This document provides information about qualitative chemical analysis including:
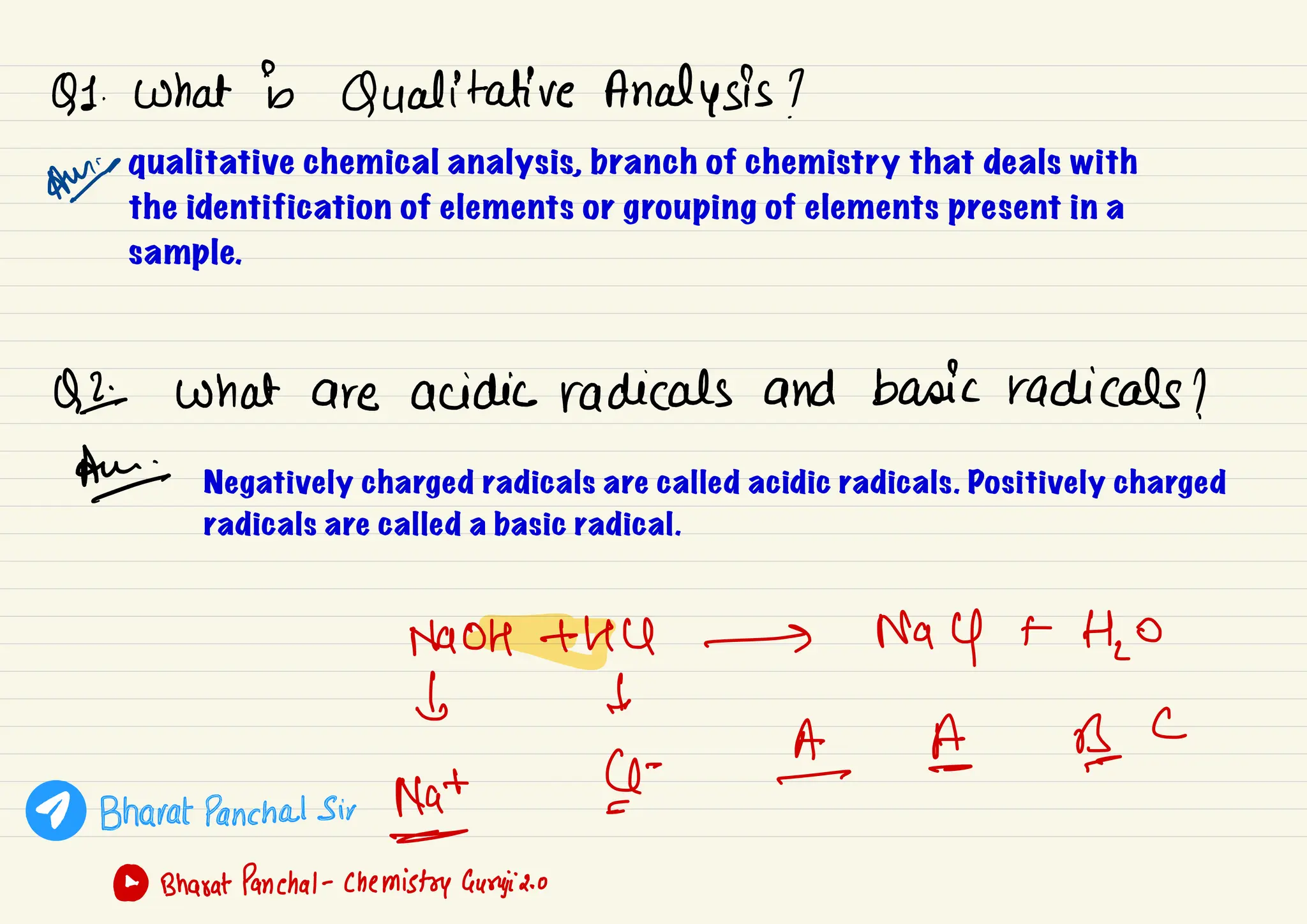
1) Qualitative chemical analysis deals with identifying elements or grouping elements present in a sample. Negatively charged radicals are called acidic and positively charged are called basic.
