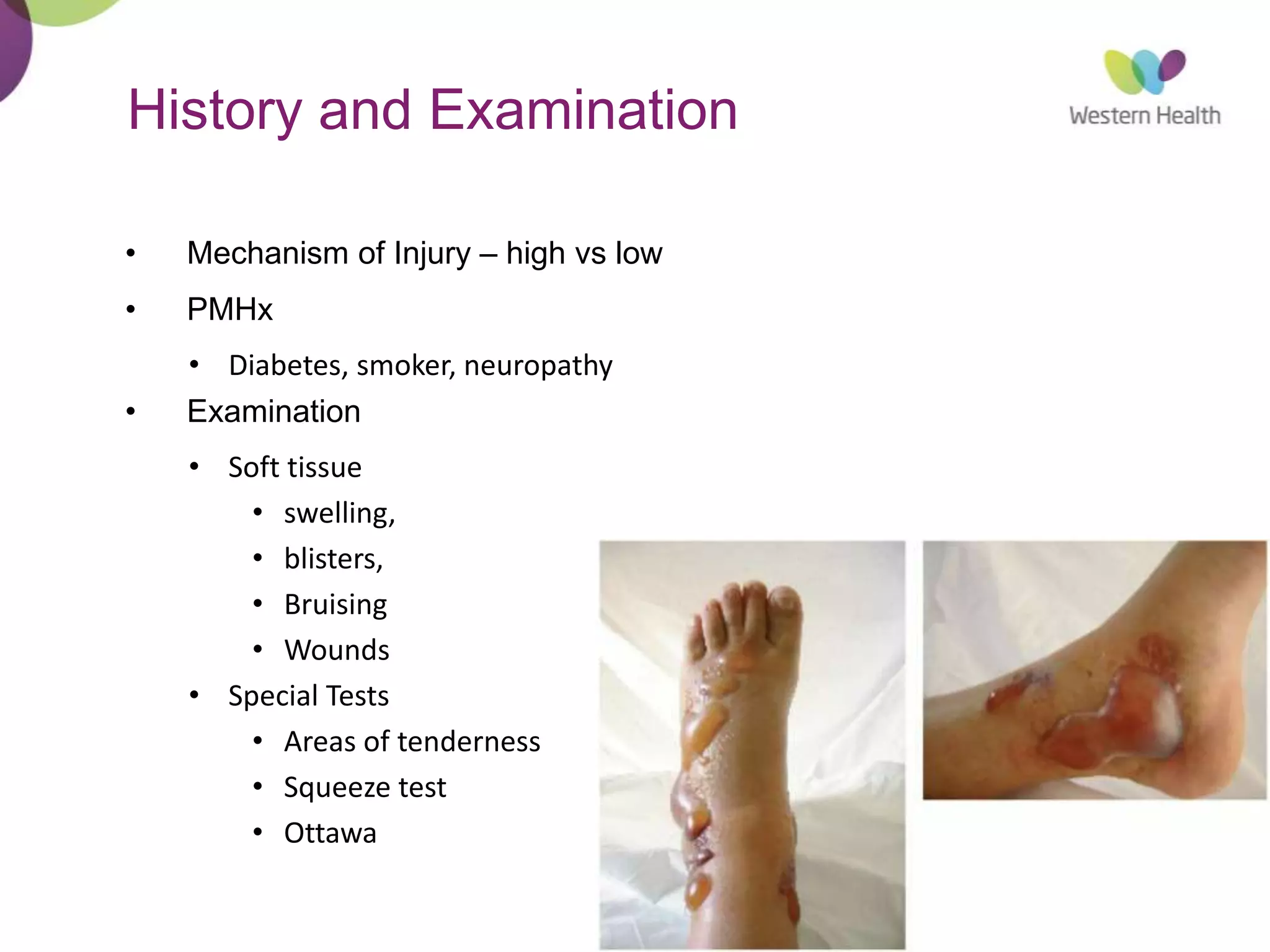
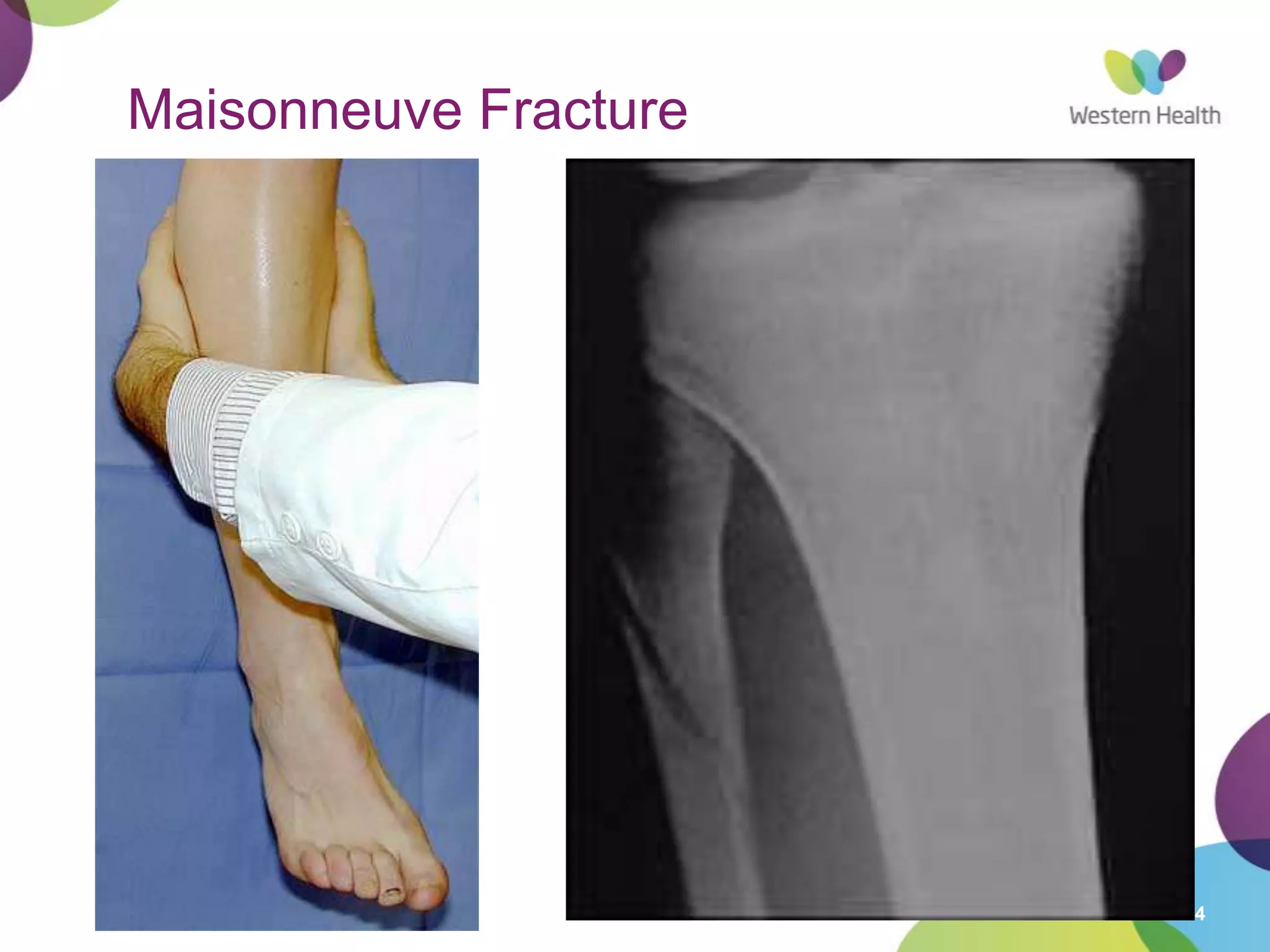
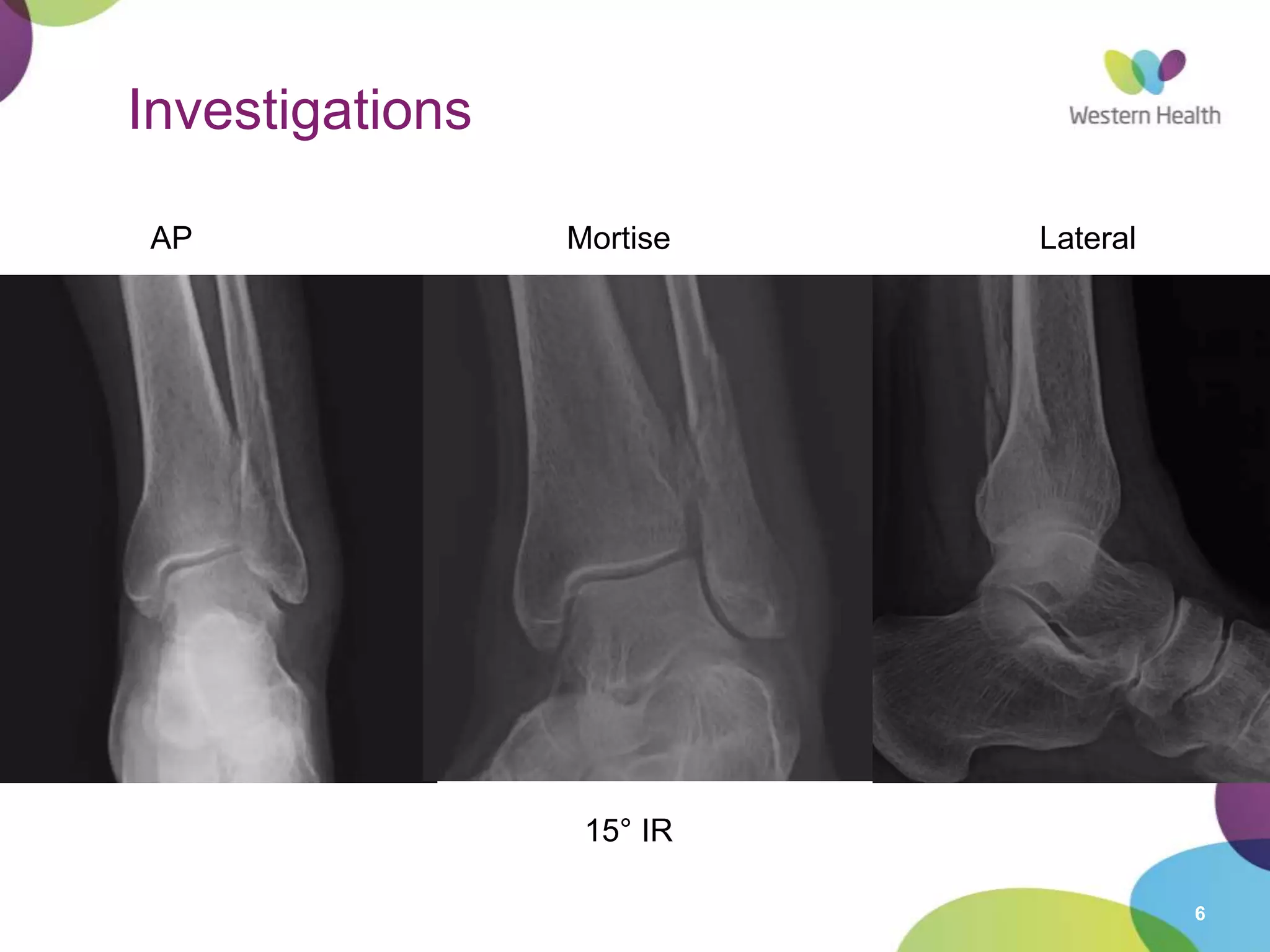
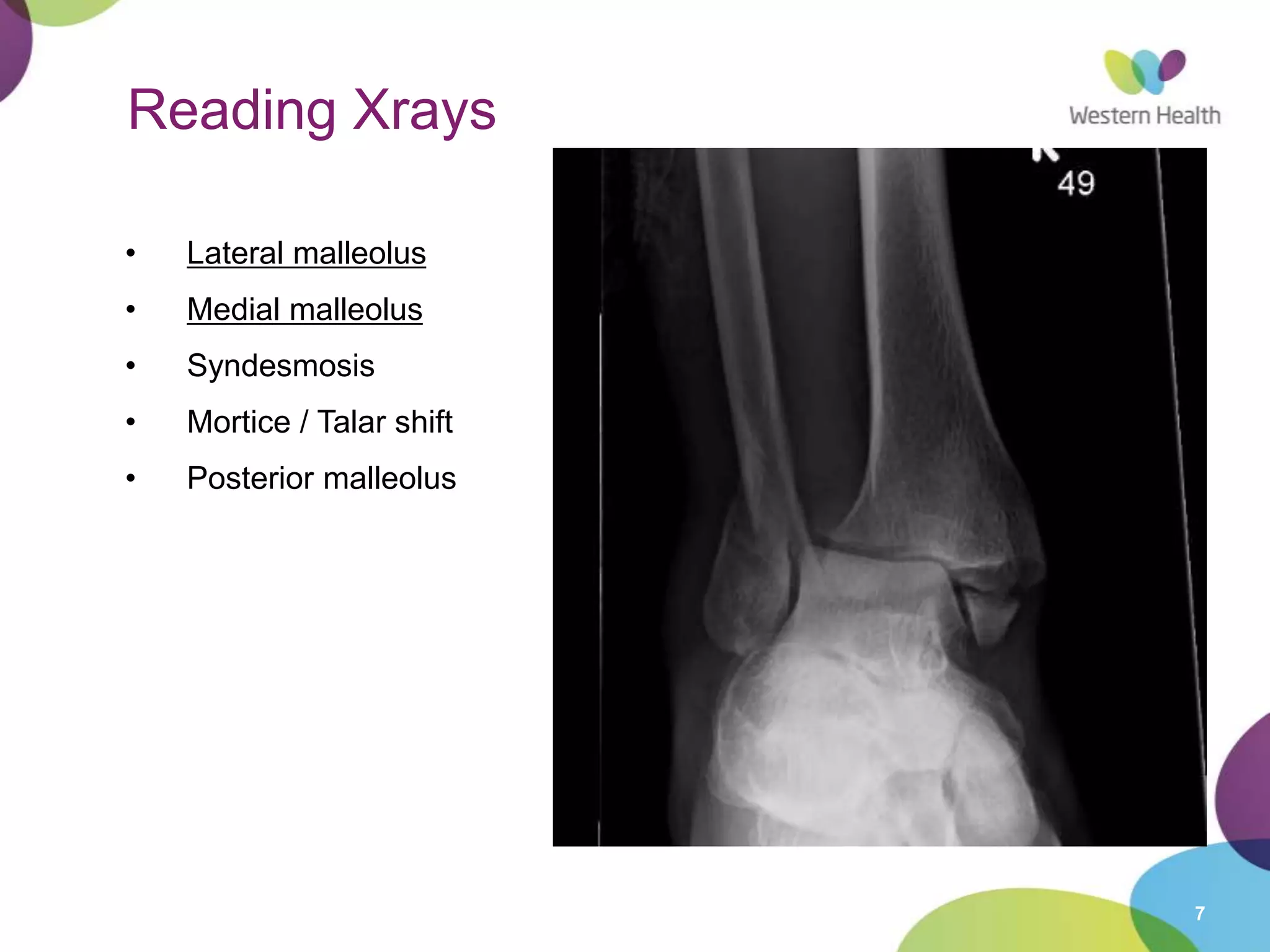
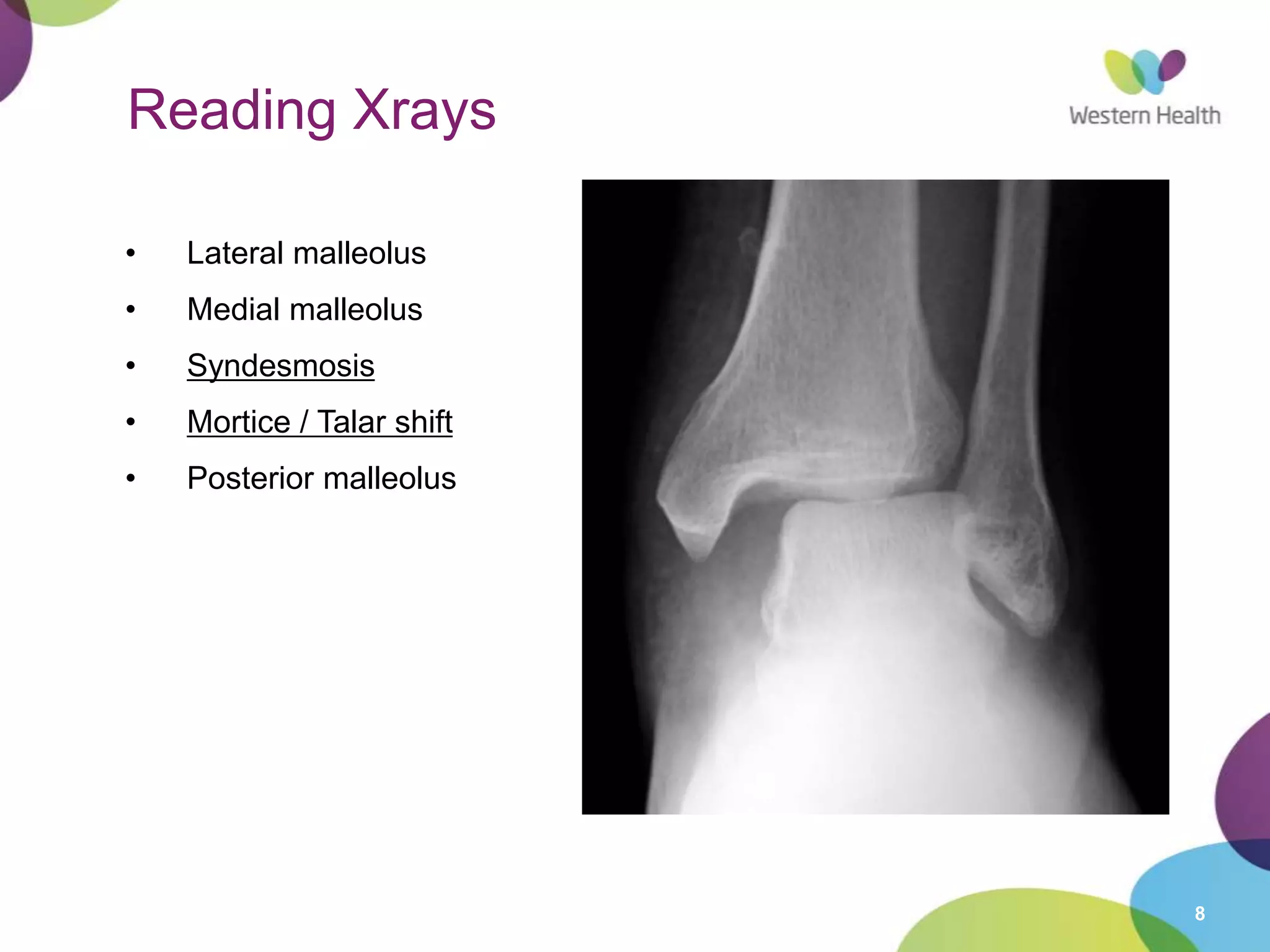
