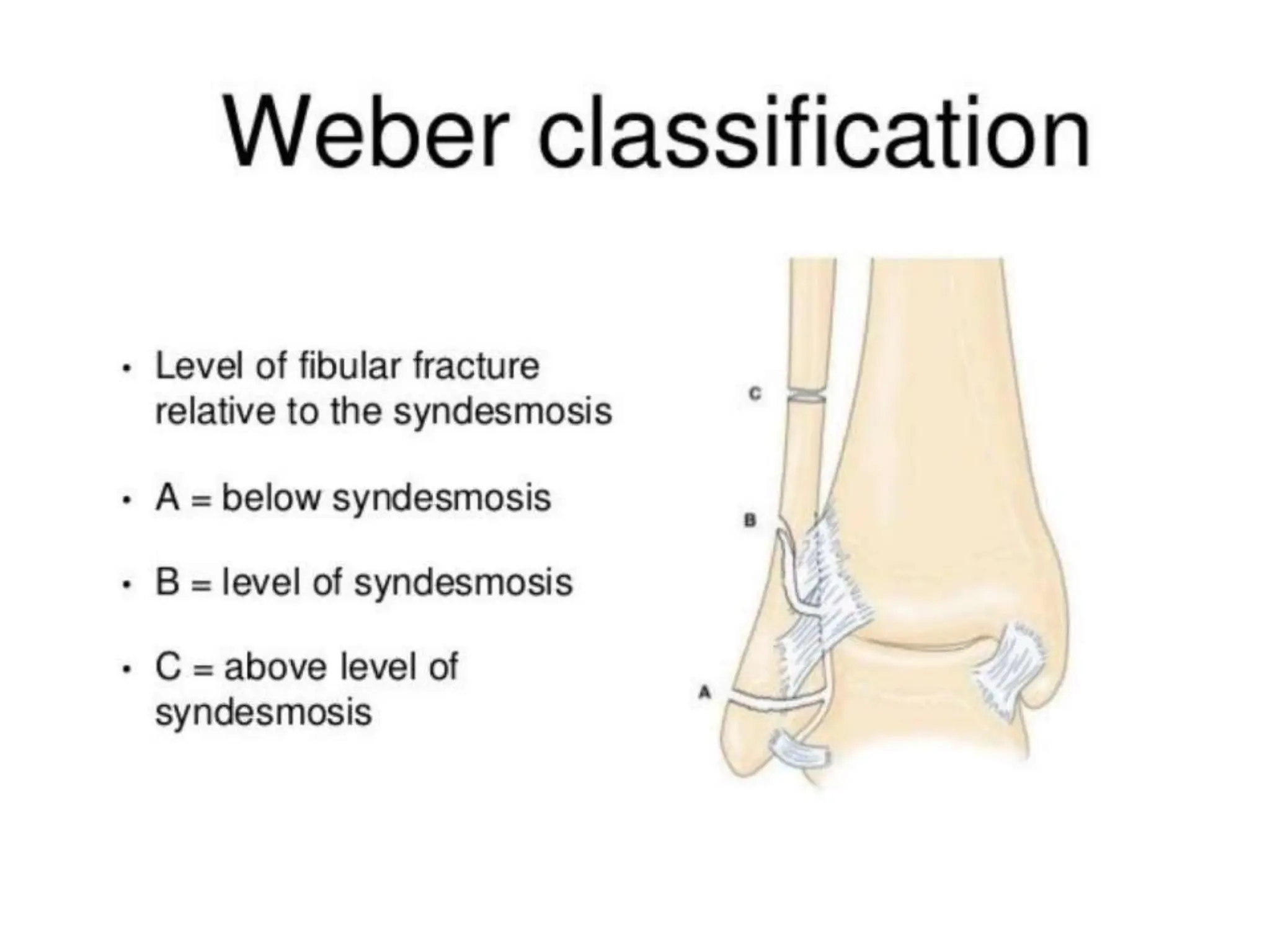
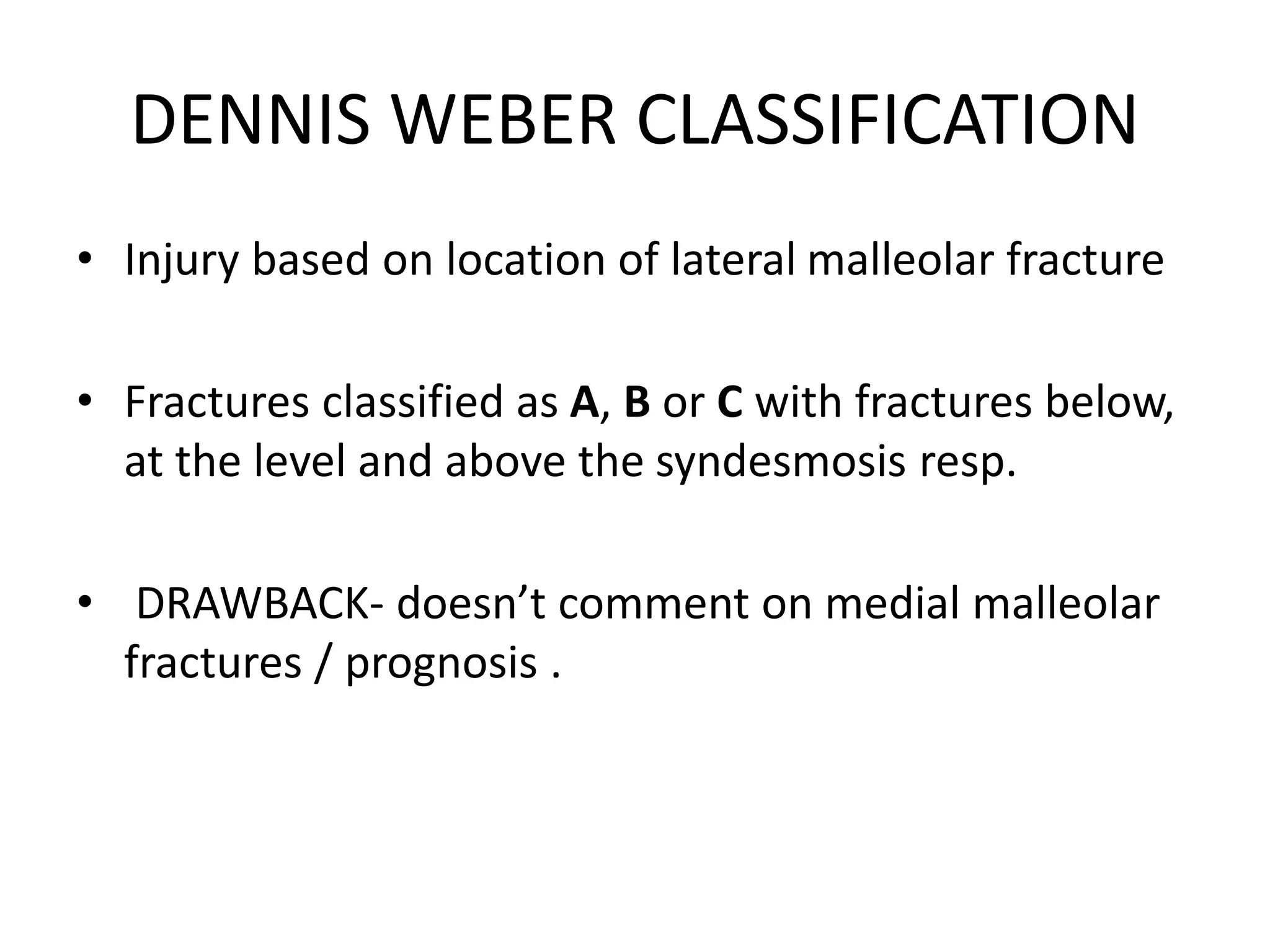
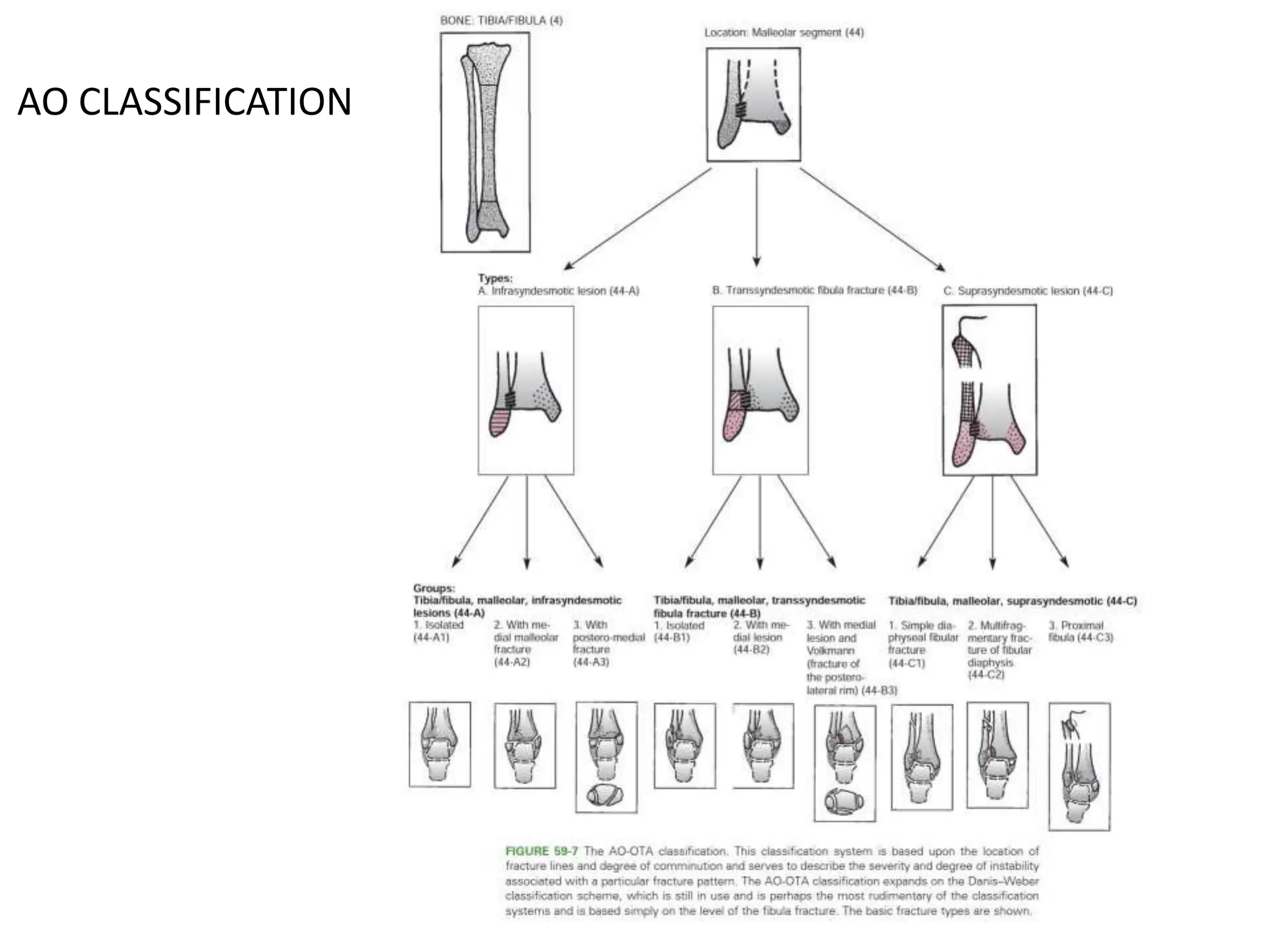

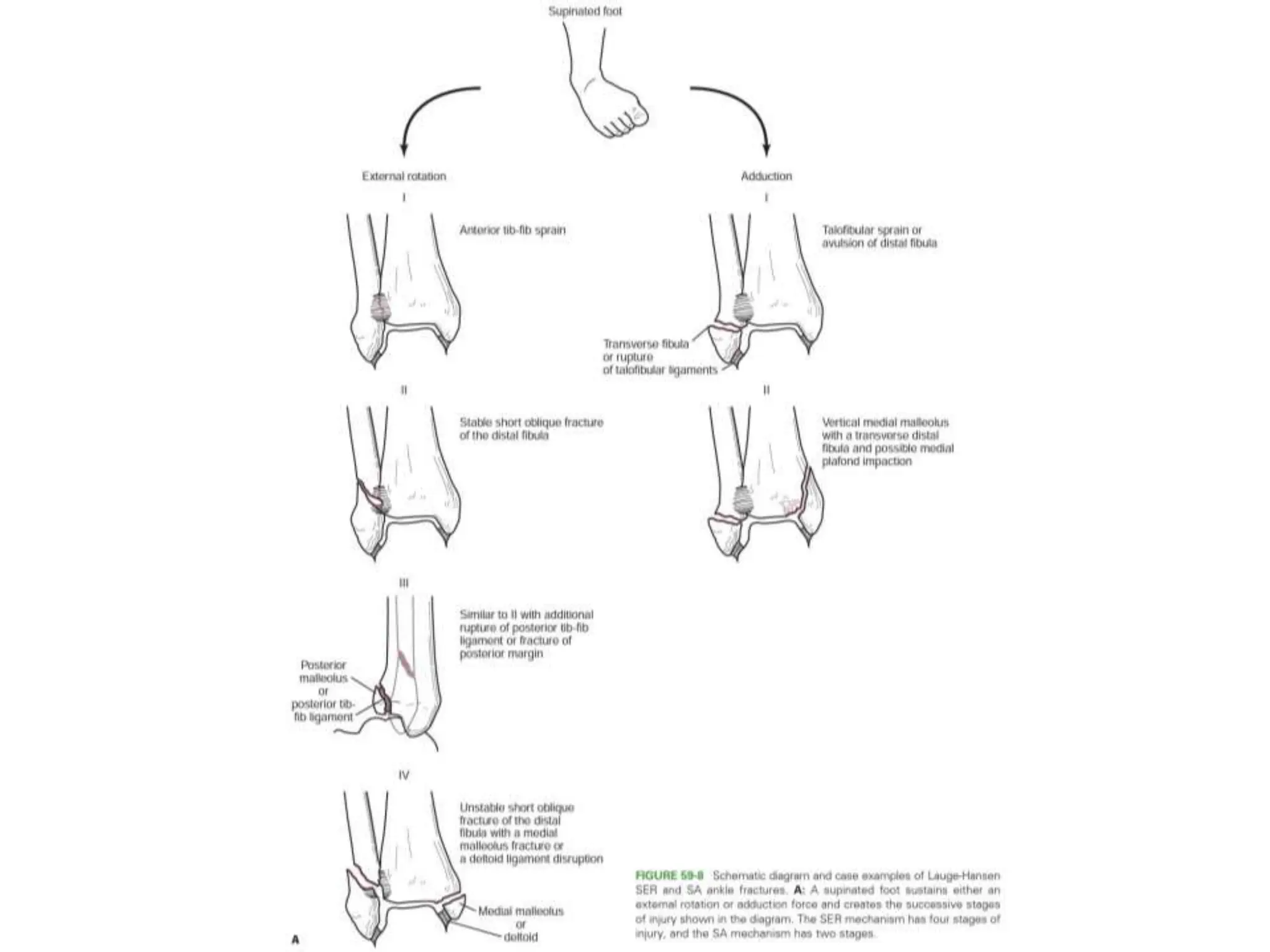