2) Common colored basic radicals include Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Cr3+, Ni2+, Co2+, and Mn2+. Ferrous salts are light green and ferric salts are brown. Nickel salts are bluish green.
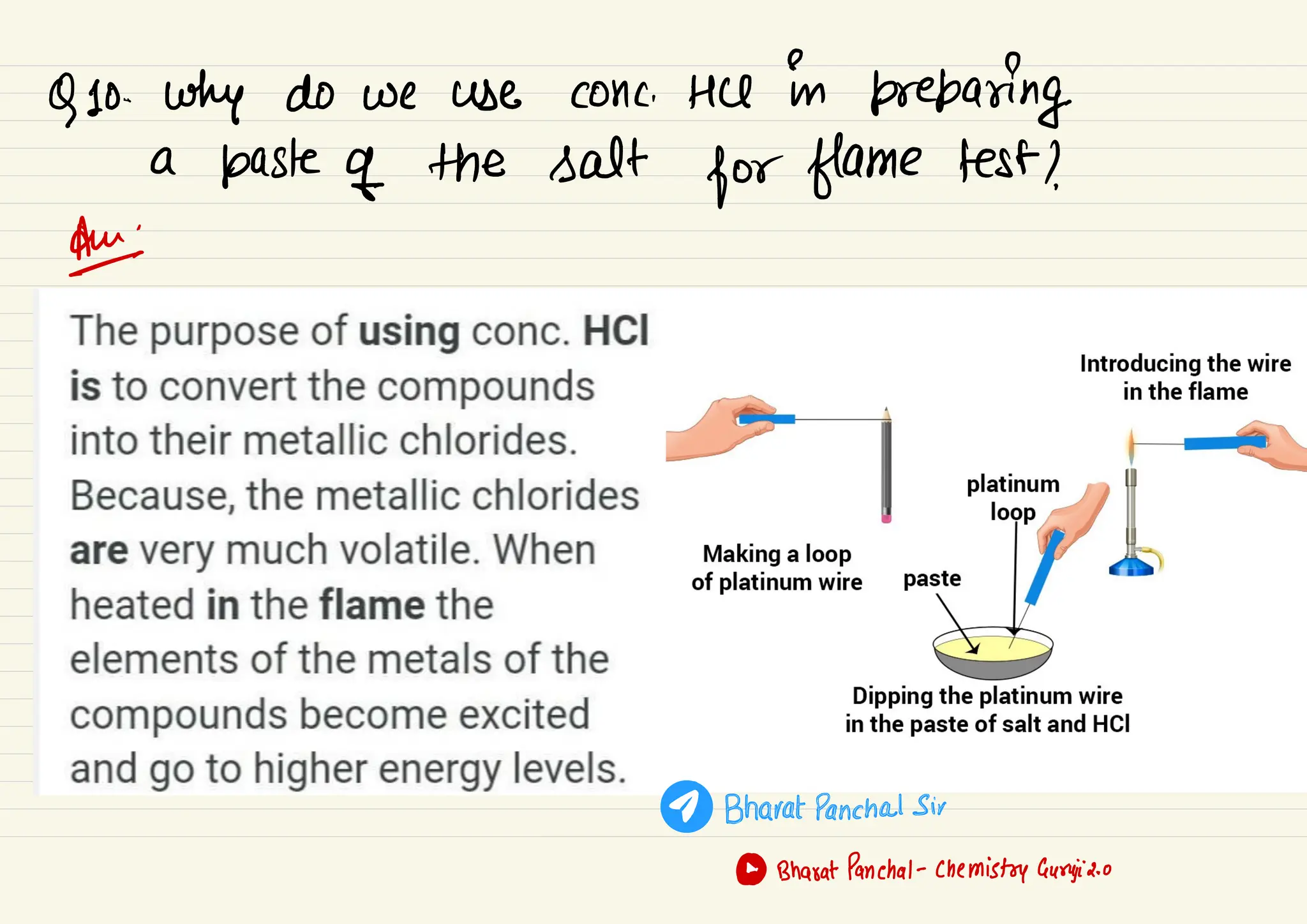
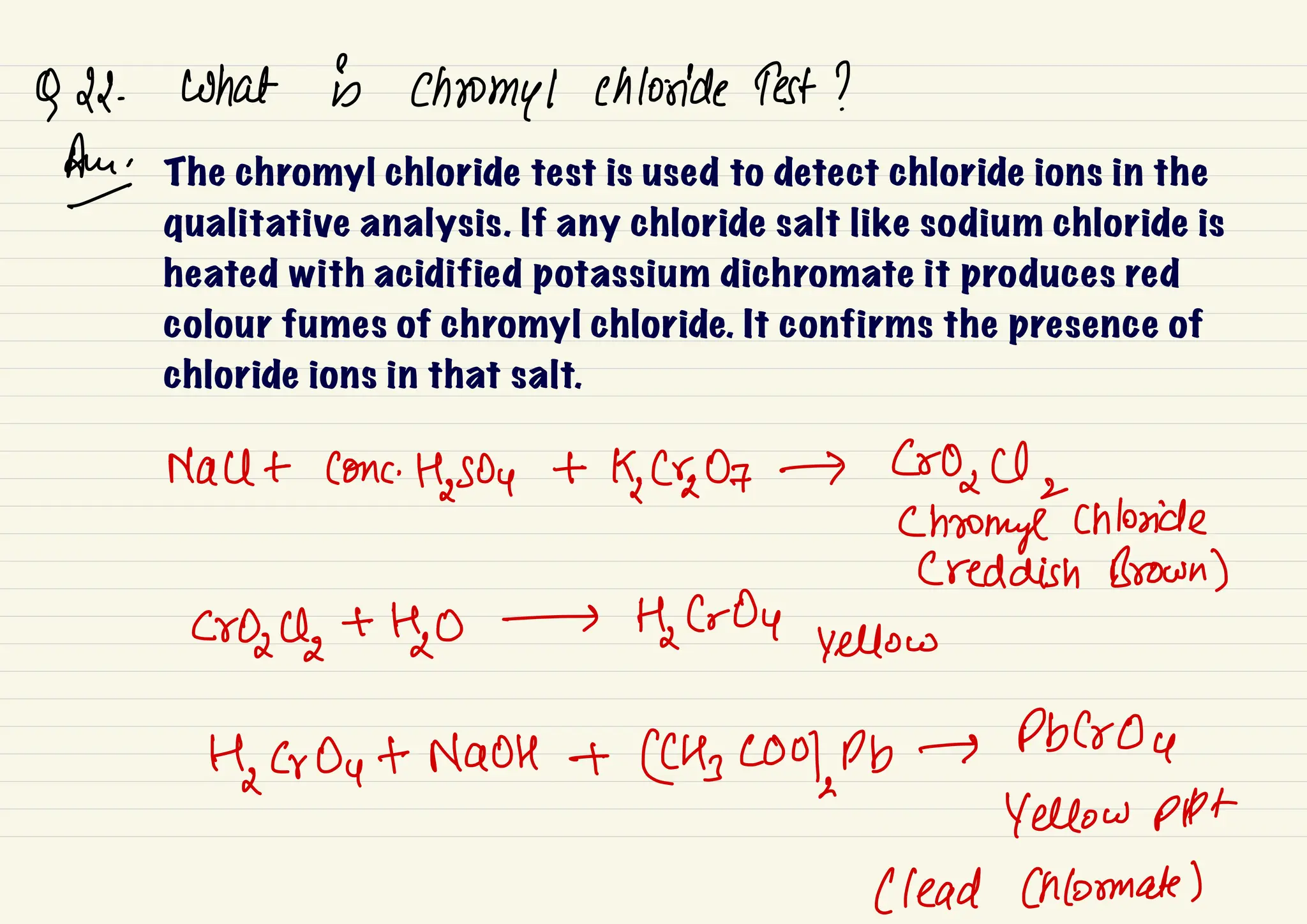
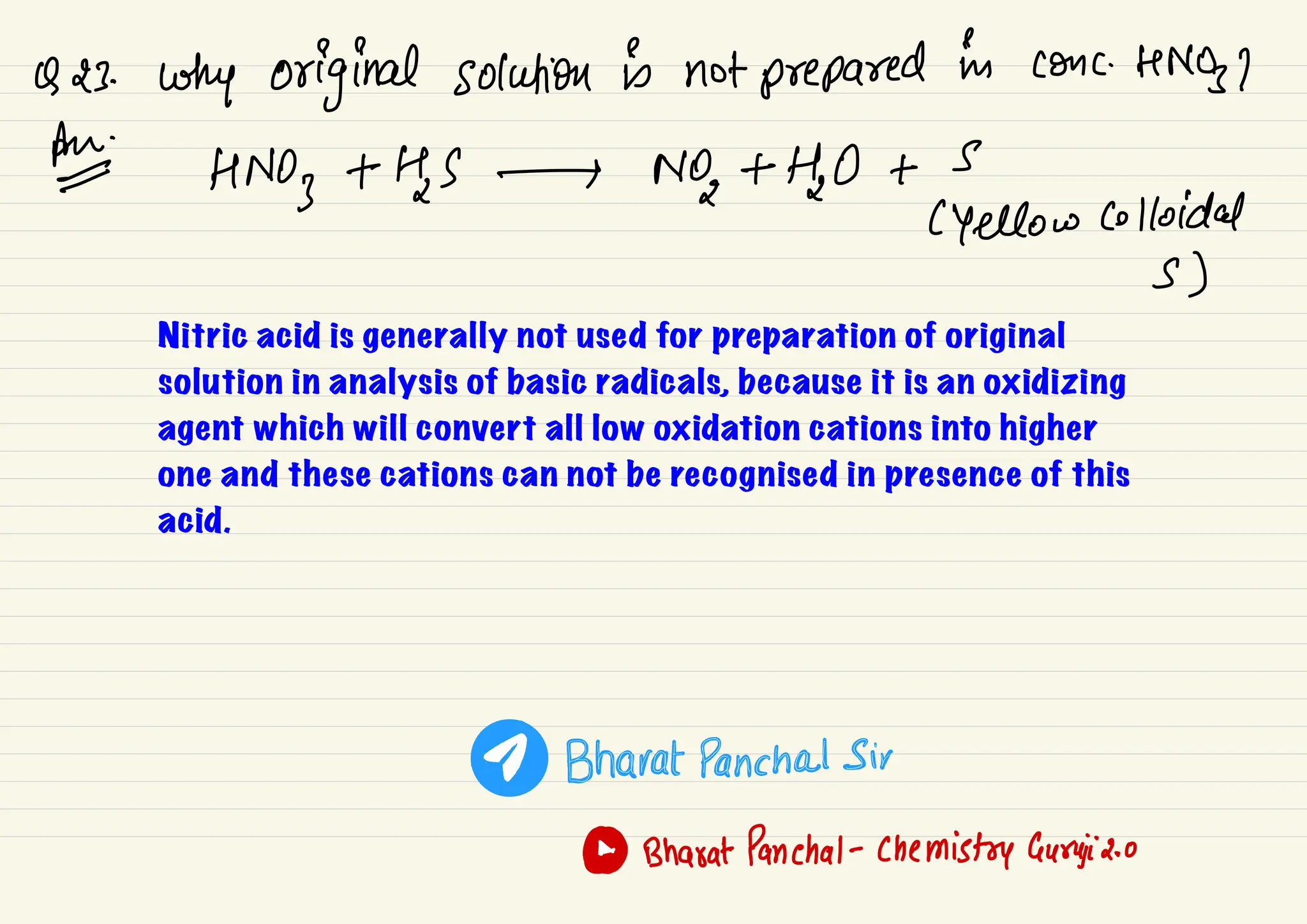
3) A salt containing lead turns black over time due to formation of black lead sulfide in the atmosphere. Preliminary tests can provide information about ions present like sodium imparting a golden yellow flame color.