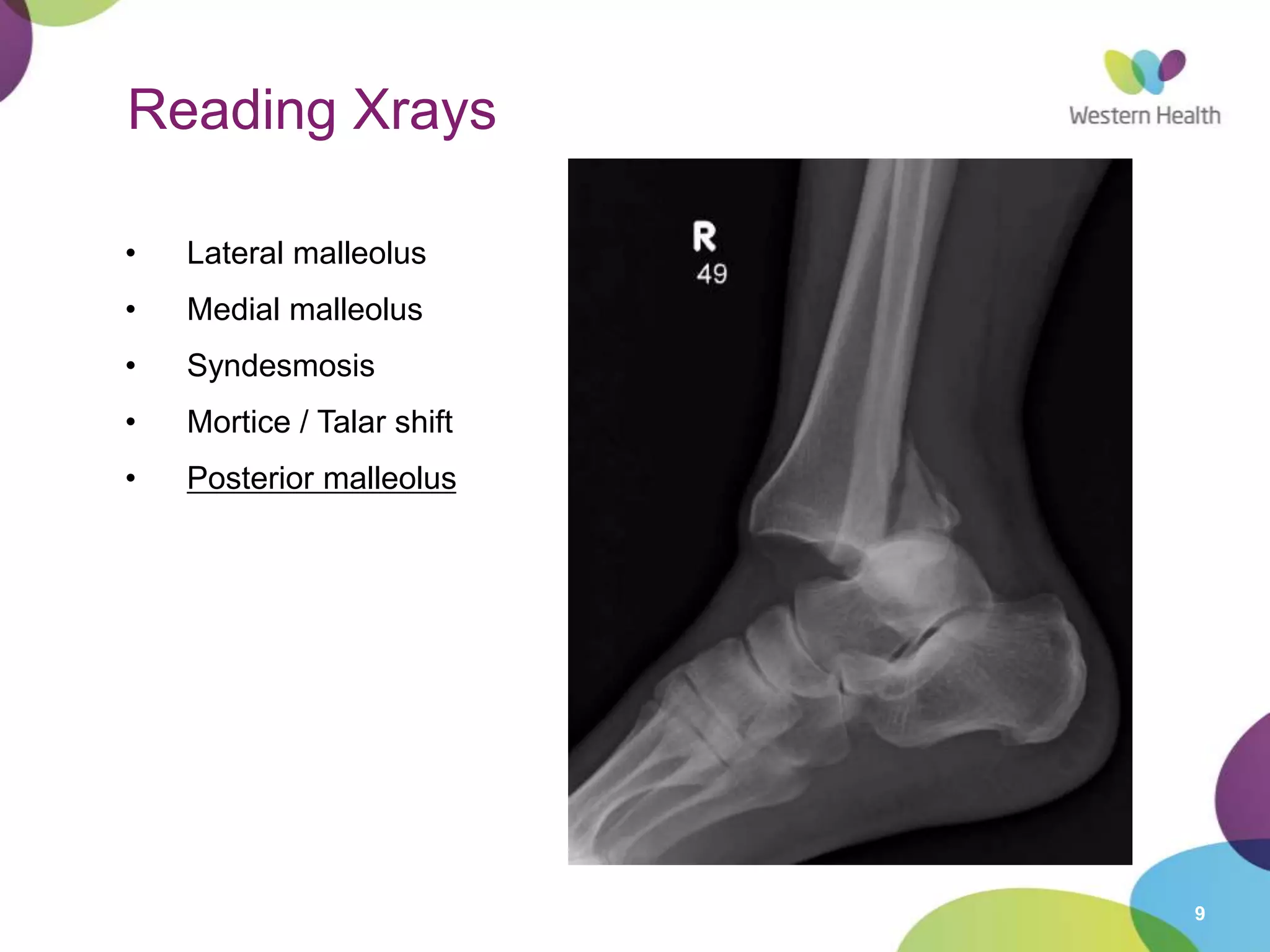
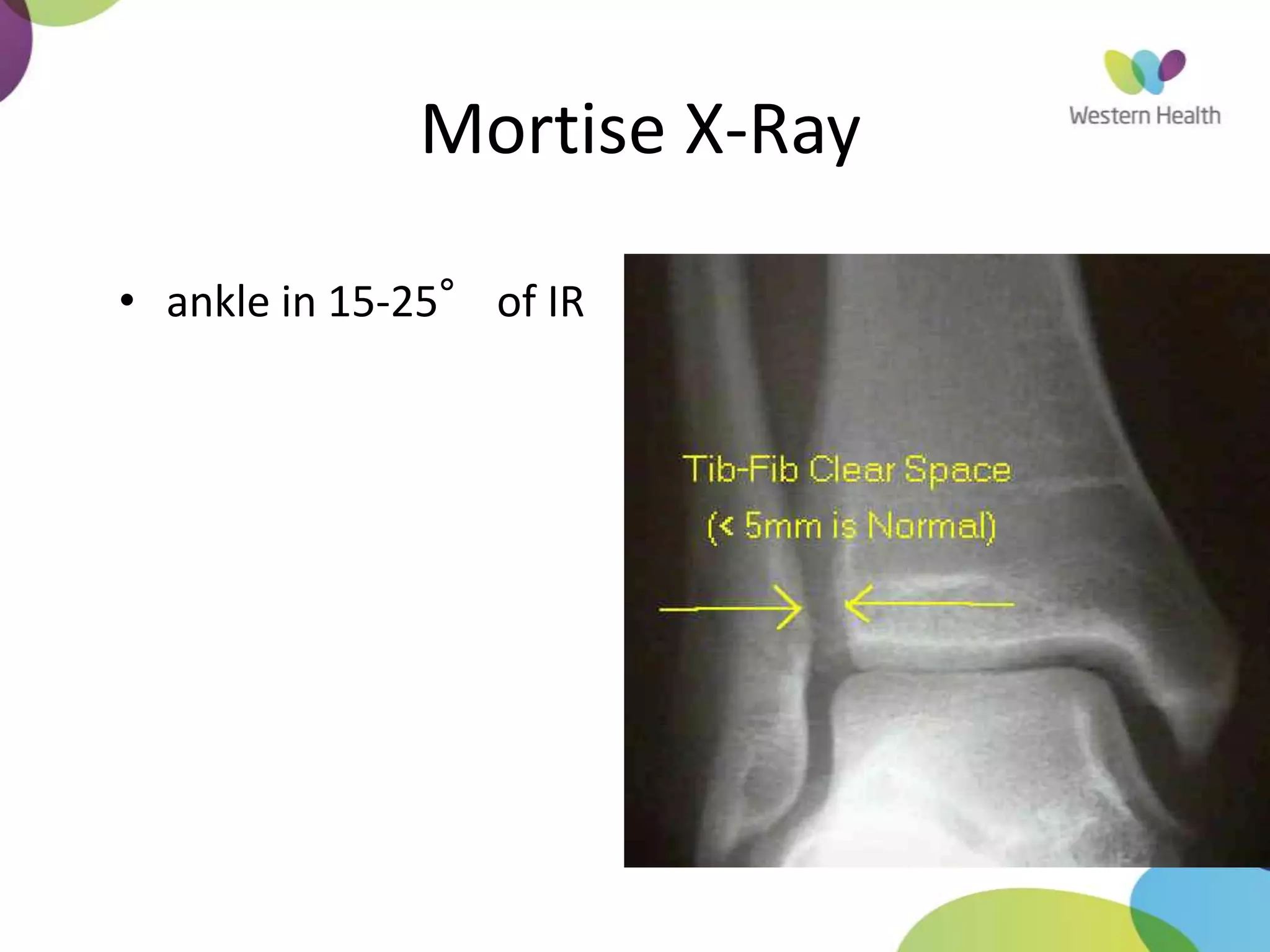
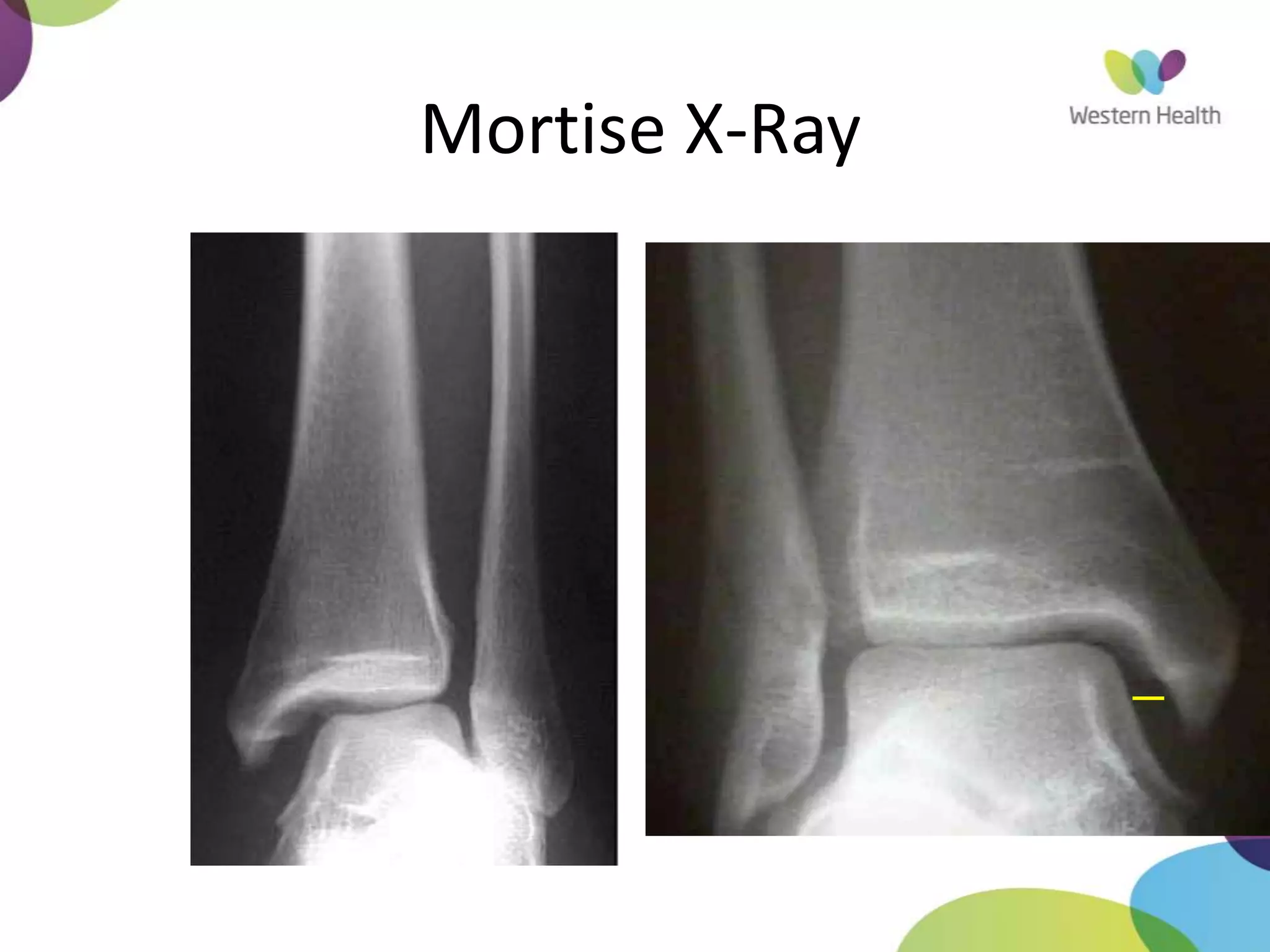
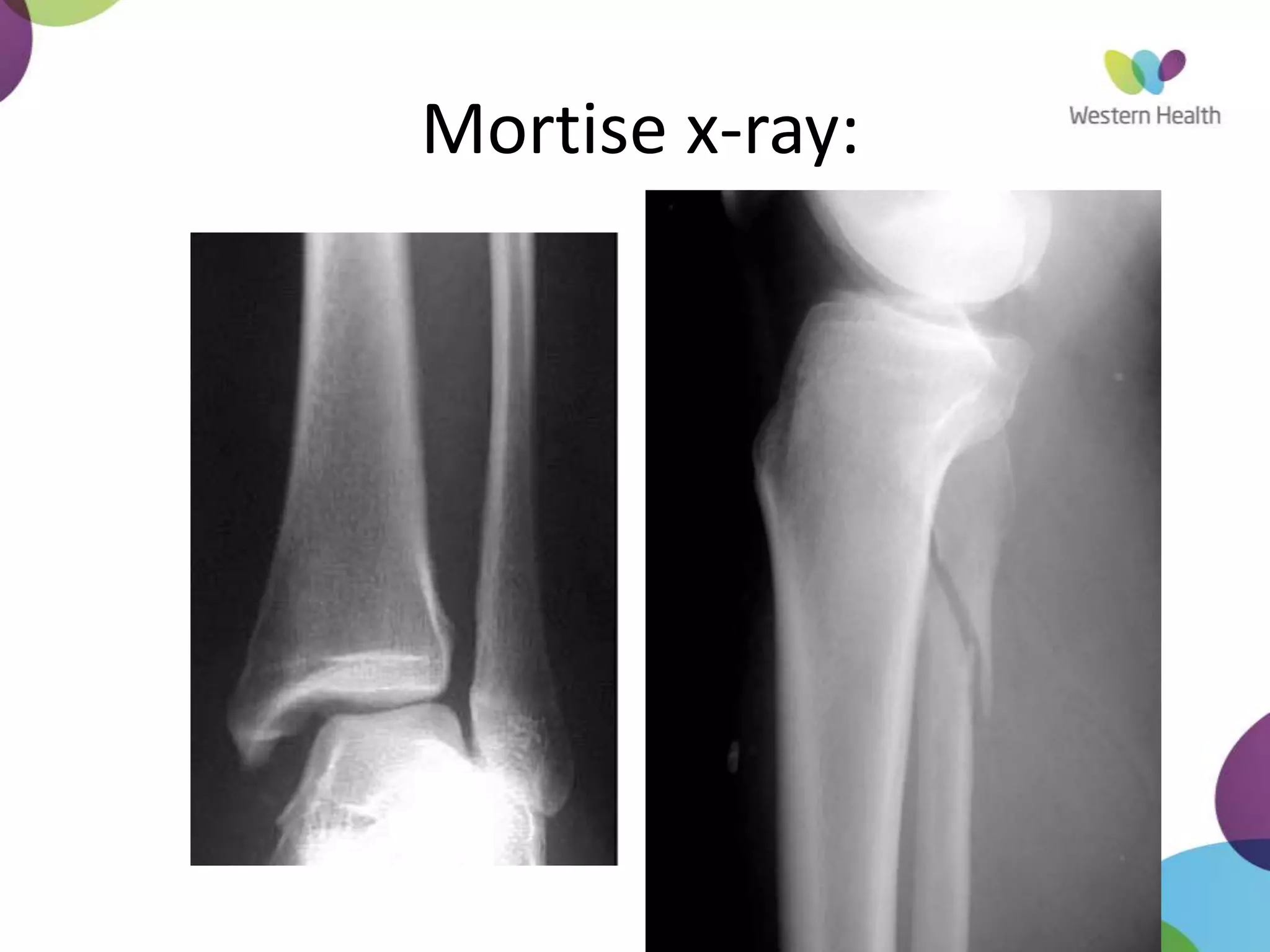