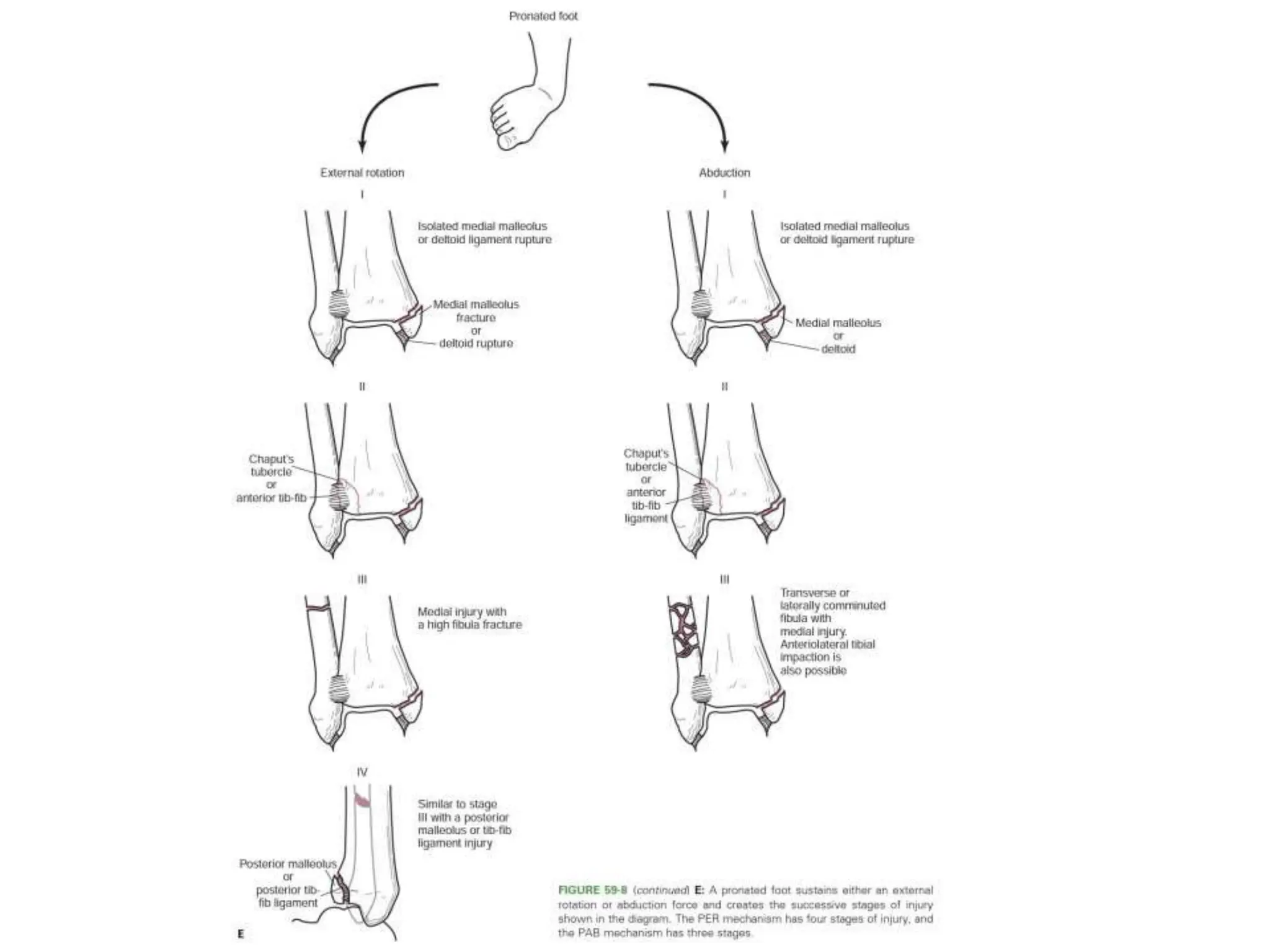

The document discusses the classification of ankle fractures according to anatomy, injury mechanics, and stability, highlighting key systems such as Pott, Denis Weber, AO/OTA, and Lauge-Hansen classifications. Pott's classification focuses on the number of fractured malleoli, while Denis Weber categorizes fractures based on the location of the lateral malleolar fracture. The Lauge-Hansen classification considers foot position and deforming forces, resulting in four classes of injury, with 'ser' being the most common.









