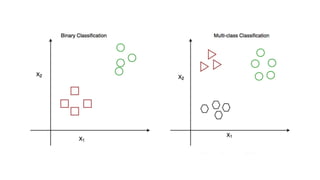
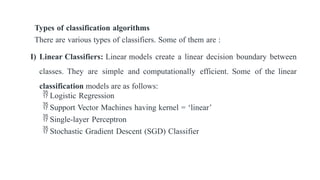
Classification is the process of categorizing data into predefined classes based on features, primarily used in machine learning as a supervised learning technique. It includes binary classification, where data is classified into two categories, and multiclass classification for multiple categories, utilizing various algorithms such as linear and non-linear classifiers. The classification process involves training a model on labeled data to predict outcomes for unseen inputs based on learned patterns.