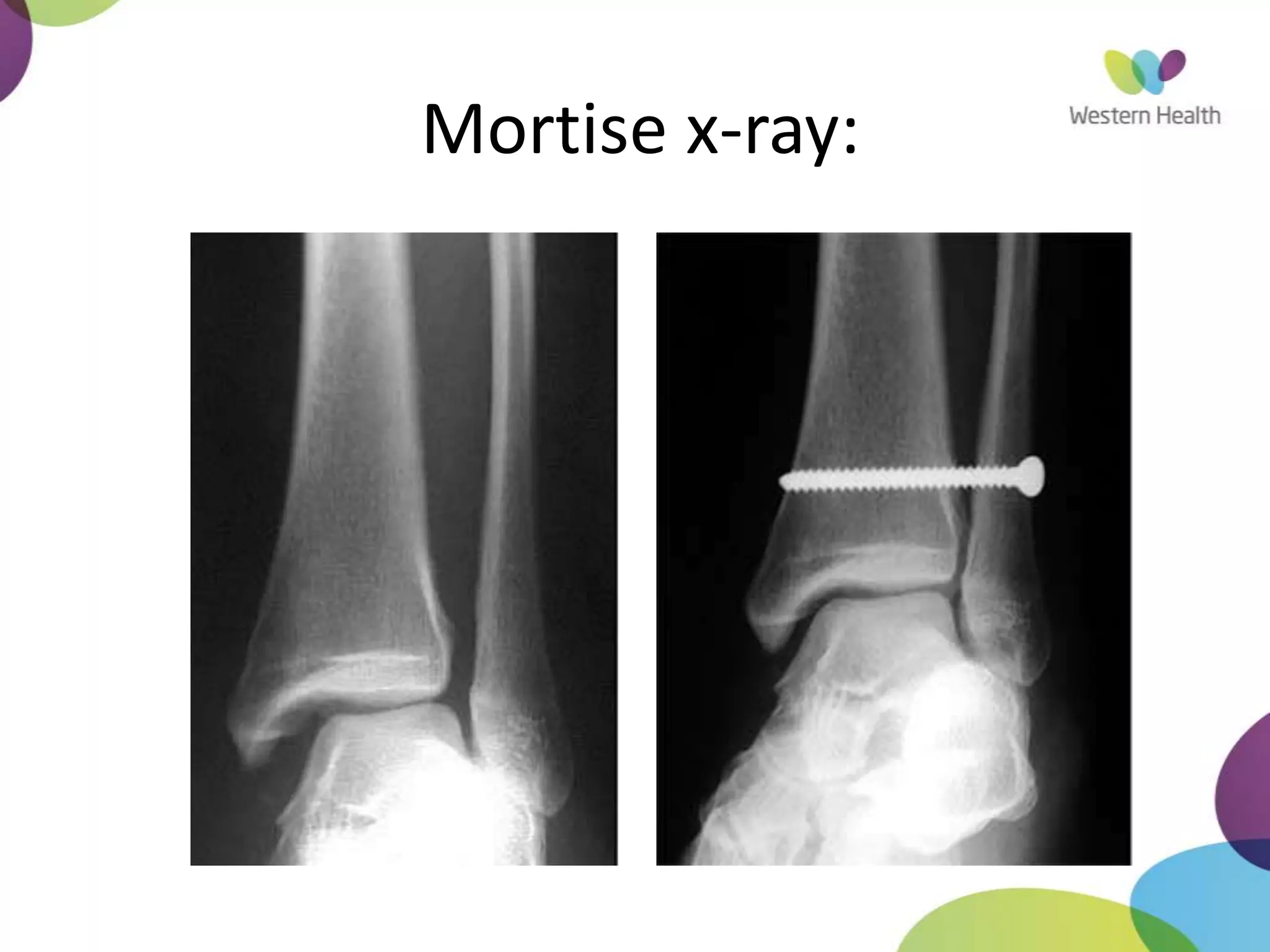
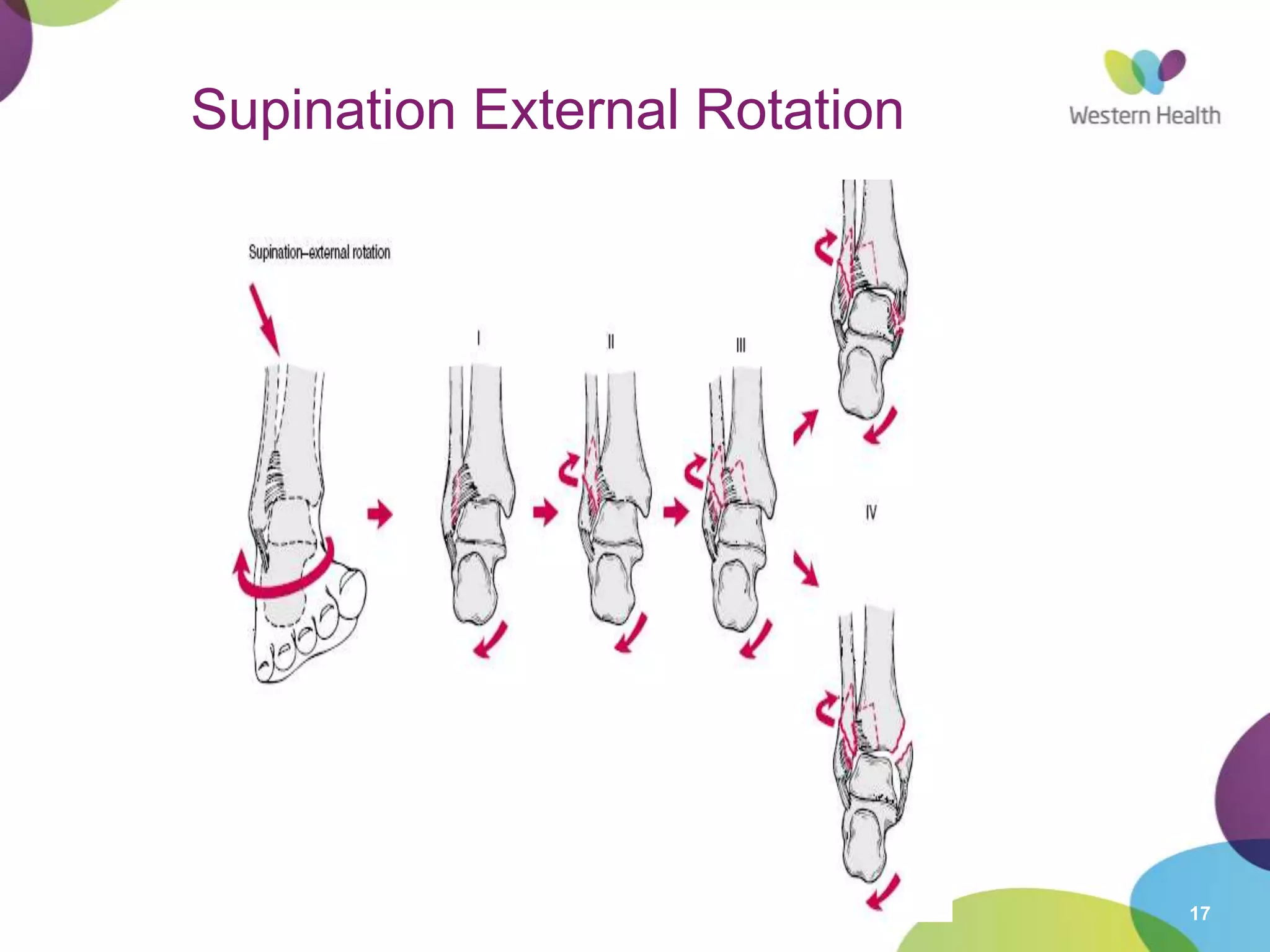
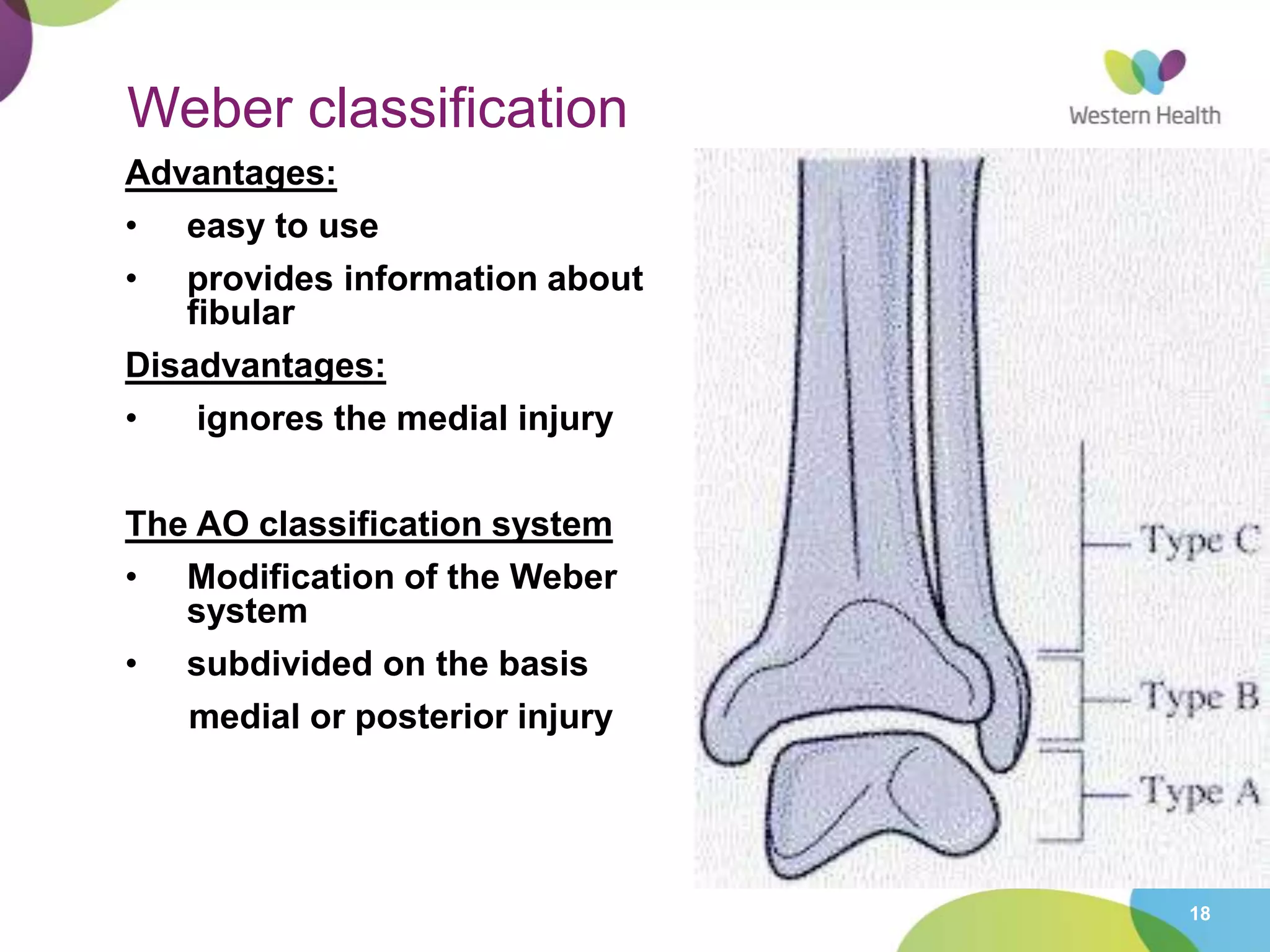
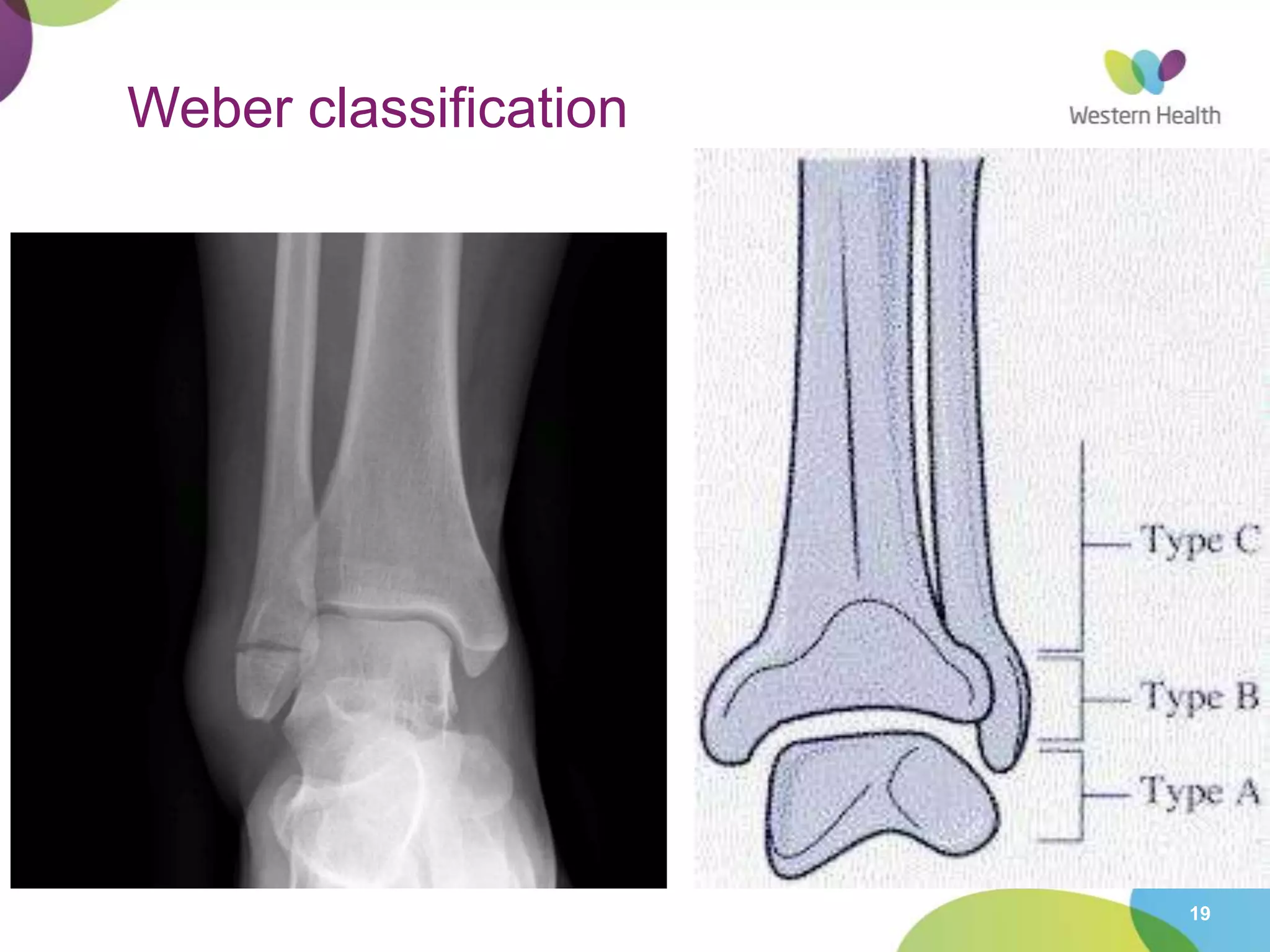
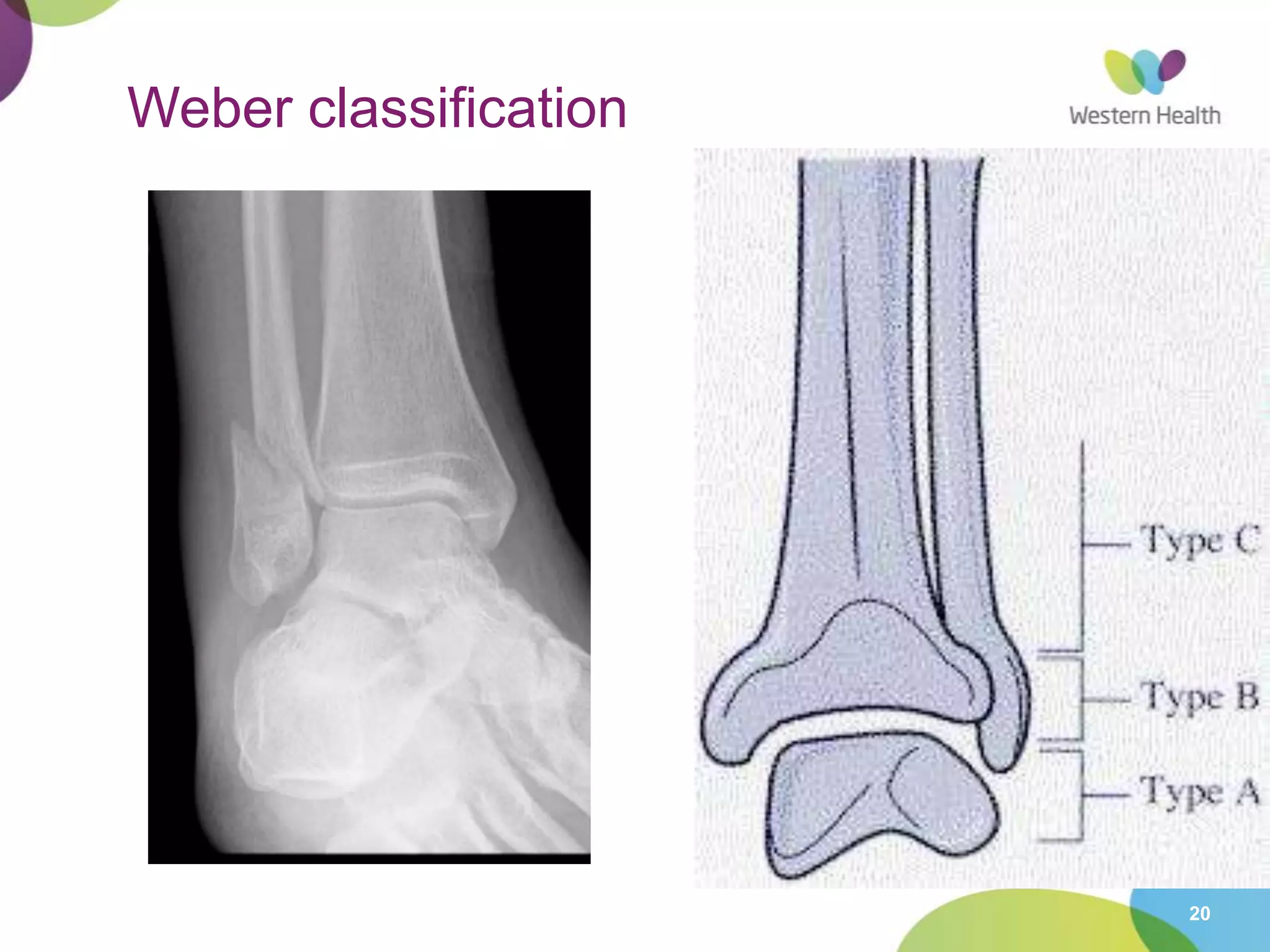
