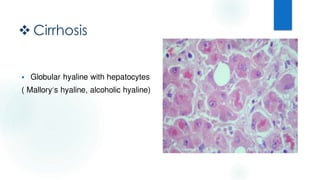
Cirrhosis is a late stage of liver scarring caused by various liver diseases, particularly alcohol-related and viral hepatitis. It often remains asymptomatic until extensive damage occurs, leading to severe complications. Histological examination reveals different types of cirrhosis, such as macro-nodular and micro-nodular, characterized by specific structural changes in liver cells.