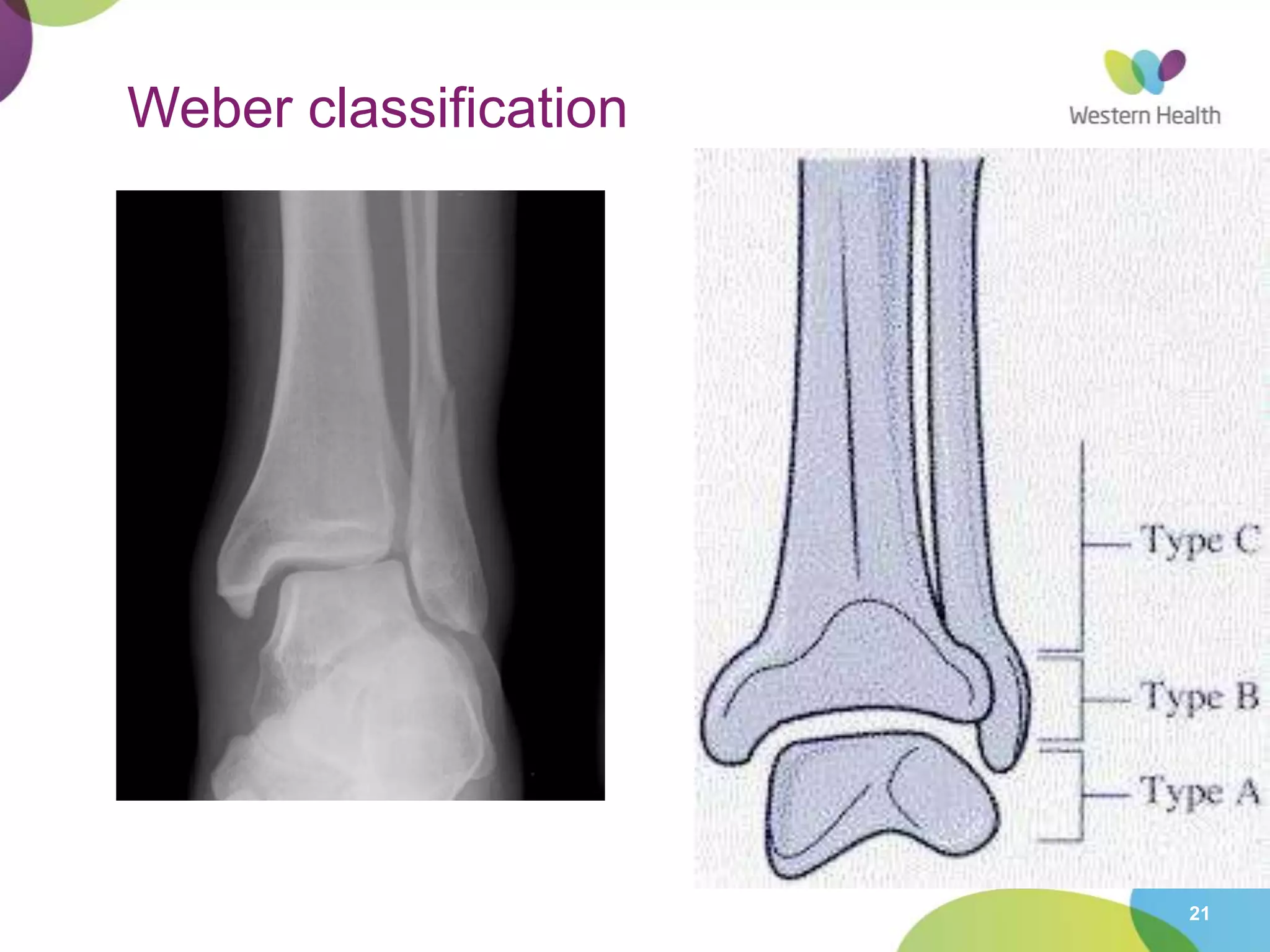
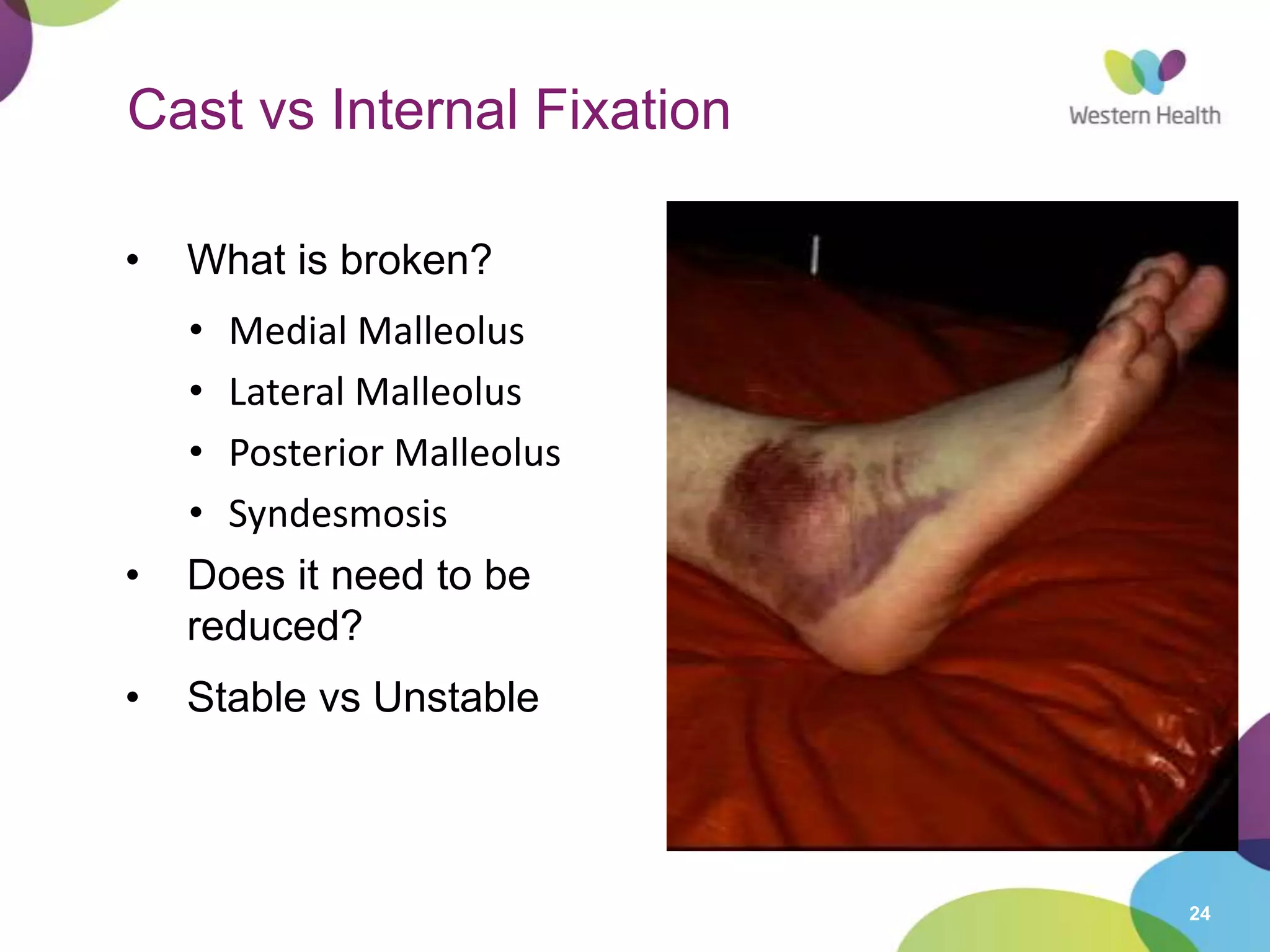
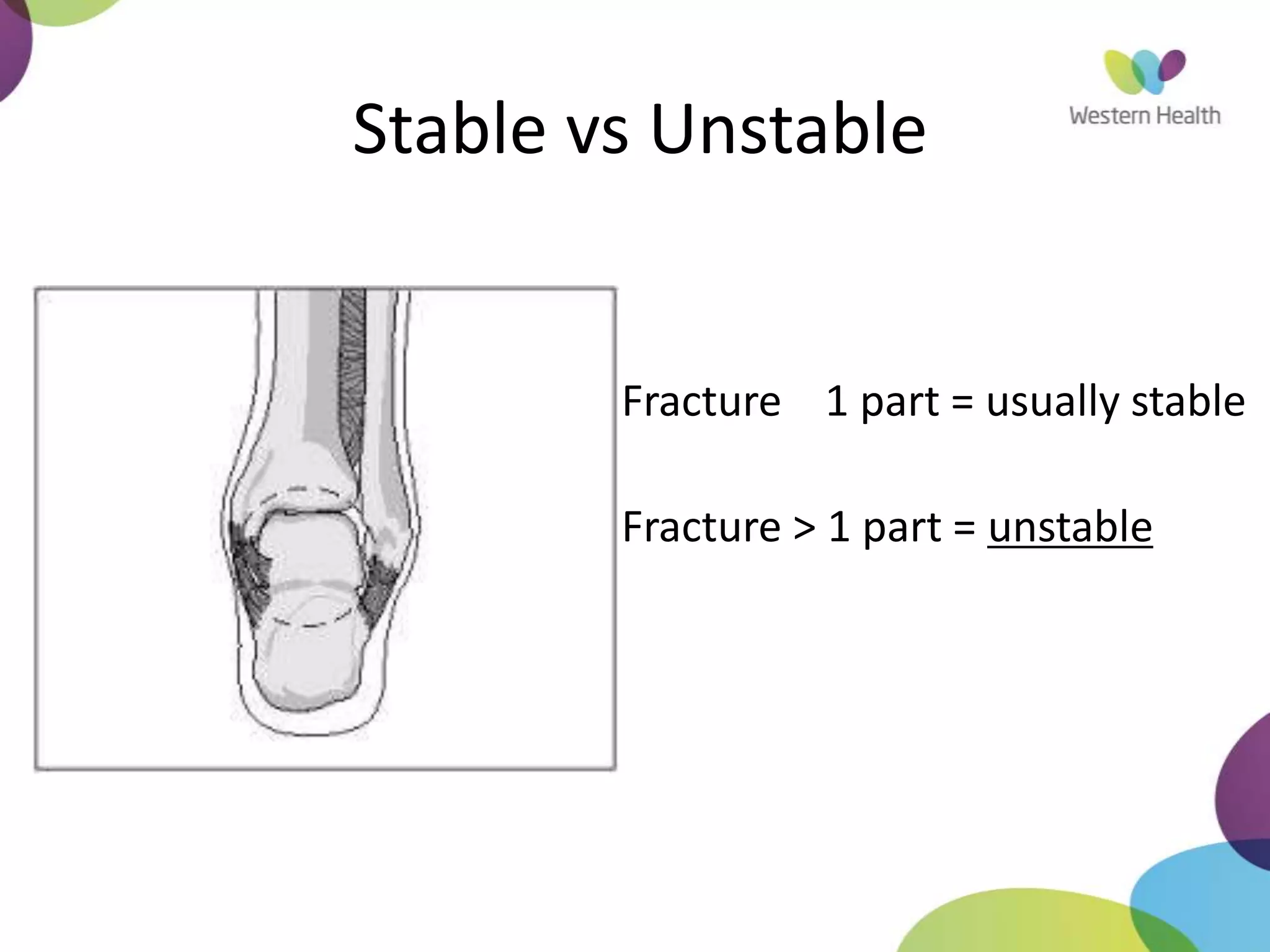
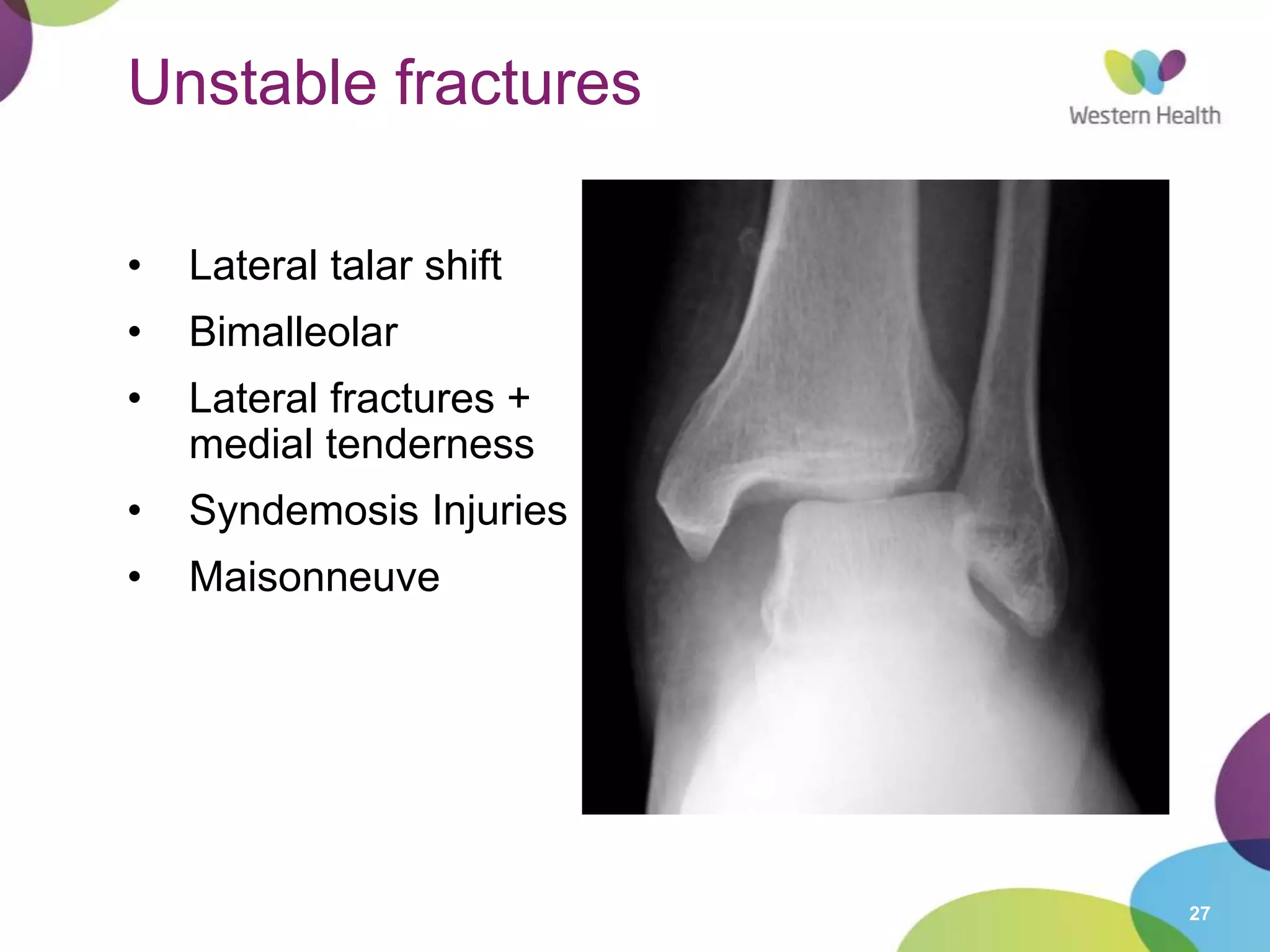
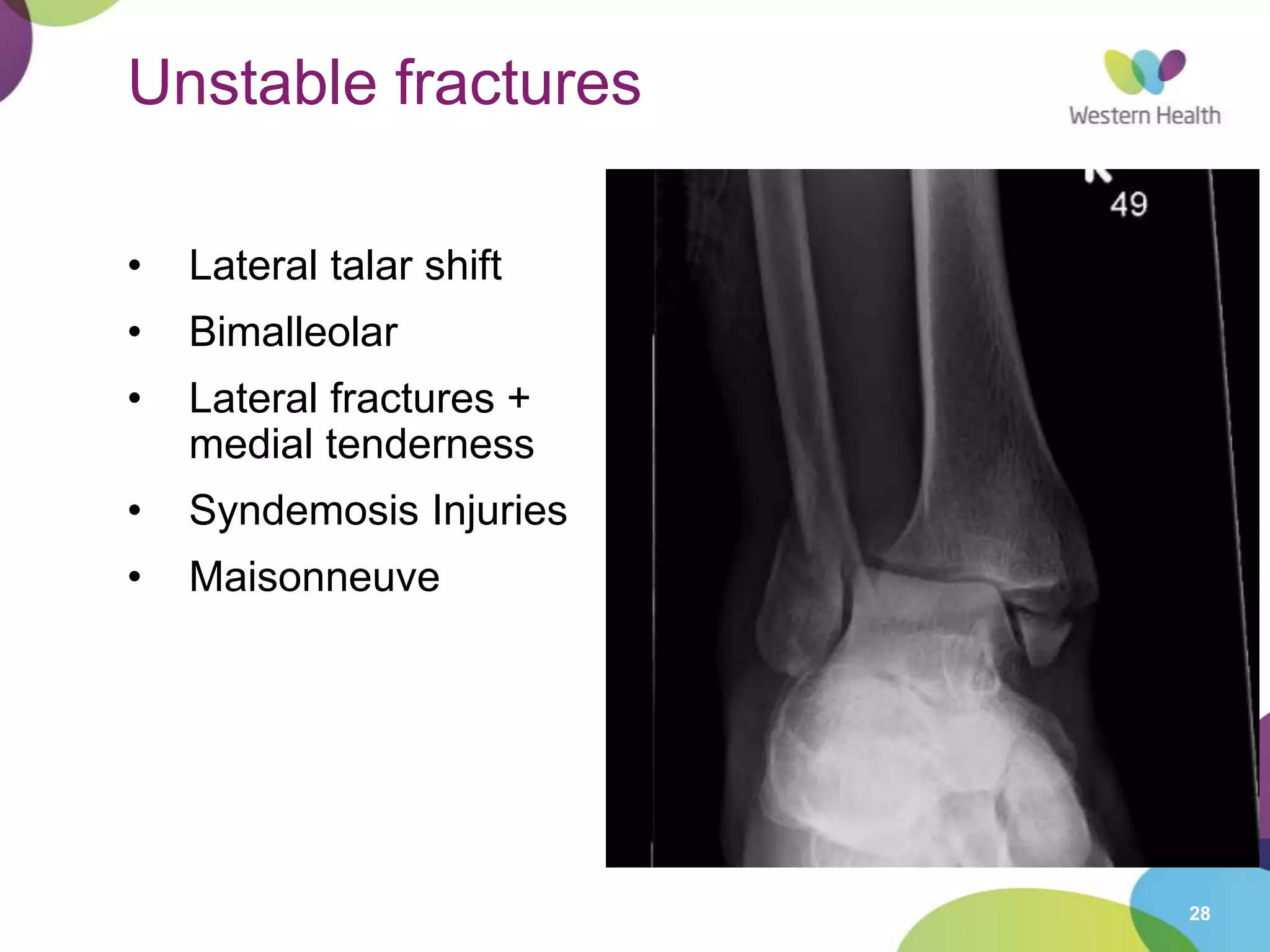
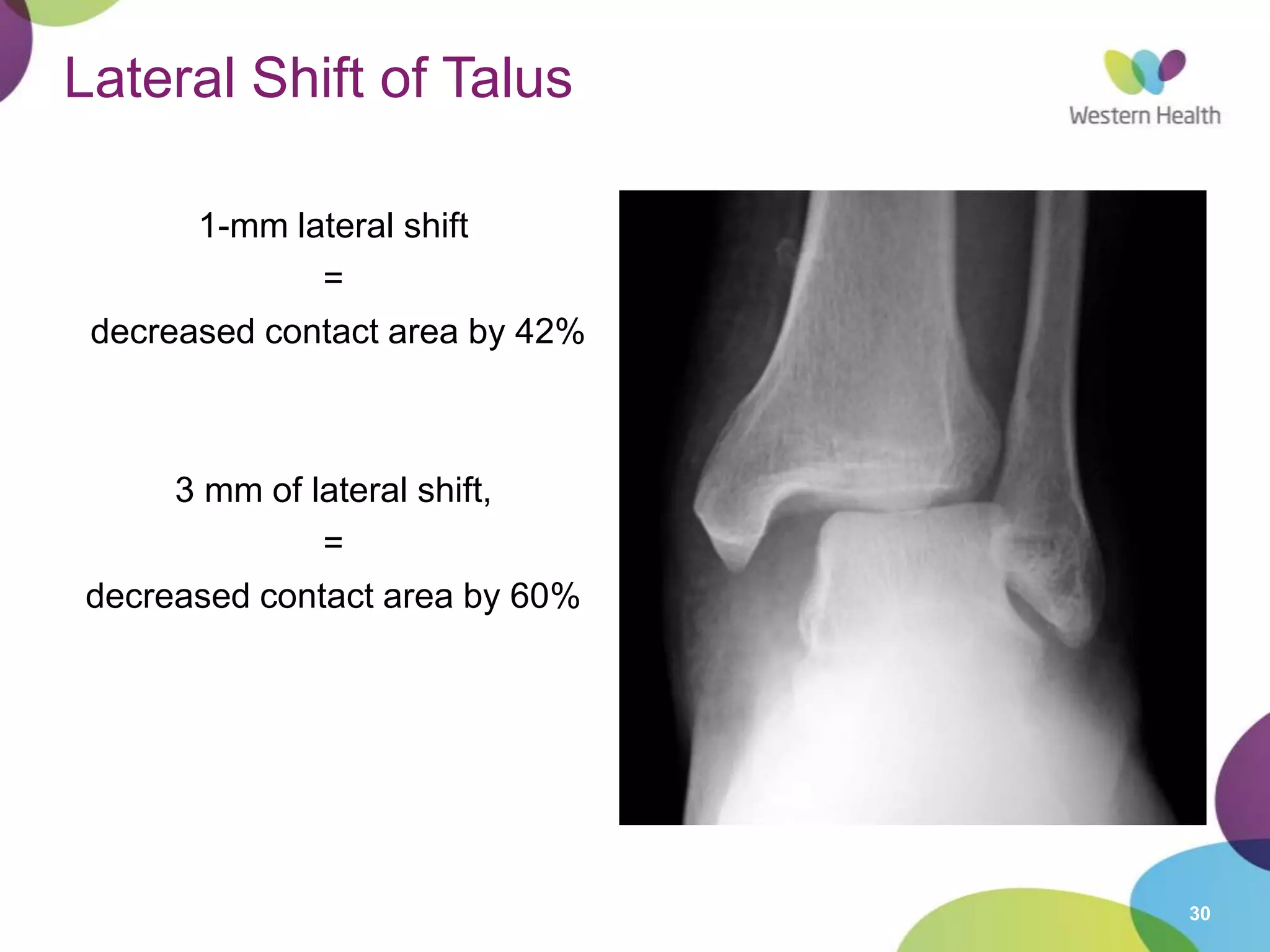
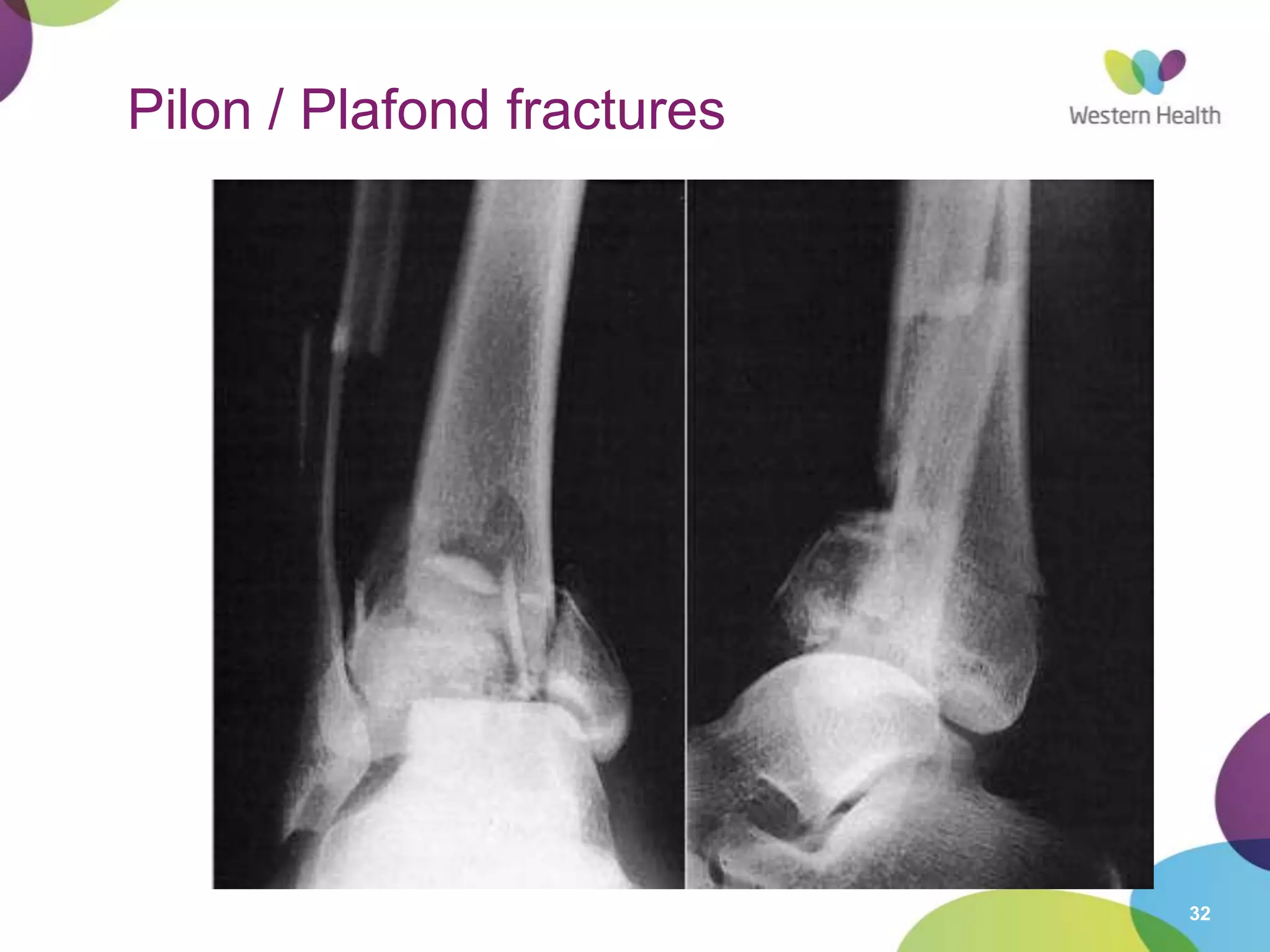
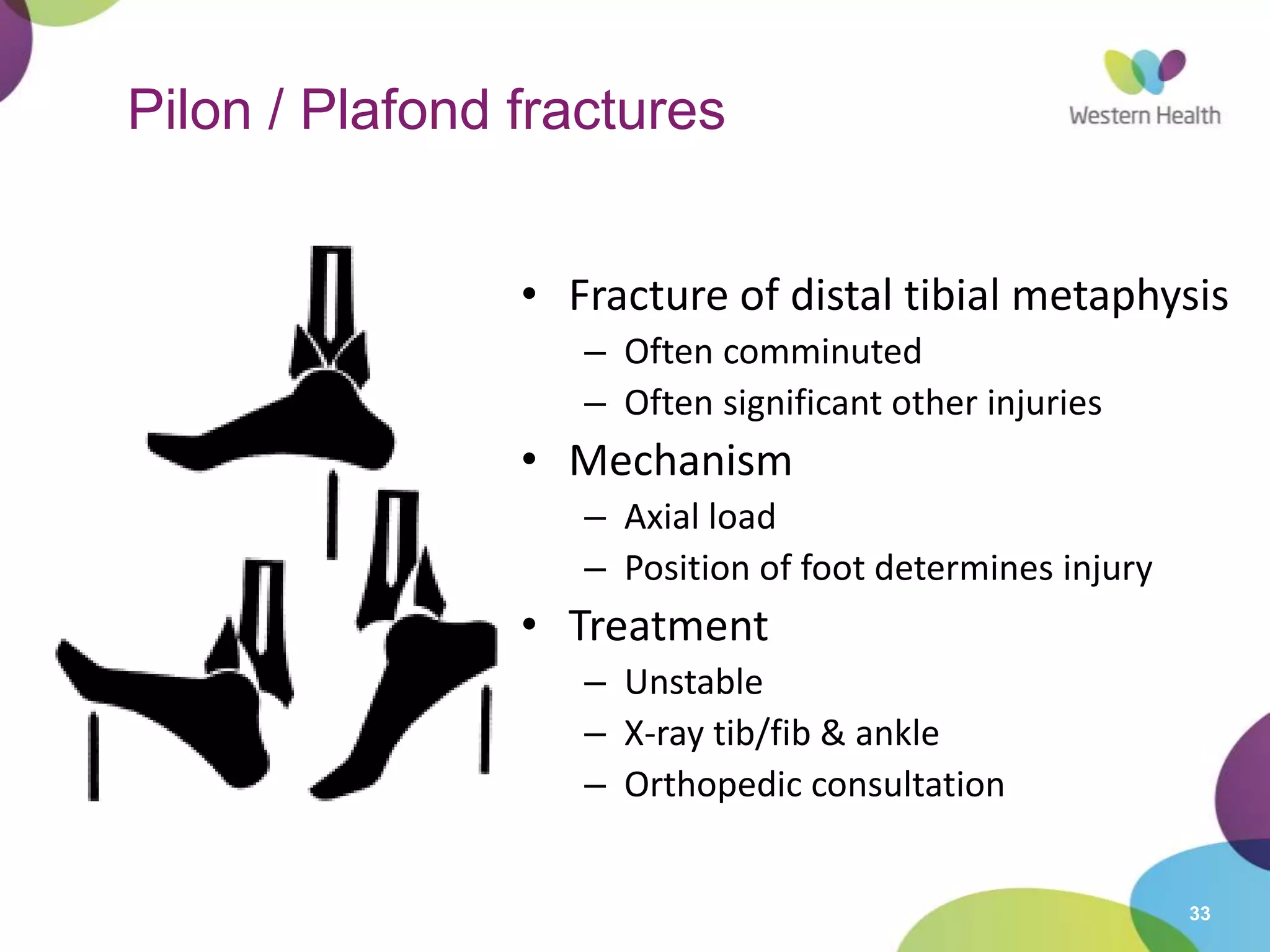
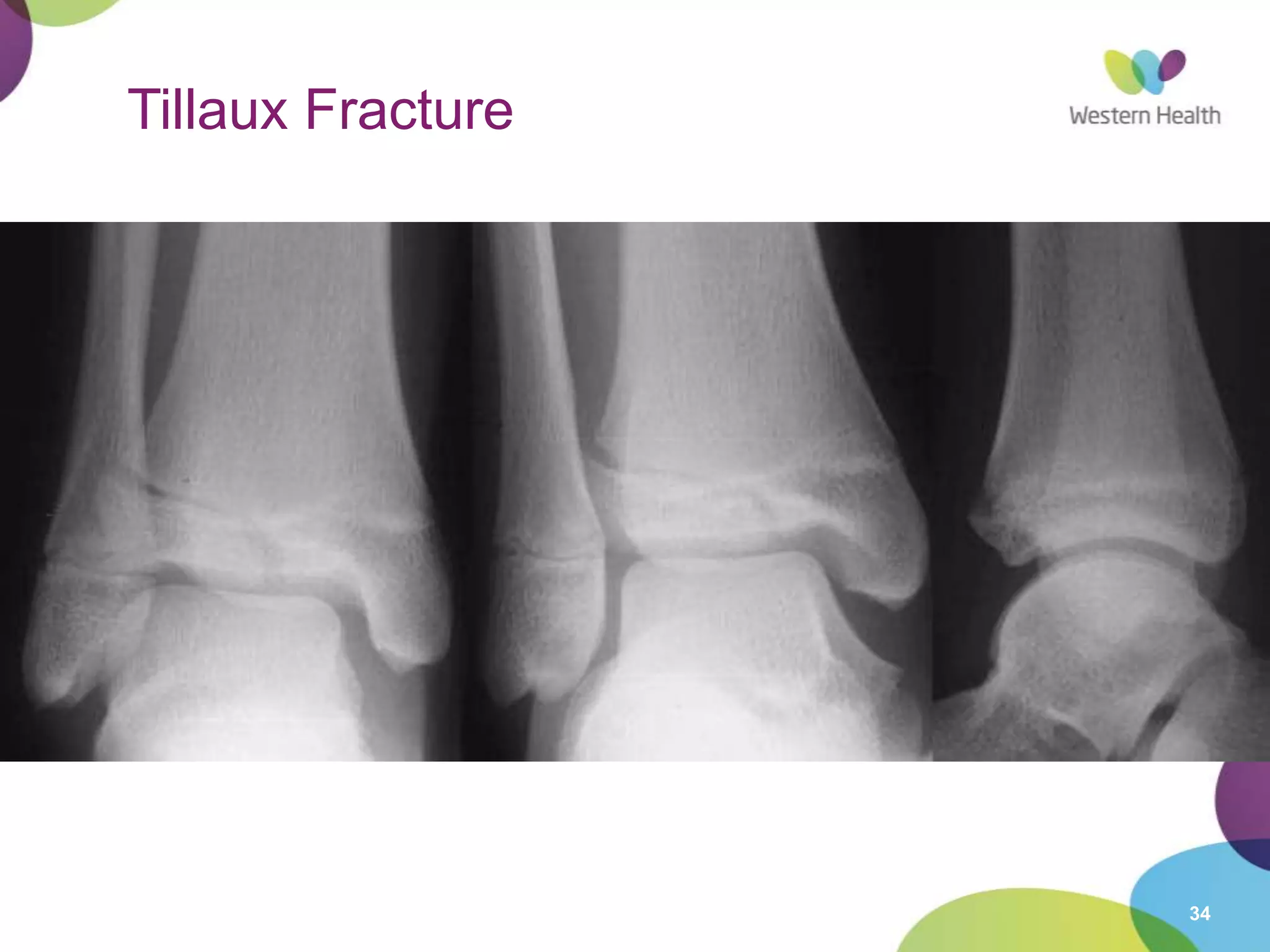
This document discusses ankle fractures, including their causes, examination, classification, and treatment. The most common ankle fractures are caused by twisting injuries and affect the lateral and medial malleoli. Examination involves assessing soft tissue damage and tenderness. Fractures are classified using systems like Lauge-Hansen or Weber/AO, which describe the fracture pattern and stability. Treatment depends on factors like displacement and number of parts broken, with unstable or displaced fractures typically requiring internal fixation while stable fractures can be treated with casting.